Medical Terminology
A
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) – The enlargement of the lower area of the major vessel which supplies blood to the body.1
Acquired Hemophilia A – Acquired Hemophilia A (AHA) is a rare bleeding disorder related to the formation of autoantibodies to Factor VIII.2
Adenocarcinoma – Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that starts in mucus-producing glandular cells of the body.3
Adenomyoma – A benign mass-forming lesion composed of smooth and glandular muscle.4
Antibiotic prophylaxis – Antibiotic usage before surgery or procedure in order to prevent bacterial infection. 5
Anti-thyroid peroxisomal antibodies – Antibodies that are associated with a thyroid disease due to an autoimmune disorder.6
Anti-thyroid receptor antibodies – Antibodies responsible for blocking, neutralizing, and activating thyroid receptors, associated with autoimmune thyrotoxicosis.7, 8
AP (Acute pancreatitis) – Acute pancreatitis means inflammation of the pancreas that develops quickly.9
APGAR score (Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity, and Respiration)10– The Apgar score is a scoring system that assesses newborn babies’ well-being using five different factors: heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, reflexes, and skin color. APGAR is a quick test performed on a baby at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. The 1-minute score determines how well the baby tolerated the birthing process. The 5-minute score tells the health care provider how well the baby is doing outside the mother’s womb. The score is based on a total score of 1 to 10. The higher the score, the better the baby is doing after birth.11
APTT or PTT – The partial thromboplastin time (PTT; also known as activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)) is a screening test that helps evaluate a person’s ability to appropriately form blood clots.12
ARDS – Acute respiratory distress syndrome.13
B
Bleeding diathesis – In medicine (hematology), bleeding diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleed (hemorrhage) mostly due to hypocoagulability (a condition of irregular and slow blood clotting), in turn, caused by a coagulopathy (a defect in the system of coagulation). 14
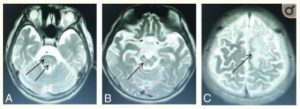
Brain MRI in Wilson disease- MR imaging is a sensitive method to evaluate the brains of patients with neurologic WD. Whereas abnormalities in the putamen are the most common feature of neurologic WD, brain shrinkage is also frequently observed. 15
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) – It is a peptide hormone that is released in response to volume expansion and the increased wall stress of cardiac myocytes.16
Bronchoscopy – Bronchoscopy is a procedure that looks inside the lung airways. It can detect tumors, signs of infection, excess mucus in the airways, bleeding, or blockages in the lungs.17
Brudzinski’s sign – Brudzinski’s sign is one of the physically demonstrable symptoms of meningitis. Severe neck stiffness causes a patient’s hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed. (Figure 3) It is used to diagnose meningitis.18
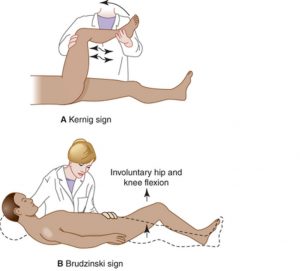
Kernig’s sign – Kernig’s sign is one of the physically demonstrable symptoms of meningitis. Severe stiffness of the hamstrings causes an inability to straighten the leg when the hip is flexed to 90 degrees. (Figure 3) It is used to diagnose meningitis.19
Bypass graft surgery – Procedure to treat coronary artery disease due to a buildup of fat in the walls of the arteries.20
C
Cardiothoracic surgery – A field of medicine involving surgical treatment of organs within the thoracic cavity.21
Carious dentition – Dental caries or cavities, more commonly known as tooth decay, are caused by a breakdown of the tooth enamel. This breakdown is the result of bacteria on teeth that break down foods and produce acid that destroys tooth enamel and results in tooth decay. 22
CEA – A carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) test is a blood test used to help diagnose and manage certain types of cancers.23
Ceruloplasmin test– Ceruloplasmin is a copper-containing enzyme that plays a role in the body’s iron metabolism. This test measures the amount of ceruloplasmin in the blood. The liver binds copper to a protein to produce ceruloplasmin and then releases it into the bloodstream. About 95% of the copper in the blood is bound to ceruloplasmin. Because of this, the ceruloplasmin test can be used along with one or more copper tests to help diagnose Wilson disease, an inherited disorder that can lead to excess storage of copper in the eyes, liver, brain, and other organs. 24
CfDNA – In addition to the classic biomarkers, cfDNA was first described in 1948, has the potential to be a useful marker in septic shock. CfDNA is released into the circulation through cell lysis, necrosis, apoptosis and active DNA release, resulting in higher concentrations of cfDNA in patients with microbial infections, trauma, cancer and other clinical conditions. Although elevated levels of cfDNA are not specific to a single disease, elevated cfDNA has been shown to be an extremely sensitive and promising prognostic marker in septic shock. This observation may be associated with the shorter half-life of cfDNA than that of PCT and CRP. According to Ahmed, cfDNA is a good prognostic predictor for patients in the ICU and, to a lesser extent, is a good marker of septic shock. However, the inevitable loss of cfDNA during extraction has become a considerable detriment, hindering its clinical applications. We previously developed a duplex real-time PCR assay with an internal control as a novel method for the accurate quantification of plasma cfDNA, which can eliminate preanalytical errors and increase precision and accuracy. Our previous studies showed the clinical value of plasma cfDNA levels, as measured by this novel method, in several conditions. CfDNA levels can be useful not only in evaluating chemotherapy effects and guiding treatment in advanced lung cancer patients but also in assessing liver injury in hepatitis B patients. In this case, cfDNA remained high until the patient died, suggesting that cfDNA could be used to monitor disease progression more effectively than PCT.25
