Digestive System (Gastrointestinal)
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the digestive system and accessory structures
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the digestive system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of digestive system medical terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the digestive system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic tests and procedures
Key Word Components
Identify meanings of key word components of the digestive system:
Prefixes
- hemi- (half)
- endo- (within, in)
- sub- (under, below)
- dys- (painful, abnormal, difficult, labored)
Combining Forms
- abdomin/o (abdomen, abdominal)
- an/o (anus)
- antr/o (antrum)
- append/o (appendix)
- appendic/o (appendix)
- cec/o (cecum)
- celi/o (abdomen, abdominal cavity)
- cheil/o (lip)
- cholangi/o (bile duct)
- chol/e (gall, bile)
- choledoch/o (common bile duct)
- col/o (colon)
- colon/o (colon)
- diverticul/o (diverticulum)
- duoden/o (duodenum)
- enter/o (intestine)
- esophag/o (esophagus)
- gastr/o (stomach)
- gingiv/o (gum)
- gloss/o (tongue)
- hepat/o (liver)
- herni/o (hernia, protrusion of an organ through a membrane or cavity wall)
- ile/o (ileum)
- jejun/o (jejunum)
- lapar/o (abdomen, abdominal cavity)
- lingu/o (tongue)
- or/o (mouth)
- palat/o (palate)
- pancreat/o (pancreas)
- peritone/o (peritoneum)
- polyp/o (polyp, small growth)
- proct/o (rectum)
- pylor/o (pylorus, pyloric sphincter)
- rect/o (rectum)
- sial/o (saliva, salivary gland)
- sigmoid/o (sigmoid colon)
- steat/o (fat)
- stomat/o (mouth)
- uvul/o (uvula)
Suffixes
- -ac (pertaining to)
- -al (pertaining to)
- -cele (hernia, protrusion)
- -centesis (surgical puncture to aspirate fluid)
- -ectomy (excision)
- -gram (the record, radiographic image)
- -graph (instrument used to record)
- -graphy (process of recording)
- -ia (condition of, diseased state, abnormal state)
- -iasis (condition)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
- -logy (study of)
- -malacia (softening)
- -oma (tumor)
- -osis (abnormal condition)
- -pathy (disease)
- -pepsia (digestion)
- -phagia (eating or swallowing)
- -plasty (surgical repair)
- -ptosis (prolapse, drooping)
- -rrhaphy (suturing, repairing)
- -rrhea (flow, discharge)
- -scope (instrument used for visualization)
- -scopy (process of viewing, visualization)
- -stomy (creation of an artificial opening)
- -tomy (incision, cut into)
Digestive System Words
Digestive System Medical Terms (Text Version)
Practice the following digestive system words by breaking into word parts and pronouncing.
- gastroenterology (gastr/o/enter/o/logy)
- study of the stomach and intestines
- cholecystitis (chol/e/cyst/itis)
- inflammation of the gallbladder
- proctoscope (proct/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the rectum
- pyloroplasty (pylor/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the pylorus
- hepatomegaly (hepat/o/megaly)
- enlarged liver
- gastric (gastr/ic)
- pertaining to the stomach
- cholangiography (cholangi/o/graphy)
- radiographic imaging of the bile duct
- gastroenterologist (gastr/o/enter/o/logist)
- specialist who studies and treats stomach and intestines
- cholangiogram (cholangi/o/gram)
- radiographic image of the bile duct
- hepatoma (hepat/oma)
- tumour of the liver
- pancreatitis (pancreat/itis)
- inflammation of the pancreas
- esophagogram (esophag/o/gram)
- radiographic image of the esophagus
- steatosis (steat/osis)
- abnormal condition of fat
- rectocele (rect/o/cele)
- protrusion of the rectum
- endoscope (endo/scope )
- instrument used to view within (hollow organs)
- abdominal (abdomin/al)
- pertaining to the abdomen
- proctoptosis (proct/o/ptosis)
- condition of prolapse of the rectum
- diverticulitis (diverticul/itis)
- inflammation of the diverticulum
- oral (or/al)
