Gastrointestinal Case Studies
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders refer to conditions affecting the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
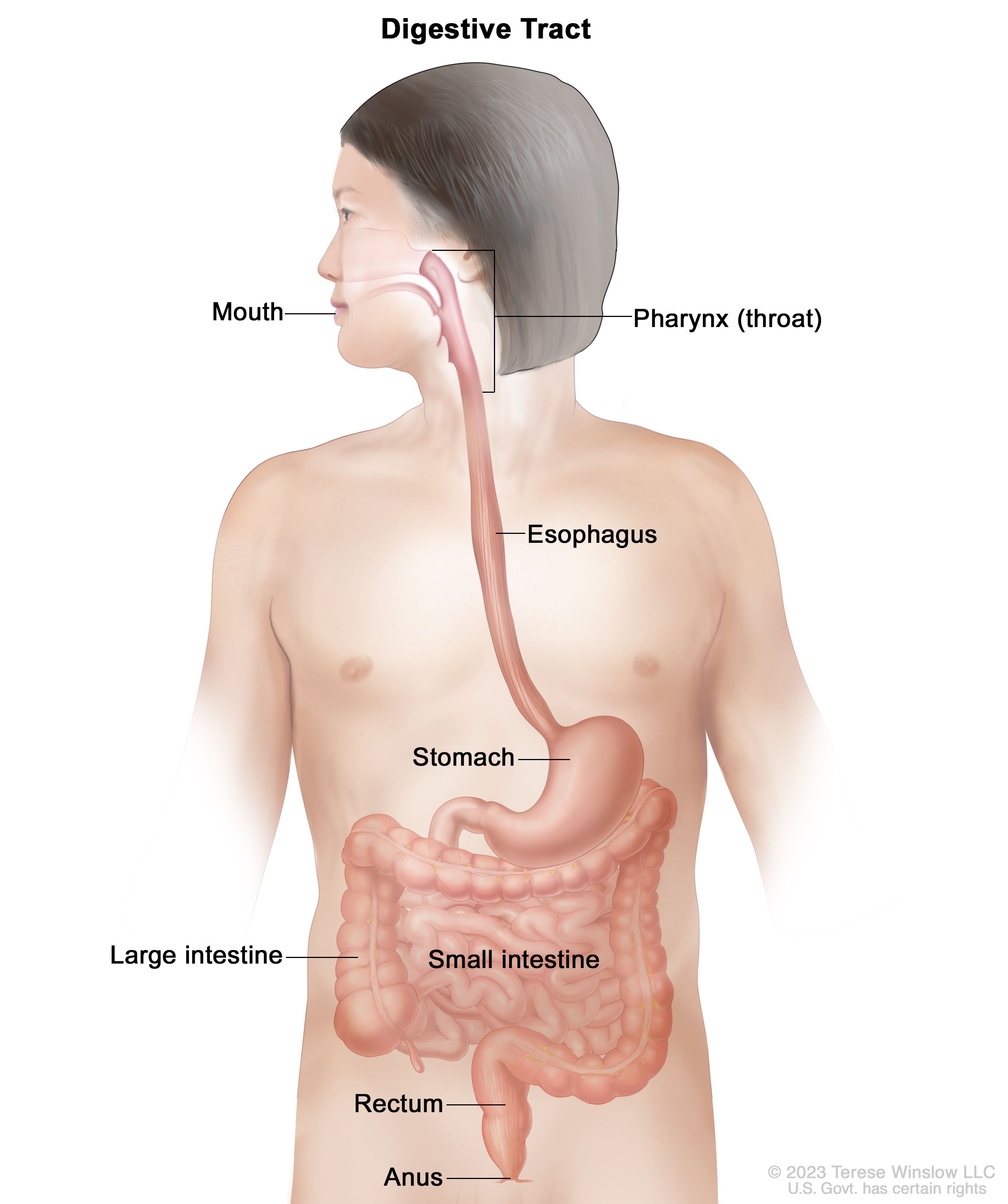
Source: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/gastrointestinal-tract
Common GI disorders
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Celiac disease
- Colorectal cancer
- Gallbladder disease
- Pancreatitis
- Hepatitis
- Gastrointestinal infections (e.g., gastroenteritis)
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms and signs of GI disorders vary depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, difficulty swallowing, heartburn, and rectal bleeding.
Diagnostic Investigation
Diagnostic tests for GI disorders may include imaging studies such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, CT scan, MRI, and ultrasound, as well as blood tests, stool tests, and breath tests.
Treatment
Options for GI disorders may include lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and exercise, medications, and surgery. Examples of treatment modalities for specific conditions include:
- GERD: proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 receptor blockers, antacids
- Peptic ulcer disease: antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori bacteria, PPIs, H2 receptor blockers, antacids
- IBD: immunomodulators, biologics, corticosteroids, aminosalicylates
- IBS: dietary changes, probiotics, antispasmodics, fiber supplements
- Celiac disease: gluten-free diet
- Colorectal cancer: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy
- Gallbladder disease: surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy)
- Pancreatitis: supportive care, pain management, enzyme supplements
- Hepatitis: antiviral medications, liver transplant
- Gastrointestinal infections: antibiotics, anti-diarrheal medications, fluid replacement therapy
Treatment plans are individualized based on the patient’s specific condition and medical history, and may involve a combination of different therapies.