Chemokines – A family of chemoattractant cytokines that are secreted by cells in response to the body’s immune system.26
Cholecystectomy – Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder. 27
Cine CMR– It consists of the acquisition of the same slice position at different phases of the cardiac cycle. 28
Circumcision – Circumcision is the surgical removal of the skin covering the tip of the penis.29
Circumflex marginal branches (obtuse marginal branches) – These are the arteries that curve to the left of the heart that branch from the circumflex arteries to supply the left ventricle.30
Class II NYHA dyspnea – Mild symptoms of shortness of breath. 31
CMR imaging – Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging.28
Computed tomography (CT) aortogram – A technique using CT scanning and an injection of contrast material into the blood vessels to examine and diagnose cardiovascular diseases.32
Computed tomography (CT) thorax – An imaging test to examine organs and chest using X-ray and computer technology.33
Congestive heart failure – A condition where the heart muscles don’t pump blood as efficiently as they should.34
Coronal computed tomography (CT) angiogram – A technique using CT scanning and an injection of contrast material into the blood vessels to evaluate structure and patency of arteries supplying lower limbs and abdomen with blood.35
Coronary Angiography – Coronary angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the arteries in the heart.36
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) – A procedure to treat coronary heart disease from the narrowing of arteries.37
Coronary artery disease (CAD) – Narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque build-up.37
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) – An imaging test used to determine plaque buildup in coronary arteries.38
CRS – Cytokine Release Syndrome. CRS is a systemic inflammatory response due to massive T cell stimulation that can be triggered by a variety of factors such as infections, and certain drugs.39The COVID-19 virus binds to alveolar epithelial cells, activating the innate and adaptive immune systems resulting in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This can lead to the CRS which is characterized by a hyperinflammatory state with raised inflammatory cytokines and biomarkers such as interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, IL-7, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, macrophage inflammatory protein 1-α, tumor necrosis factor-α, CRP, ferritin, Pro-BNP and D-dimer.40
CT scan – Computerized Tomography scan. (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body. 41
Cytokines – Group of glycoproteins, peptides and proteins secreted by cells in response to the immune system, they regulate and mediate immunity. 42
D
D-dimers – It is a small protein fragment present in the blood after the degradation of a blood clot. D-dimer concentration help to diagnose thrombosis and intravascular coagulation.43
Diagonal 1 – Branches of the left anterior descending coronary artery that supply the left ventricle.44
Dysarthria – Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder in which the muscles that are used to produce speech are damaged, paralyzed, or weakened. The person with dysarthria cannot control their tongue or voice box and may slur words.45
Dysphagia – Difficulty in swallowing.46
Dyspnea – Dyspnea means difficulty in breathing, breathlessness, or a feeling of suffocation.47
E
Ecchymosis – Medical term for common bruise caused by the impact of an injury.48
ECG – An electrocardiogram or ECG is a test to record the electrical signals in the heart.49
Echocardiogram – An echocardiogram (echo) is a graphic outline of the heart’s movement done by ultrasound.50
Electrocardiogram (ECG) stress test – A method used to record heart’s blood pressure, electrical activity, and rate under physical exercise conditions.51
Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) – Invasive procedure that aids in assessing digestive and lung disease.52
Endoscopy – An endoscopy is a procedure in which your doctor uses specialized instruments to view and operate on the internal organs and vessels of your body.53
Epigastric/ Epigastric region – Upper central region of the abdomen.54,55
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine (the duodenum).56
F
Factor IX – Essential clotting factor deficient in Hemophilia B.57
Factor VIII – Essential clotting factor deficient in Hemophilia A.57
Fibrinogen level – Fibrinogen is a plasma glycoprotein synthesized by the liver and is the major structural component of a clot.58
Flow-limiting stenosis (and values) – “Lesion with a diameter narrowing exceeding 50%”59
Fractional flow reserve computed tomography (FFR-CT) – Ratio of maximum flow between a stenotic artery to a maximum blood flow of a normal artery of the same type.60
Frenulum- Elastic band of tissue under the glans penis.61
FST2WI – Fat Suppressed T2-Weighted Imaging.4 FST2WI fusion technology improves signal differences with surrounding structures and facilitates the better evaluation of disease.62