- pertaining to the mouth
- appendectomy (append/ectomy)
- excision of the appendix
- esophagoscopy (esophag/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the esophagus
- cheilorrhaphy (cheil/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of the lip
- glossorrhaphy (gloss/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of the tongue
- pyloromyotomy (pylor/o/my/o/tomy)
- incision into the pyloric muscle
- gastroplasty (gastr/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the stomach
- colectomy (col/ectomy)
- excision of the colon
- sigmoidoscopy (sigmoid/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the sigmoid colon
- palatitis (palat/itis)
- inflammation of the palate
- esophageal (esophag/eal)
- pertaining to the esophagus
- colitis (col/itis)
- inflammation of the colon
- ileocecal (ile/o/cec/al)
- pertaining to the ileum and cecum
- gastrectomy (gastr/ectomy)
- excision of the stomach
- anoplasty (an/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the anus
- cholelithiasis (chole/lith/iasis)
- condition of gallstones
- gastroscopy (gastr/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the stomach
- colostomy(col/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening in the colon
- polyposis (polyp/osis)
- abnormal condition of (multiple) polyps
- laparoscopy (lapar/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the abdominal cavity
- cholecystectomy (chole/cyst/ectomy)
- excision of the gallbladder to remove stones
- glossitis (gloss/itis)
- inflammation of the tongue
- cholangioma (cholangi/oma)
- tumour of the bile duct
- pancreatic (pancreat/ic)
- pertaining to the pancreas
- stomatitis (stomat/itis)
- inflammation of the mouth
- ileocecal (ile/o/cec/al)
- pertaining to the ileum and cecum
- nasogastric (nas/o/gastr/ic)
- pertaining to the nose and stomach
- proctoscopy (proct/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the rectum
- herniorrhaphy (herni/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of a hernia
- appendicitis (appendic/itis)
- inflammation of the appendix
- gingivectomy (gingiv/ectomy)
- excision of the gums
- gastroenterocolitis (gastr/o/enter/o/col/itis)
- inflammation of the stomach, intestines, and colon
- choledocholithotomy (choledoch/o/lith/o/tomy)
- incision into the common bile duct to remove stones
- gastroscope (gastr/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the stomach
- diverticulosis (diverticul/osis)
- abnormal condition of having diverticula
- uvulitis (uvul/itis)
- inflammation of the uvula
- dysphagia (dys/phagia)
- difficult swallowing
- gastrostomy (gastr/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening in the stomach
- hemicolectomy (hemi/col/ectomy)
- excision of half of the colon
- choledocholithiasis (choledoch/o/lith/iasis)
- condition of stones in the common bile duct
- uvulectomy (uvul/ectomy)
- excision of the uvula
- peritoneal (periton/eal)
- pertaining to the peritoneum
- ileostomy (ile/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening in the ileum
- steatorrhea (steat/o/rrhea)
- discharge of fat
- sialolith (sial/o/lith)
- stone in the salivary gland
- proctology (proct/o/logy)
- study of disease and disorders of the rectum
- gastrojejunostomy (gastr/o/jejun/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening between the stomach and the jejunum
- rectal (rect/al)
- pertaining to the rectum
- gingivitis (gingiv/itis)
- inflammation of the gums
- colonoscopy (colon/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the colon
- colorectal (col/o/rect/al)
- pertaining to the colon and rectum
- anal (an/al)
- pertaining to the anus
- duodenal (duoden/al)
- pertaining to the duodenum
- abdominocentesis (abdomin/o/centesis)
- surgical puncture to aspirate fluid from the abdomen
- hepatitis (hepat/itis)
