This post is adapted for the Health & Medical Case Studies created by the Master of Medical Biotechnology program of the University of Windsor. This work licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC-ND) 4.0 International License.
7 Case 2-2021: A 54-year-old male with chest pain
Clinical judgement in chest pain: a case report. Journal Of Medical Case Reports, 15(1). doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02666-z
Goel, M., Dhillon, S., Kumar, S., & Tegeltija, V.
Case Summary 1
A 54-year-old Caucasian male is admitted to the emergency department with chest pain. The patient has a history of tobacco smoking and gastroesophageal reflux (GERD). There was no family history of cardiac events. An asymptomatic electrocardiogram (ECG) stress test was conducted. Cardiac catheterization and coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) would assist in diagnosing this patient.
Learning Objectives
- Investigating the clinical history of the patient and selecting appropriate examinations to diagnose this cardiological disease.
- Interpreting the patient’s examinations to propose the appropriate diagnosis.
- Familiarizing and defining new medical terminology associated with cardiac disease.
- Extrapolating key lifestyle factors that have contributed to the cardiac disease and treatment measure that needs to be put in place.
Clinical History 1
- Age: 54 years old
- Sex: Male
- Ethnicity: Caucasian
Medical History 1
- History of tobacco smoking.
- No significant family history of cardiac events.
- BMI 29.
Symptoms 1
- Three weeks of intermediate chest pain, radiating to his left arm and jaw.
Examinations (Clinical Assays/Tests/Imaging) 1
Physical Examination 1
- Blood pressure of 139/85 mmHg.
- Heart rate of 81 beats per minute.
- The intermediate pretest probability of CAD (coronary artery disease) is based on age and sex.
Electrocardiogram (EKG) 1
- No ischemic changes, no left ventricular hypertrophy or left bundle branch block.
Laboratory Investigations 1
- Serial troponin enzyme < 0.010 ng/mL (normal range: <0.04).6
- Lipid panel showed:
- Total cholesterol: 235 mg/dL (normal range: < 200 mg/dL).5
- Triglycerides: 408 (normal range: <149 mg/dL), HDL: 26 (normal range: < 40 mg/dL) and LDL could not be calculated (normal range: <100 mg/dL).5
- Patient achieved 95% of maximum predicted heart rate.
- 10 METs (metabolic equivalents) of exercise with normalization of T wave (ventricular repolarization) inversions were seen in leads V2 (right ventricle), V3(septum) and V4 (septum)at rest.8
- Led to maximum asymptomatic stress test results.
- Intermediate probability of ischemia.
- Led to maximum asymptomatic stress test results.
- Showed normal left ventricular function with no wall motion or significant valvular abnormalities.
Echocardiogram1
- Normal left ventricular function and no significant valvular or wall motion abnormalities.
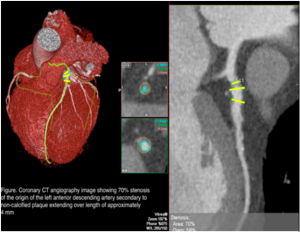
- Showed approximate 70% stenosis (narrowing) of origin of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and noncalcified plaque with an approximate length of 4 mm (figure 1, yellow lines).
- Approximate 40-50% stenosis of proximal ramus intermedius (variant coronary artery) branch secondary to mixed calcified and noncalcified plaque and scattered noncalcified and calcified plaque along obtuse and circumflex marginal branches (branches from the main artery) with luminal diameter stenosis (diameter of permissible blood flow) of approximately 30-40%.12
Fractional Flow Reserve-Computed Tomography (FFR-CT) 1
- Results showed a high likelihood of flow-limiting stenosis, less than 0.5 secondary to significant stenosis at LAD origin, with a low likelihood of flow-limiting stenosis in ramus intermedius (variant main coronary artery), right coronary arteries, and left circumflex (branch off left coronary artery).
Cardiac Catheterization 1
- Showed 95% stenotic lesion of LAD with partial perfusion (TIMI grade 2 flow) –penetration without perfusion (incomplete filing of distal coronary bed).7
- This would give rise to diagonal 1 (a branch from the left anterior descending artery), with an ostial and proximal (narrowing of the ostium) 70% stenosis.
- “Ramus intermedius (variant coronary artery) with proximal 70% segmental stenosis”
- “Circumflex, nondominant vessel – a mild disease in proximal-distal segments – giving rise to obtuse marginal 1 (on or close to the left obtuse margin of the heart) with proximal 70% stenosis.”16
Question & Answers Leading to Diagnosis:
Question 1: Based on the patient’s complaint of recurrent chest pains, EKG and serial troponin test, what could be the possible diagnosis?
Question 2: What investigations could be suggested to confirm this patient’s diagnosis?
Question 3: In order to characterize further risk stratification for this patient, what other investigations could be done? How would you classify this patient on the TIMI scale?