G
Gastric body – Synonymous for the stomach.63
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – The backflow of stomach acid between the stomach and the mouth through the esophagus.64
Gastroesophageal varices- Gastroesophageal varices or esophageal varices are abnormal, enlarged veins in the tube that connects the throat and stomach (esophagus). This condition occurs most often in people with serious liver diseases.65
Ground-glass opacities – According to Dr. Cortopassi, Ground glass opacities are a pattern that can be seen when the lungs are sick, while normal lung CT scans appear black, an abnormal chest CT with GGOs will show lighter-colored or gray patches. Those lighter patches don’t completely obscure the other structures in the lungs. There is haziness seen overlying an area of the lung, but the underlying structures of the lung (airways, blood vessels, lung tissue) can still be identified. It resembles ground glass or glass that is still transparent but has a matte finish.66
GGOs aren’t specific to COVID-19 and can be seen in so many different settings. GGOs in chest CT scans can also indicate congestive heart failure, inflammatory interstitial lung diseases, and diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (bleeding into the airspaces of the lungs), among other issues. But one of the most common diagnoses for GGOs is viral pneumonia, most often caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, and coronavirus.66
In terms of COVID-19, Dr. Cortopassi explains GGOs on a CT scan are indicative of COVID-19-related pneumonia, or lung inflammation caused by the viral infection.66
A study published in the journal Radiology found that, among 51 Chinese patients with confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia, GGOs showed up in the chest CT scans of 77% of patients. And original research from scientists in China, also published in Radiology, found that CT scans were able to find 97% of COVID-19 infections overall, while blood tests were only able to correctly identify 59% of cases.66
Growth factor – Substance required for growth stimulation in living cells.67
H
Haptoglobin – Haptoglobin is a protein produced by the liver that the body uses to clear free hemoglobin (found outside of red blood cells) from circulation. This test measures the amount of haptoglobin in the blood.68
HDL (high-density lipoprotein) – “Good” cholesterol is responsible for carrying absorbed cholesterol to the liver in order to remove it from the body.69
Hematemesis- Hematemesis is a serious condition in which blood is expelled from the mouth. The blood can be bright red, black or dark brown. Blood that is vomited usually comes from what is referred to as the upper GI, or gastrointestinal tract. Pancreatic problems can also be the source of blood vomiting.70
Hematocrit – The hematocrit is the proportion, by volume, of the blood that consists of red blood cells. For example, a hematocrit of 25% means that there are 25 milliliters of red blood cells in 100 milliliters of blood.71
Hematological – Relating to blood and body tissue.72
Hemoglobin electrophoresis – Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a test that measures the different types of hemoglobin in the blood. It also looks for abnormal types of hemoglobin. Normal types of hemoglobin include:
Hemoglobin (Hgb) A, the most common type of hemoglobin in healthy adults
Hemoglobin (Hgb) F, fetal hemoglobin. This type of hemoglobin is found in unborn babies and newborns. HgbF is replaced by HgbA shortly after birth.73
High-sensitive cardiac troponin T – Cardiac troponin is the preferred biomarker for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction and high-sensitive cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) assay permits detection of very low levels of cTnT.74
Hypertension – Condition where blood vessels persistently have raised pressure.75
Hyperthyroidism – An overactive thyroid, occurring when the thyroid gland produces an excess amount of hormone thyroxine.76
Hypochromic RBC – Hypochromia means that the red blood cells have less color than normal when examined under a microscope. This usually occurs when there is not enough of the pigment that carries oxygen (hemoglobin) in the red blood cells.77
Hypoxemia – Hypoxemia refers to a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) or oxygen saturation in the blood.78
Hypoxia – A condition where the body or an area of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen in the tissues.79
Hypoxic – A condition where the areas of the body or the body do not have an adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level.80
I
IgG – Immunoglobulin G-antibody. IgG is synthesized mostly in the secondary immune response to pathogens.81
IgM – Immunoglobulin M-antibody.81
Immunophenotyping – A method used to couple specific antibodies to a fluorescent probe which provides a signal to measure a specific expression of a protein.82
Infective endocarditis – Inflammation of the heart that is caused by a fungal or bacterial infection of the heart valves or the inner lining of the heart.83
Interstitial change in lung – When these interstitial changes occur, your physician may see “increased interstitial markings” on your chest x-ray or CT scan because the inflammation, swelling or scarring of the interstitium makes the tissue denser so that it is now visible as white “interstitial markings” on the x ray or scan.84
Ischemic heart disease (or coronary heart/artery disease) – Disease with the heart is getting an inadequate supply of blood and oxygen due to narrowing of arteries.85
K