- inflammation of the liver
- laparoscope (lapar/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the abdominal cavity
- antrectomy (antr/ectomy)
- excision of the antrum (of the stomach)
- enterorrhaphy (enter/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of the intestine
- esophagitis (esophag/itis)
- inflammation of the esophagus
- uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
- uvul/o/palat/o/pharyng/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the uvula, palate, and pharynx
- peritonitis (periton/itis)
- inflammation of the peritoneum
- diverticulectomy (diverticul/ectomy)
- excision of the diverticula
- enteropathy (enter/o/pathy)
- disease of the intestines
- proctologist (proct/o/logist)
- Specialist who studies and treats diseases of the rectum
- gastritis (gastr/itis)
- inflammation of the stomach
- abdominoplasty (abdomin/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the abdomen
- celiotomy (celi/o/tomy)
- incision into the abdominal cavity
- gastroenteritis (gastr/o/enter/itis)
- inflammation of the stomach and intestines
- endoscopy (endo/scopy)
- process of viewing within (hollow organs)
- palatoplasty (palat/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the palate
- laparotomy (lapar/o/tomy)
- incision into the abdominal cavity
- colonoscope (colon/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the colon
- polypectomy (polyp/ectomy)
- excision of polyps
- gastrojejunostomy (gastr/o/jejun/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening between the stomach and the jejunum
- CT colonography (CT colon/o/graphy)
- radiographic imaging of the colon using computed tomography
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- esophag/o/gastr/o/duoden/o/scopy
- process of viewing the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
- stomatogastric (stomat/o/gastr/ic)
- pertaining to the mouth and stomach
- celiac (celi/ac)
- pertaining to the abdomen
- gastromalacia (gastr/o/malacia)
- softening of the stomach
- dyspepsia (dys/pepsia)
- difficult digestion
- esophagogastroplasty (esophag/o/gastr/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the esophagus and stomach
- sublingual (sub/lingu/al)
- pertaining to under the tongue
- steatohepatitis (steat/o/hepat/itis)
- inflammation of liver associated with fat
Activity source: Digestive System Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Digestive System Medical Terms
Digestive System terms (Text Version)
Practice the following digestive system medical terms that are not easily broken into word parts.
- ascites
- abnormal intraperitoneal accumulation of fluid with large number of proteins and electrolytes
- hemorrhoids
- distended and swollen veins in the rectum and anus
- nausea
- urge to vomit
- stoma
- surgical opening between an organ and the surface of the body
- adhesion
- band of scar tissue that binds anatomic surfaces to each other
- emesis
- vomiting
- cirrhosis
- chronic degenerative disease of the liver
- polyp
- small tumour-like growth that extends from the surface of a mucous membrane
- feces
- stool, fecal matter
- obesity
- abnormal increase in the proportion of fat cells resulting in excess body weight for height
- dysentery
- inflammation of the intestine presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea
- melena
- black tarry stool that contains blood from the GI tract
- flatus
- gas in the GI tract
- reflux
- abnormal backward flow
- palpate
- physical examination technique: The examiner feels for texture, size, consistency, and location of body parts with hands.
Activity source: Digestive System terms not easily broken down into word parts by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Commonly Abbreviated Digestive System Terms
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated digestive system terms:
