This post is adapted for the Health & Medical Case Studies created by the Master of Medical Biotechnology program of the University of Windsor. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC-ND) 4.0 International License.
19 Case 3-2017: A 40-year-old female with epigastric pain, nausea and vomiting
Acute Pancreatitis: An Atypical Presentation. Case reports in gastroenterology, 2017, 11(2), 359–363. https://doi.org/10.1159/000475920
Nadhem, O., & Salh, O.
Case Summary 1
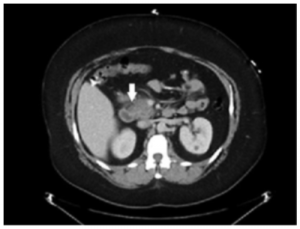
A 40-year-old woman is presented with severe, sharp epigastric pain radiating to the back with symptoms of nausea and vomiting. She has a medical history of hypertension and cholecystectomy three years prior to this hospital admission. Upon examination epigastric tenderness was present. Lab investigations showed whole blood cell counts were high (22.1 × 103/μL with neutrophils 87%) while serum amylase and lipase level were normal. To exclude further diagnosis an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan was done which showed fat stranding in the pancreatic head.
Learning Objectives
- Investigating the clinical history of the patient and selecting appropriate examinations for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
- Understanding the atypical presentation of acute pancreatitis and identifying those presented in the patient.
- Familiarizing and defining new medical terminology associated with acute pancreatitis.
Clinical History 1
- Age: 40 years old
- Sex: Female
Medical History 1
- Hypertension
- Bipolar disorder
- Cholecystectomy (three years prior to this hospital admission)
Symptoms 1
- Severe, sharp epigastric abdominal pain radiating to the back.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Examinations (Clinical Assays/Tests/Imaging) 1
Physical Examination 1
- Heart rate – 105 beats/min
- Blood pressure – 132/84 mm Hg
- Severe epigastric tenderness- present.
Blood Investigations 1
- WBC: 22.1 × 103/μL with neutrophils 87%, (normal range: 4000-10,000/μL, 45%-75% neutrophils)6
- Hemoglobin: 14.0 g/dL (normal range:12.0-15.5g/dl)8
- Platelets: 380 × 103/μL. (normal range:150×109-400×109/L)7
- Potassium level: 2.7 mEq/L (normal range: 3.5-5.5 mEq/L)2
- Triglyceride level: 53 mg/dL (normal range: <150 mg/dL)3
- Serum amylase: 31 IU/L (normal range: 20–160)1
- Serum lipase: 14 IU/L (normal range: 8–78)1
Abdominal Computed Tomography (CT) Scan 1
Question & Answers Leading to Diagnosis:
Question 1: Based on the physical, imaging and laboratory investigations, what results would support this patient’s diagnosis? Does she meet all the criteria for this diagnosis?
Question 2: If this were a clear acute pancreatitis case, what lab results would we expect to see?
Question 3: What factors would lead to normal amylase and lipase levels in acute pancreatitis?
** For answers please check the next chapter.
Medical terminology/Abbreviations:
- AP (Acute pancreatitis) – Acute pancreatitis means inflammation of the pancreas that develops quickly.10
- CT scan – Computerized Tomography scan. (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside your body. 11
- Cholecystectomy – Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder. 4
- Epigastric region – Epigastric region is the upper central region of the abdomen.5
References
- Nadhem, O., & Salh, O. (2017). Acute Pancreatitis: An Atypical Presentation. Case reports in gastroenterology, 11(2), 359–363. https://doi.org/10.1159/000475920
- Rastegar, A. (2021). Serum Potassium. Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK307/
- Lee, Y., & Siddiqui, W. (2021). Cholesterol Levels. Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542294/
- (2021). Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/cholecystectomy.
- epigastric region. (2021). Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/epigastric+region
- Blumenreich, M. (2021). The White Blood Cell and Differential Count. Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK261/
- Daly, M. (2010). Determinants of platelet count in humans. Haematologica, 96(1), 10-13. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.035287
- Hemoglobin test – Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/hemoglobin-test/about/pac-20385075#:~:text=The%20normal%20range%20for%20hemoglobin,to%2015.5%20grams%20per%20deciliter
- Banks PA, Freeman ML: Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:2379–400.
- Knott, D. (2021). Acute Pancreatitis | Symptoms, Causes and Treatment | Patient. Retrieved 28 May 2021, from https://patient.info/digestive-health/gallstones-and-bile/acute-pancreatitis
- CT scan – Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 28 May 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-scan/about/pac-20393675
Creative Commons License
upper central region of the abdomen
Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder.
Acute pancreatitis means inflammation of the pancreas that develops quickly.
Computerized Tomography scan. (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside your body.