Kayser-Fleischer (KF) ring – Kayser–Fleischer (KF) rings are a common ophthalmologic finding in patients with Wilson disease. Initially thought to be due to the accumulation of silver, they were first demonstrated to contain copper in 1934. KF rings are seen in most of the patients with neurologic involvement from Wilson disease. These rings are caused by the deposition of excess copper on the inner surface of the cornea in the Descemet membrane. A slit lamp examination is mandatory to make a diagnosis of KF rings particularly in the early stages unless the rings are visible to the naked eye in conditions of severe copper overload. Kayser–Fleischer rings do not cause any impairment of vision but disappear with treatment and reappear with disease progression. KF rings are not specific to Wilson disease alone, they are also seen in other chronic cholestatic disorders such as primary biliary cholangitis and children with neonatal cholestasis.86
Ki-67 – A protein associated with cellular proliferation and used in immunohistochemistry.87
L
Late gadolinium enhancement – Gadolinium is a chemical agent used as a contrast, administered intravenously to achieve optimum contrast between normal and infarcted myocardium.88
LDL (low-density lipoprotein) – “Bad” cholesterol as an accumulation of this cholesterol leads to plaque buildup in arteries.89
Leads V2, V3 and V4 – Electrodes that are used to monitor the heart during an electrocardiogram, V2 represents the right ventricle, V3 and V4 represent the septum.90
Left anterior descending artery (LAD) – Artery which runs anterior to the interventricular septum and is the largest coronary artery.91
Left circumflex – Branch off the left coronary artery.92
Lesion – Any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism.93
Leukopenia – A low white blood cell count.94
Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) or pneumonia – An infection that involves the lungs abscess and acute bronchitis.95
Luminal diameter stenosis – Diameter of permissible blood flow.96
Lymphopenia – Reduced leukocytes count.97
M
Macroglossia – Macroglossia is the abnormal enlargement of the tongue in proportion to other structures in the mouth. It usually occurs secondary to an underlying disorder that may be present from birth (congenital) or acquired.98
Mantoux test – The Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST) is one method of determining whether a person is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis99. A standard dose of five tuberculin units (TU) (0.1ml) is injected intradermally (into the skin) and read 48 to 72 h later. A person who has been exposed to the bacteria is expected to mount an immune response in the skin containing the bacterial proteins.100
MCH – MCH stands for “mean corpuscular hemoglobin.” An MCH value refers to the average quantity of hemoglobin present in a single red blood cell.101
MCV – MCV stands for mean corpuscular volume. There are three main types of corpuscles (blood cells) in our blood–red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. An MCV blood test measures the average size of your red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes. Red blood cells move oxygen from lungs to every cell in our body. Our cells need oxygen to grow, reproduce and stay healthy. If our red blood cells are too small or too large, it could be a sign of a blood disorder such as anemia, a vitamin deficiency, or other medical condition.102
MDB- Mallory bodies (MB), also known as Mallory-Denk bodies (MDB), are cytoplasmic hyaline inclusions of hepatocytes, once thought to be specific for alcoholic hepatitis now occur in other liver diseases which include nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cholestatic liver diseases, primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).103
Metastatic/Metastasis – Spread of cancer calls from a localized area to another area in the body.104,105
METs – Metabolic equivalents – oxygen consumed while at rest.106
MINOCA – Myocardial infarction with nonobstructive coronary arteries (MINOCA) is clinically defined by the presence of the universal acute myocardial infarction (AMI) criteria, absence of obstructive coronary artery disease (≥50% stenosis), and no overt cause for the clinical presentation at the time of angiography.107
Murphy’s sign – Murphy’s sign is elicited in patients with acute cholecystitis by asking the patient to take in and hold a deep breath while palpating the right subcostal area. If pain occurs on inspiration, when the inflamed gallbladder meets the examiner’s hand, Murphy’s sign is positive.108
Myalgia – Myalgia describes muscle aches and pain, which can involve ligaments, tendons and fascia, the soft tissues that connect muscles, bones and organs.109
Myelofibrosis – A rare blood cancer, a form of chronic leukemia.110
N
NASH- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat in the liver. It is part of a group of conditions called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.111
Nephrectomy – Surgical removal of whole or parts of a kidney.112
Noncalcified plaque – Refers to plaque buildup that may be reversible in the arteries and risk of myocardial infractions.113
O
Obtuse marginal 1 – On or close to the left obtuse margin of the heart.114
Odynophagia – Painful swallowing.115
Oedema – Oedema is a collection of fluid in the spaces between cells of the body. Fluid leaks out of damaged cells. The fluid cannot be simply drained with a needle and may not improve if you take ‘water pills’ (diuretics).116
Oliguria – Oliguria is defined as passing a reduced urine volume. It is defined as a urine output that is117:
Less than 1 mL/kg/hour in infants.