** For answers please check the next chapter.
Medical terminology/Abbreviations:
- Bypass graft surgery – Procedure to treat coronary artery disease due to a buildup of fat in the walls of the arteries.2
- Cardiothoracic surgery – Field of medicine involving surgical treatment of organs within the thoracic cavity.3
- Circumflex marginal branches (obtuse marginal branches) – Arteries that curve to the left of the heart that branch from the circumflex arteries to supply the left ventricle.4
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) – Procedure to treat coronary heart disease from the narrowing of arteries.14
- Coronary artery disease (CAD) – Narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque build-up.14
- Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) – Imaging test used to determine plaque build-up in coronary arteries.15
- Diagonal 1 – Branches of the left anterior descending coronary artery that supply the left ventricle.16
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) stress test – Method used to record heart’s blood pressure, electrical activity, and rate under physical exercise conditions.17
- Flow-limiting stenosis (and values) – “Lesion with a diameter narrowing exceeding 50%”.18
- Fractional flow reserve computed tomography (FFR-CT) – Ratio of maximum flow between a stenotic artery to a maximum blood flow of a normal artery of the same type.19
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – The backflow of stomach acid between the stomach and the mouth through the esophagus.20
- HDL (high-density lipoprotein) – “Good” cholesterol is responsible for carrying absorbed cholesterol to the liver in order to remove it from the body.21
- LDL (low-density lipoprotein) – “Bad” cholesterol as an accumulation of this cholesterol leads to plaque build-up in arteries.22
- Leads V2, V3, and V4 – Electrodes that are used to monitor the heart during an electrocardiogram, V2 represents the right ventricle, V3 and V4 represent the septum.23
- Left anterior descending artery (LAD) – Artery which runs anterior to the interventricular septum and is the largest coronary artery.24
- Left circumflex – Branch off the left coronary artery.25
- Luminal diameter stenosis – Diameter of permissible blood flow.12
- METs – Metabolic equivalents, oxygen consumed while at rest.26
- Noncalcified plaque – Refers to plaque buildup that may be reversible in the arteries and risk of myocardial infractions.27
- Obtuse marginal 1 – Located on or close to left obtuse margin of the heart.16
- Partial perfusion (TIMI grade 2 flow) – Slow or delayed complete filling of distal coronary bed.13
- Ramus intermedius – Variant coronary artery.16
- Right coronary artery – One of the two main coronary blood vessels supplying blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, and sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes – responsible for the heart’s natural rhythm.28
- Serial troponin enzyme – Enzymes used to measure the potential evidence of a myocardial infraction.29
- Stenosis – In this case study, it represents the narrowing of blood flow and passage diameter.1
- TIMI grade flow – Method used for assessing coronary artery flow in acute coronary syndromes, below is the grading scale.13
- T wave – Ventricular repolarization during an electrocardiogram stress test.1
- Triglycerides – Fat type found within the blood.30
References
- Goel, M., Dhillon, S., Kumar, S., & Tegeltija, V. (2021). Clinical judgement in chest pain: a case report. Journal Of Medical Case Reports, 15(1). doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02666-z
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. (2021). Retrieved 6 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/coronary-artery-bypass-graft-surgery#:~:text=Coronary%20artery%20bypass%20graft%20surgery%20(CABG)%20is%20a%20procedure%20used,nutrients%20to%20the%20heart%20muscle.
- Ordem dos Médicos – Portal Oficial. (2021). Retrieved 6 April 2021, from https://ordemdosmedicos.pt/?lop=conteudo&op=02522a2b2726fb0a03bb19f2d8d9524d
- Circumflex Artery | Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy. (2021). Retrieved 6 April 2021, from http://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/coronary-arteries/circumflex-artery/index.shtml
- What Are the Recommended Cholesterol Levels by Age?. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/high-cholesterol/levels-by-age#adults
- Mahajan, V., & Jarolim, P. (2011). How to Interpret Elevated Cardiac Troponin Levels. Circulation, 124(21), 2350-2354. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.111.023697
- Sarkar A, Grigg WS, Lee JJ. TIMI Grade Flow. [Updated 2020 Aug 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482412/
- ECG (EKG) Interpretation – Oxford Medical Education. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.oxfordmedicaleducation.com/ecgs/ecg-interpretation/
- Myocardial ischemia – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/myocardial-ischemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20375417
- Troponin I. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://testguide.labmed.uw.edu/public/view/TROPIG
- (ACR), R. (2021). Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angiocoroct#:~:text=Coronary%20computed%20tomography%20angiography%20(CCTA)%20is%20a%20heart%20imaging%20test,vessels%20that%20supply%20the%20heart.
- Paolillo, V., Gastaldo, D., & Vaudano, G. (2006). An unusual course of the ramus intermedius: shown by multislice computed tomographic coronary angiography. Texas Heart Institute journal, 33(3), 406–407.