- APR (abdominoperineal resection)
- BE (barium enema)
- EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
- EUS (endoscopic ultrasound)
- FOBT (fecal occult blood test)
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
- GI (gastrointestinal)
- H.pylori (Helicobacter pylori)
- IBS (irritable bowel syndrome)
- N&V (nausea and vomiting)
- PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy)
- UC (ulcerative colitis)
- UGI (upper gastrointestinal)
- UPPP (uvulopalatopharyngoplasty)
Sorting Terms
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories:
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Digestive System Structures
Label the following digestive system anatomy:
Digestive System Anatomy (Text Version)
Label the diagram with correct words listed below:
- Gallbladder
- Mouth
- Jejunum
- Tongue
- Ileum
- Sigmoid colon
- Liver
- Submandibular gland
- Anal canal
- Parotid gland
- Descending colon
- Duodenum
- Esophagus
- Tranverse colon
- Pharynx
- Anus
- Sublingual gland
- Ascending colon
- Cecum
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Rectum
- Appendix
- Pancreas
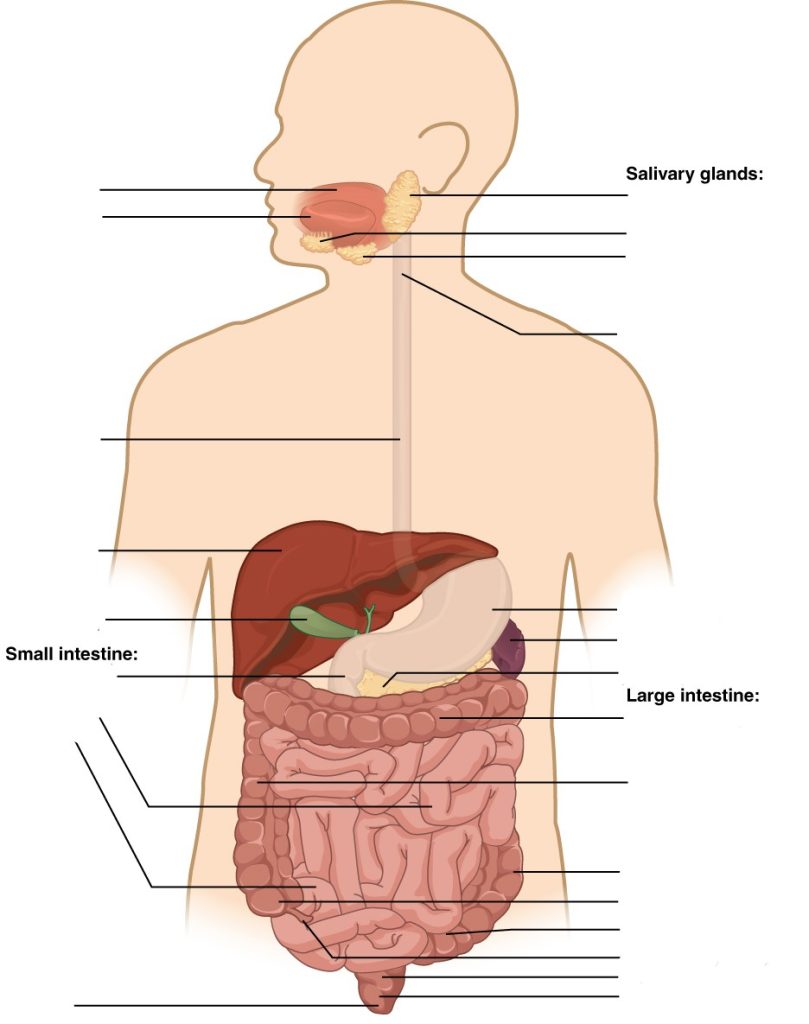
Digestive System Anatomy Diagram (Text Version)
This diagram shows an anterior view of the head and torso of the human body with the anatomical organs and structures comprising the digestive system identified. From the top working clockwise. Located in the mouth or oral cavity are three glands which secrete saliva containing enzymes to aid in digestion these include: _______[Blank 1], ______[Blank 2], and the _________[Blank 3]. When the ingested food is ready to leave the mouth, it is transferred to the throat to swallow, the throat is also known as the ________[Blank 4]. The ________[Blank 5] is a muscular hollow organ which aids in the digestive process by breaking down food for digestion. While the _______[Blank 6] located under the left portion of the diaphragm, helps to filter blood. The ______[Blank 7] is an accessory organ responsible for producing a hormone known as insulin and insulin is critical in the metabolism of sugars. The large intestines have many structural components ________[Blank 8],_________[Blank 9], ________[Blank 10], ________[Blank 11], and _______[Blank 12] with these structures responsible for the final stage of digestion known as elimination. A small finger-like projections hangs from the cecum known as the ________[Blank 13] and this structure has a role in the development of the immune system in early human development. As a continuation of the sigmoid colon a hollow structure known as the _________[Blank 14] is identified. Next, is the final segment of the digestive system and is a structure measuring about 3 to 4 cm long known as the _______[Blank 15]. Fecal matter is expelled through the terminal opening in the digestive system called the ______[Blank 16]. The small intestines divided into three distinct parts; the is the third part ______[Blank 17], the _______[Blank 18] is the second part, and the _______[Blank 19] is the first part. The _______[Blank 20] is an accessory organ of digestion and is responsible for storing bile for when it is needed to breakdown fats in the process of digestion. The _______[Blank 21] located in the upper right side of the abdomen is responsible for producing the bile to send to the gallbladder for storage until it the bile is released. The _______[Blank 22] connects the pharynx to the stomach it is responsible for gently moving the food from the pharynx to the stomach. The _______[Blank 23] located in the mouth is responsible for moving the food around in the mouth during the chewing or mastication process. The _______[Blank 24] also known as the oral cavity contains the saliva glands, the teeth and tongue and begins the process of digestion.