Less than 0.5 mL/kg/hour in children.
Less than 400 mL/day in adults.
P
Partial perfusion (TIMI grade 2 flow) – Slow or delayed complete filling of distal coronary bed.118
Partial thromboplastin time – Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes blood to clot.119
PCT (procalcitonin) – A peptide precursor of the hormone calcitonin. serum PCT concentrations remain normal in uncomplicated cases of COVID-19 and inflated values may indicate bacterial co-infection in severe cases.120
Periorbital edema – Swelling around the eye.121
Platelet function testing with screening epinephrine – The PFA is a screening test for platelet dysfunction. The cartridge membrane is coated with collagen, and with one of two platelet agonists (epinephrine or ADP). The platelets adhere to the collagen and aggregate in response to the collagen and epinephrine (or ADP).122
Portal hypertension- Portal hypertension is an increase in the pressure within the portal vein, which carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver. The most common cause is cirrhosis of the liver, but thrombosis (clotting) might also be the cause.123
Pressure dressing – It is a pressure bandage that’s designed to apply pressure to a particular area of the body to prevent bleeding.124
Pretibial myxedema – It describes localized lesions of the skin due to the deposition of hyaluronic acid, a rare thyroid disease.125
Pro-BNP – Pro-B-type natriuretic peptide is a hormone produced by the heart.126
Procalcitonin – Procalcitonin is a substance produced by many types of cells in the body, often in response to bacterial infections but also in response to tissue injury. The level of procalcitonin in the blood can increase significantly in systemic bacterial infections and sepsis. This test measures the level of procalcitonin in the blood.127
Prognathism – Prognathism is an extension or bulging out (protrusion) of the lower jaw (mandible). It occurs when the teeth are not properly aligned due to the shape of the facial bones.128
Pro-inflammatory biomarkers – Regulatory proteins that can be used to detect inflammation.129
PT – Prothrombin time, a test to evaluate blood clotting.130
Pulmonary stenosis/outflow – Associated with structurally abnormal or immunocompromised states of the heart.131
R
Ramus intermedius – Variant of the coronary artery.132
RDW – The red cell distribution width (RDW) blood test measures the amount of red blood cell variation in volume and size. Normal red blood cells maintain a standard size of 6 to 8 micrometers (µm) in diameter.133
Rhinorrhea – Rhinorrhea refers to a thin, mostly clear nasal discharge.134
Right coronary artery – One of the two main coronary blood vessels supplying blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, and sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes – responsible for the heart’s natural rhythm.135
S
Sepsis – A condition where the body’s response to an existing infection begins to damage its own tissues, this can be a potentially life-threatening.136
Serial troponin enzyme – Enzymes used to measure the potential evidence of a myocardial infraction.137
Slit-lamp examination – A slit lamp is a microscope with a bright light used during an eye exam. It gives your ophthalmologist a closer look at the different structures at the front of the eye and inside the eye. It’s a key tool in determining the health of your eyes and detecting eye disease.138
Splenomegaly – The enlargement of the spleen.160
Stenosis – It represents the narrowing of blood flow and passage diameter.139
Sub pulmonary stenosis – A condition when there is blockage below the pulmonary valve due to too much muscle (muscular bundles).140
Subepithelial – Underneath the epithelium.141
Systolic ejection murmur – It is turbulent blood flow by the obstruction across semilunar valves, arteries and outflow tracts.142
T
T wave – Ventricular repolarization during the electrocardiogram stress test.143
T1 mapping- It is a cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging technique, which shows early clinical promise particularly in the setting of diffuse fibrosis. 144
Tachycardia – A condition where a pulse exceeds 100 beats per minute.145
Thyroid acropachy – Rare autoimmune thyroid disease.146
Thyroid dermopathy – Thickening of the skin usually in the pretibial area, a symptom of hyperthyroidism.147
Thyroid-stimulating hormone – Hormone made in the pituitary gland to regulate your weight, body temperature, muscle strength and mood.148
Thyrotoxicosis – Excess thyroid hormone in the body.149
TIMI grade flow – Method used for assessing coronary artery flow in acute coronary syndromes.150
TnI – Troponin I- cardiac bio marker. Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) and troponin I (cTnI) are cardiac regulatory proteins that control the calcium-mediated interaction between actin and myosin.151