- Appleby, M.A., Michaels, A.D., Chen, M. et al. Importance of the TIMI frame count: implications for future trials. Trials 1, 31 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1186/cvm-1-1-031
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/coronary-artery-bypass-graft-surgery
- (ACR), R. (2021). Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angiocoroct#:~:text=Coronary%20computed%20tomography%20angiography%20(CCTA)%20is%20a%20heart%20imaging%20test,inner%20lining%20of%20the%20arteries.
- Morgan, M. (2021). Diagonal branches of the left anterior descending artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://radiopaedia.org/articles/diagonal-branches-of-the-left-anterior-descending-artery#:~:text=Diagonal%20branches%20of%20the%20left%20anterior%20descending%20coronary%20artery%20supply,parent%20vessel%20at%20acute%20angles.
- Exercise Electrocardiogram. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.heartandstroke.ca/heart-disease/tests/exercise-electrocardiogram
- Gaemperli, O., Husmann, L., Schepis, T., Koepfli, P., Valenta, I., & Jenni, W. et al. (2009). Coronary CT angiography and myocardial perfusion imaging to detect flow-limiting stenoses: a potential gatekeeper for coronary revascularization?. European Heart Journal, 30(23), 2921-2929. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp304
- Lee, J. H., Hartaigh, B. Ó., Han, D., Rizvi, A., Lin, F. Y., & Min, J. K. (2016). Fractional Flow Reserve Measurement by Computed Tomography: An Alternative to the Stress Test. Interventional cardiology (London, England), 11(2), 105–109. https://doi.org/10.15420/icr.2016:1:2
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gerd/symptoms-causes/syc-20361940
- HDL cholesterol: How to boost your ‘good’ cholesterol. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/hdl-cholesterol/art-20046388
- Topics, H. (2021). LDL: The “Bad” Cholesterol: MedlinePlus. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ldlthebadcholesterol.html#:~:text=LDL%20stands%20for%20low%2Ddensity,stands%20for%20high%2Ddensity%20lipoproteins.
- ECG (EKG) Interpretation – Oxford Medical Education. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.oxfordmedicaleducation.com/ecgs/ecg-interpretation/
- Rehman I, Kerndt CC, Rehman A. Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Left Anterior Descending (LAD) Artery. [Updated 2020 Jul 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482375/
- Circumflex Artery | Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from http://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/coronary-arteries/circumflex-artery/index.shtml
- Jetté, M., Sidney, K., & Blümchen, G. (1990). Metabolic equivalents (METS) in exercise testing, exercise prescription, and evaluation of functional capacity. Clinical cardiology, 13(8), 555–565. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.4960130809
- Pan, X., & Dylan Wolman, M. (2021). Cardiac risk factors associated with noncalcified plaque burden in asymptomatic patients | 2 Minute Medicine. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.2minutemedicine.com/cardiac-risk-factors-associated-with-noncalcified-plaque-burden-in-asymptomatic-patients/#:~:text=Noncalcified%20plaque%20is%20both%20the,direct%20measure%20for%20patient%20risk
- Anatomy and Function of the Coronary Arteries. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/anatomy-and-function-of-the-coronary-arteries
- van Domburg, R. T., Cobbaert, C., Kimman, G. J., Zerback, R., & Simoons, M. L. (2000). Long-term prognostic value of serial troponin T bedside tests in patients with acute coronary syndromes. The American journal of cardiology, 86(6), 623–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9149(00)01040-7
- Can triglycerides affect my heart health?. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/triglycerides/art-20048186#:~:text=Triglycerides%20are%20a%20type%20of,triglycerides%20for%20energy%20between%20meals.
Creative Commons License
Method used to record heart’s blood pressure, electrical activity, and rate under physical exercise conditions.
Narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque build-up.
Enzymes used to measure the potential evidence of a myocardial infraction.
Fat type found within the blood.
Metabolic equivalents, oxygen consumed while at rest.
Ventricular repolarization during an electrocardiogram stress test.
Electrodes that are used to monitor the heart during an electrocardiogram, V2 represents the right ventricle, V3 and V4 represent the septum.
Imaging test used to determine plaque build-up in coronary arteries.
In this case study, it represents the narrowing of blood flow and passage diameter.
Artery which runs anterior to the interventricular septum and is the largest coronary artery.
Refers to plaque buildup that may be reversible in the arteries and risk of myocardial infractions.
Variant coronary artery.
Circumflex marginal branches (obtuse marginal branches) – Arteries that curve to the left of the heart that branch from the circumflex arteries to supply the left ventricle.
Diameter of permissible blood flow.
Branch off the left coronary artery.
Slow or delayed complete filling of distal coronary bed.
Branches of the left anterior descending coronary artery that supply the left ventricle.
Located on or close to left obtuse margin of the heart.