Check your answers [1]
Activity source: Digestive System Anatomy by Gisele Tuzon, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation, illustration from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax), licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Digestive System(Text version)
Fill in the blanks using the following list of words:
- polyp
- palpate
- obesity
- hemorrhoids
- emesis
- melena
- flatus
- ascites
- feces
- reflux
- nausea
- cirrhosis
- dysentery
- adhesion
- stoma
The Physician during an examination will ________[Blank 1] to feel for texture, size, consistency and location of body parts with hands.
A _______[Blank 2] is a small tumour-like growth that extend from the surface of a mucous membrane.
___________[Blank 3] is an abnormal increase in the proportion of fat cells resulting in excess body weight for height.
Distended and swollen veins in the rectum and anus are called ___________[Blank 4].
The medical term for vomiting is ____________[Blank 5].
__________[Blank 6] is black tarry stool that contains blood from the gastrointestinal tract.
_________[Blank 7] is the medical term for gas in the gastrointestinal tract.
Abnormal intraperitoneal accumulation of fluid with large amount of proteins and electrolytes is _________[Blank 8].
____________ is fecal matter.
Abnormal backward flow is called ____________[Blank 10].
The urge to vomit is __________[Blank 11].
__________[Blank 12] is a chronic degenerative disease of the liver due to alcohol abuse.
___________[Blank 13] is an inflammation of the intestine presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea.
A band of scar tissue that binds anatomic surfaces to each other is called an ___________[Blank 14].
The surgical opening between an organ and the surface of the body is called a ___________[Blank 15].
Check your answers: [2]
Activity source: Digestive System by Alyssa Arsenault, licensed under CC BY- 4.0 from “Digestive System” in Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Converted to Text.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Digestive System – Consultation Report (Text version)
Use the words below to fill in the consultation report:
- diarrhea
- treatment
- electrolytes
- Glucose
- resists walking
- session
- vomiting
- stools
- eyes
- gait
PATIENT NAME: Alex WEBB
AGE: 30
DOB: November 10
SEX: Male
CONSULTANT: Louis D. Wainwright, MD, Gastroenterology
REQUESTING PHYSICIAN: Trevor Sharpe, MD, Family Medicine
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Please evaluate GI distress.
I was asked to see this 30-year old male in consultation because of unremitting nausea, _______[Blank 1], __________[Blank 2], abdominal pain, dizziness, and low-grade fever. The patient has a poor appetite but reports no weight loss. He has noted some postprandial cramping, midepigastric pain, and unremitting diarrhea but no blood in the _________[Blank 3]. He states he is “healthier,” but he still has some dizziness.
Initial treatment consisted of IV fluids and control of __________[Blank 4]. Thereafter, the patient was progressed to clear fluids and soft diet. He has done well on this routine; however, his dizziness has persisted. Fever has resolved.
On admission, the patient’s lab data revealed CBC with hematocrit of 142, hemoglobin 25 with differential of neutrophils 51%, bands 8%, lymphocytes 26%, monocytes 6%, basophils none. Serum electrolytes were normal. Potassium was low at 3.5, BUN: creatinine ratio was normal. ________[Blank 5] was within normal range. Stool studies were within normal.
On examination, I find the patient to be lethargic and uncomfortable with mild nausea and dizziness. He prefers to keep his eyes closed. On examination of the ________[Blank 6], I find no nystagmus. There is pallor to the skin, and he seems cool to the touch. Upon standing by the bedside, the patient is unsteady. Although he _________[Blank 7], when he attempts to walk, his __________[Blank 8] is halting, and he tends to fall to the left side. Abdomen is flat and nontender. Bowel sounds are WNL. Rectal exam deferred.
RECOMMENDATIONS: I think we should continue essential ________[Blank 9] of this gentleman. Because of the symptoms of dizziness on admission, we may want to consider a CT scan to rule out an intracerebral bleed or subdural hematoma. My opinion at this time is that we are dealing with a resolving __________[Blank 10] of gastritis.