Tocilizumab – Interleukin-6 antagonist used for CRS treatment. Tocilizumab binds specifically to both soluble and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors.152
TOF – Tetralogy of Fallot, a form of cyanotic congenital heart disease.153
Toxic granulations – Toxic granulations are purple or dark-blue staining azurophilic granules in the cytoplasm of neutrophils, bands and metamyelocytes resulting from an abnormality in the maturation of the primary granules with consequent retention of their azurophilic property,79 while toxic vacuolizations are vacuoles representing phagocytosis and depletion of toxic granules.154
Transesophageal echocardiography – Specific type of echocardiogram to look more closely at the heart to examine potential blood clots.155
Triglycerides – A type of fat found within the blood.156
V
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) – A hole in the wall (septum) that separates the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart, this is a birth defect of the heart.157
Von Willebrand factor – Von Willebrand factor is a glycoprotein that plays a key role in blood clotting. The deficiency of this factor leads to Von Willebrand disease.158
X
X-linked recessive – X-linked recessive inheritance refers to genetic conditions associated with mutations in genes on the X chromosome. A male carrying such a mutation will be affected because he carries only one X chromosome. A female carrying a mutation in one gene, with a normal gene on the other X chromosome, is generally unaffected.159
REFERENCES:
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/abdominal-aortic-aneurysm/symptoms-causes/syc-20350688
- Kaur, K. & Kalla, A. (2018). A case of acquired hemophilia A in an elderly female. Journal of community hospital internal medicine perspectives, 8(4), 237-240. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2018.1487246
- Moyer, N. (2019, January 25). Adenocarcinoma Symptoms: Learn Symptoms of the Most Common Cancers. Healthline. Retrieved March 16, 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/cancer/adenocarcinoma-symptoms#symptoms
- Adenomyoma – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (2021). Retrieved 2 March 2021, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/adenomyoma
- Prophylactic Antiobiotics: Types, Uses, and Administration. (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/prophylactic-antibiotic-premedication
- Thyroid peroxidase antibody test: What is it?. (2021). Retrieved 26 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/thyroid-disease/expert-answers/faq-20058114#:~:text=The%20presence%20of%20TPO%20antibodies,that%20mistakenly%20attack%20normal%20tissue.
- D. Thyroid Autoantibodies (TPOAb, TgAb and TRAb). (2003). Thyroid, 13(1), 45-56. doi: 10.1089/105072503321087024
- Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody, Serum -Mayo Clinic Laboratories | Neurology Catalog. (2021). Retrieved 26 March 2021, from https://neurology.testcatalog.org/show/THYRO
- Knott, D. (2021). Acute Pancreatitis | Symptoms, Causes and Treatment | Patient. Retrieved 28 May 2021, from https://patient.info/digestive-health/gallstones-and-bile/acute-pancreatitis
- Nemours KidsHealth – the Web’s most visited site about children’s health. (2021). Retrieved 3 August 2021, from https://kidshealth.org/
- Encyclopedia, M., & score, A. (2021). Apgar score: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003402.htm
- Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT, aPTT) | Lab Tests Online. Labtestsonline.org. (2021). Retrieved 14 May 2021, from https://labtestsonline.org/tests/partial-thromboplastin-time-ptt-aptt
- (2021). Retrieved 29 April 2021, from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/acute-respiratory-distress-syndrome
- Team, D. (2021). Bleeding Diathesis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments. Retrieved 30 July 2021, from https://www.doctorshealthpress.com/general-health-articles/bleeding-diathesis/
- Yu, X., Gao, S., Yang, R., & Han, Y. (2019). MR Imaging of the Brain in Neurologic Wilson Disease. American Journal Of Neuroradiology, 40(1), 178-183. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a5936
- What is the role of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) measurement in the diagnosis of cor pulmonale?(2021). Retrieved 22April2021, from https://www.medscape.com/answers/154062-69198/what-is-the-role-of-brain-natriuretic-peptide-bnp-measurement-in-the-diagnosis-of-cor-pulmonale
- Bronchoscopy. (n.d.). National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Retrieved March 16, 2021, from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/bronchoscopy
- Brudzinski’s Sign. Physiopedia. (2021). Retrieved 11 June 2021, from https://www.physio-pedia.com/Brudzinski%E2%80%99s_Sign.