Thank you for asking me to see this patient. I will be glad to follow him with you throughout his hospital stay.
____________________________________
Louis D. Wainwright, MD, Gastroenterology
Check your answers: [3]
Activity source: Digestive System – Consultation Report by Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Digestive System – Operative Report (Text version)
Use the words listed below to fill in the operative report:
- esophagitis
- ulceration
- lateral
- stomach
- GE
- sporadic
- retroflexion
- bleeding
- antrum
- duodenum
- lidocaine
- duodenitis
PATIENT NAME: Bruce WEBSTER
AGE: 48
SEX: Male
DOB: September 23
DATE OF ADMISSION: July 2
DATE OF PROCEDURE: July 2
ADMITTING PHYSICIAN: Trevor Sharpe, MD, Family Medicine
SURGEON: Louis D. Wainwright, MD, Gastroenterology
PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: GI Bleed.
POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSES:
- Severe _______[Blank 1].
- Gastroesophageal ________[Blank 2].
- No Significant bleeding seen in the stomach.
OPERATIVE PROCEDURE: Gastrointestinal endoscopy.
ANESTHESIA: _________[Blank 3] 1%.
PROCEDURE: The patient was placed into the left _________[Blank 4] position. A scope was introduced from the mouth, under visualization and advanced to the upper part of the _______[Blank 5], upper part of esophagus, middle of esophagus, ________[Blank 6] junction, and some __________[Blank 7] bleeding was seen at the GE junction. The scope was moved through the upper part of the stomach into the _________[Blank 8]. The __________[Blank 9] showed some inflammation and the scope was then brought out. ________[Blank 10] was not performed. The scope was then brought back slowly. Mild _________[Blank 11] was also seen and a little bit of ulceration noted at GE junction.
CONCLUSION: Severe esophagitis, may be some source of __________[Blank 12] from there, but no active bleeding at this time.
___________________________________
Louis D. Wainwright, MD, Gastroenterology
Check your answers: [4]
Activity source: Digestive System – Operative Report by Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Test Your Knowledge
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below:
Digestive System Glossary Reinforcement Activity (Text version)
- ______ [Blank 1] is a band of smooth muscle at the junction between the pylorus of the stomach and the duodenum of the small intestine.
- Ampulla
- Quadrate
- Pyloric sphincter
- Fatty tissue that stretches over the abdomen, plays a role in immune response and the growth of certain cancers is called _____[Blank 2].
- Fundus
- Convex
- Omentum
- The process of breaking down the fat into smaller blood cells which makes it easy for enzymes to function and digest food is called _____[Blank 3].
- Bicarbonate
- Malabsorption
- Emulsification
- ______[Blank 4] is the location where the diaphragm has a small opening through which the esophagus passes before connecting.
- Hiatal
- Lacteals
- Hilum
- Situated nearer to the center of the body or the point of attachment is the ____ [Blank 5].
- Proximal
- Distal
- Quadrate
Check your answers: [5]
Activity source: Digestive System Glossary Reinforcement Activity by Gisele Tuzon, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Downloadable Worksheets
View or download & print the PDF or Word format worksheet below:
Worksheet – Digestive System – Chapter 12 [Word]
12. Digestive System – Definitions Using Word Parts [Word]
12. Digestive System – Scenarios [Word]
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this book is adapted from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al. (2022), Nicolet College, CC BY 4.0 International. / A derivative of Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Carter & Rutherford (2020), and Anatomy and Physiology by Betts, et al., CC BY 4.0, which can be accessed for free at OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology.