- Kernig’s Sign. Physiopedia. (2021). Retrieved 11 June 2021, from https://www.physio-pedia.com/Kernig%27s_Sign.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. (2021). Retrieved 6 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/coronary-artery-bypass-graft-surgery#:~:text=Coronary%20artery%20bypass%20graft%20surgery%20(CABG)%20is%20a%20procedure%20used,nutrients%20to%20the%20heart%20muscle.
- Ordem dos Médicos –Portal Oficial .(2021).Retrieved 6 April 2021, from https://ordemdosmedicos.pt/?lop=conteudo&op=02522a2b2726fb0a03bb19f2d8d9524d
- Hygiene-related Diseases | Hygiene-related Diseases | Hygiene | Healthy Water | CDC. Cdc.gov. (2021). Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/hygiene/disease/dental_caries.html.
- Cafasso, J. (2020, April 1). Carcinoembryonic Antigen Test (CEA). Healthline. Retrieved March 16, 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/cea
- Ceruloplasmin | Lab Tests Online. Labtestsonline.org. (2021). Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://labtestsonline.org/tests/ceruloplasmin.
- Liu J, Zhang S, Pan S. Value of dynamic plasma cell-free DNA monitoring in septic shock syndrome: A case report. World Journal of Clinical Cases. 2020;8(1):200-207.
- Chemokines: Introduction | British Society for Immunology. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.immunology.org/public-information/bitesized-immunology/receptors-and-molecules/chemokines-introduction
- (2021). Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/cholecystectomy.
- Daire, J., Jacob, J., Hyacinthe, J., Croisille, P., Montet-Abou, K., & Richter, S. et al. (2008). Cine and tagged cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in normal rat at 1.5 T: a rest and stress study. Journal Of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 10(1), 48. doi: 10.1186/1532-429x-10-48
- Circumcision (male) – Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/circumcision/about/pac-20393550
- Circumflex Artery | Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy. (2021). Retrieved 6 April 2021, from http://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/coronary-arteries/circumflex-artery/index.shtml
- Sousa, P., Santos, W., Marques, N., Cordeiro, P., Ferrinha, R., & Pereira, S. et al. (2013). A 72-year-old woman with an uncorrected tetralogy of Fallot presenting with possible pulmonary endocarditis: a case report. Journal Of Medical Case Reports, 7(1). doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-150
- (ACR), R. (2021). CT Angiography (CTA). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angioct
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Chest. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ct-scan-of-the-chest
- Heart failure – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-failure/symptoms-causes/syc-20373142
- SWSLHD – Medical Imaging – Abdominal Aortagram. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021,from https://www.swslhd.health.nsw.gov.au/medicalImaging/serv_CT_Aortagram_Abdominal.html
- Coronary angiography. (n.d.). Medine Plus. Retrieved March 16, 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003876.htm
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/coronary-artery-bypass-graft-surgery
- (ACR), R. (2021). Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angiocoroct#:~:text=Coronary%20computed%20tomography%20angiography%20(CCTA)%20is%20a%20heart%20imaging%20test,inner%20lining%20of%20the%20arteries
- Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A. et al.Cytokine release syndrome. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer vol. 6 (2018).
- Schleicher, G. K., Lowman, W. & Richards, G. A. Case Study: A Patient with Asthma, COVID-19 Pneumonia and Cytokine Release Syndrome Treated with Corticosteroids and Tocilizumab. Wits J. Clin. Med.2, 47 (2020).
- CT scan – Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 28 May 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-scan/about/pac-20393675
- What are Cytokines. (2021). Retrieved 9 April 2021, from https://www.sinobiological.com/resource/cytokines/what-are-cytokines#:~:text=Cytokines%20are%20a%20large%20group,regulate%20immunity%2C%20inflammation%20and%20hematopoiesis.