-
↵
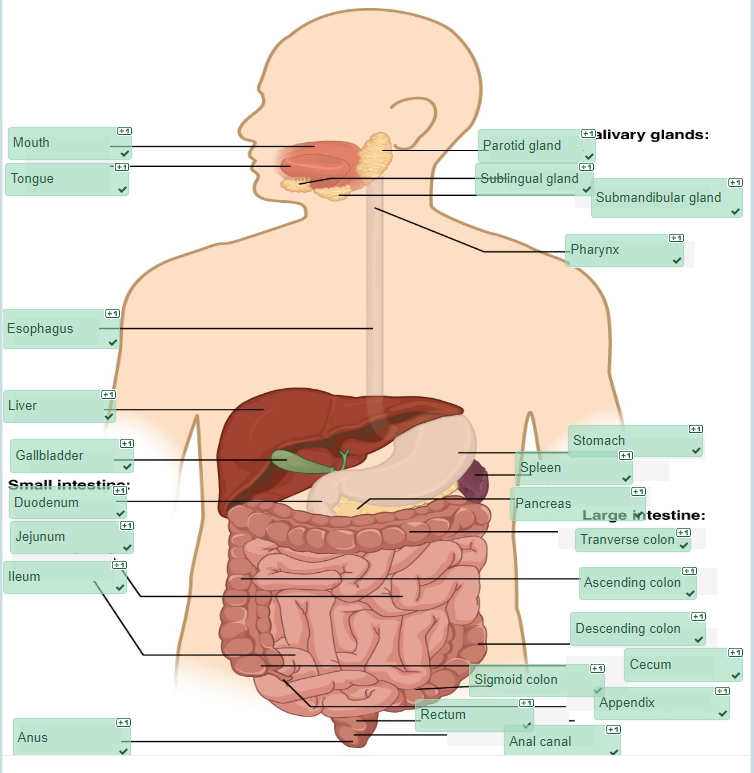
Check your answers: Digestive System Anatomy Diagram (Text Version)
This diagram shows an anterior vies of the head and torso of the human body with the anatomical organs and structures comprising the digestive system identified. From the top working clockwise Located in the mouth or oral cavity are three glands which secrete saliva containing enzymes to aid in digestion these include: parotid gland, sublingual gland, and the submandibular gland. When the ingested food is ready to leave the mouth, it is transferred to the throat to swallow, the throat is also known as the pharynx. The stomach is a muscular hollow organ which aids in the digestive process by breaking down food for digestion. While the spleen located under the left portion of the diaphragm, helps to filter blood. The pancreas is an accessory organ responsible for producing a hormone known as insulin and insulin is critical in the metabolism of sugars. The large intestines have many structural components transverse colon, ascending colon, descending colon, cecum, and sigmoid colon with these structures responsible for the final stage of digestion known as elimination. A small finger-like projections hangs from the cecum known as the appendix and this structure has a role in the development of the immune system in early human development. As a continuation of the sigmoid colon a hollow structure known as the rectum is identified. Next, is the final segment of the digestive system and is a structure measuring about 3 to 4 cm long known as the anal canal. Fecal matter is expelled through the terminal opening in the digestive system called the anus. The small intestines divided into three distinct parts; the is the third part ileum, the jejunum is the second part, and the duodenum is the first part. The gall bladder is an accessory organ of digestion and is responsible for storing bile for when it is needed to breakdown fats in the process of digestion. The liver located in the upper right side of the abdomen is responsible for producing the bile to send to the gallbladder for storage until it the bile is released. The esophagus connects the pharynx to the stomach it is responsible for gently moving the food from the pharynx to the stomach. The tongue located in the mouth is responsible for moving the food around in the mouth during the chewing or mastication process. The mouth also known as the oral cavity contains the saliva glands, the teeth and tongue and begins the process of digestion. - 1. palpate, 2. polyp, 3. obesity, 4. hemorrhoids, 5. emesis, 6. melena, 7. flatus, 8.ascites, 9. feces, 10. reflux, 11. nausea, 12. cirrhosis, 13. dysentery, 14. adhesion, 15. stoma ↵
- 1.diarrhea, 2.vomiting, 3.stools, 4. electrolytes, 5.Glucose, 6.eyes, 7.resists walking, 8.gail 9.treatment, 10.session ↵
- 1. esophagitis, 2.ulceration, 3. lidocaine, 4.lateral, 5.stomach, 6.GE, 7.sporadic, 8.antrum, 9.duodenum, 10.retroflexion, 11.duodenitis, 12.bleeding ↵
- 1. Pyloric sphincter, 2. Omentum, 3. Emulsification, 4. Hiatal, 5. Proximal, ↵