- Tasic N, Paixao T, Goncalves L (January 2020). “Biosensing of D-dimer, making the transition from the central hospital laboratory to bedside determination”. Talanta.207(2): 120270. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120270. PMID 19008457
- Morgan, M. (2021). Diagonal branches of the left anterior descending artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://radiopaedia.org/articles/diagonal-branches-of-the-left-anterior-descending-artery#:~:text=Diagonal%20branches%20of%20the%20left%20anterior%20descending%20coronary%20artery%20supply,parent%20vessel%20at%20acute%20angles.
- Dysarthria & Speech: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments. Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 11 June 2021, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17653-dysarthria.
- Dysphagia. (n.d.). Mayoclinic. Retrieved 16 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dysphagia/symptoms-causes/syc-20372028
- Troublebreathing(2021).Retrieved27April2021, fromhttps://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/shortness-of-breath/basics/definition/sym-20050890
- Osborn, C. O. (2018, September 18). Understanding Ecchymosis. Healthline. Retrieved 16 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/ecchymosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). (n.d.). Mayoclinic. Retrieved March 16, 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ekg/about/pac-20384983
- Echocardiogram. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved March 16, 2021, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/16947-echocardiogram#:~:text=An%20echocardiogram%20(echo)%20is%20a,pumping%20action%20of%20the%20heart
- Exercise Electrocardiogram. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.heartandstroke.ca/heart-disease/tests/exercise-electrocardiogram
- Endoscopic ultrasound – Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/endoscopic-ultrasound/about/pac-20385171#:~:text=Endoscopic%20ultrasound%20(EUS)%20is%20a,and%20liver%2C%20and%20lymph%20nodes
- Krans, B. (2018, October 12). Endoscopy. Healthline. Retrieved 16 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/endoscopy
- (2021). Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://www.healthgrades.com/right-care/digestive-health/epigastric-pain
- epigastric region. (2021). Retrieved 21 May 2021, from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/epigastric+region
- Encyclopedia, M., & esophagogastroduodenoscopy, E. (2021). EGD – esophagogastroduodenoscopy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003888.htm.
- 6 Factor VIII Concentrates, Factor VIII/von Willebrand Factor Concentrates, Factor IX Concentrates, Activated Prothrombin Complex Concentrates. (2009). Transfusion Medicine And Hemotherapy, 36(6), 409-418. doi: 10.1159/000268062
- Kaur, J., & Jain, A. (2021). Fibrinogen. Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537184/
- Gaemperli, O., Husmann, L., Schepis, T., Koepfli, P., Valenta, I., & Jenni, W. et al. (2009). Coronary CT angiography and myocardial perfusion imaging to detect flow-limiting stenoses: a potential gatekeeper for coronary revascularization?. European Heart Journal, 30(23), 2921-2929. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp304
- Lee, J. H., Hartaigh, B. Ó., Han, D., Rizvi, A., Lin, F. Y., & Min, J. K. (2016). Fractional Flow Reserve Measurement by Computed Tomography: An Alternative to the Stress Test. Interventional cardiology (London, England), 11(2), 105–109. https://doi.org/10.15420/icr.2016:1:2
- Jessen, C. (2010). Can I just ask?. London: Hay House from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/ventricularseptaldefect.html#:~:text=A%20ventricular%20septal%20defect%20(pronounced,(ventricles)%20of%20the%20heart
- Feng, S., Huang, M., Dong, Z., Xu, L., Li, Y., & Jia, Y. et al. (2019). MRI T2-Weighted Imaging and Fat-Suppressed T2-Weighted Imaging Image Fusion Technology Improves Image Discriminability for the Evaluation of Anal Fistulas. Korean Journal Of Radiology, 20(3), 429. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0260
- Sipponen, P., & Stolte, M. (1997). Clinical impact of routine biopsies of the gastric antrum and body. Endoscopy, 29(7), 671–678. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1004278
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gerd/symptoms-causes/syc-20361940
- Esophageal varices – Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/esophageal-varices/symptoms-causes/syc-20351538#:~:text=Esophageal%20varices%20are%20abnormal%2C%20enlarged,scar%20tissue%20in%20the%20liver.
- How Lung Scans Can Detect Coronavirus in Some Patients. Health.com. (2021). Retrieved 11 June 2021, from https://www.health.com/condition/infectious-diseases/coronavirus/ground-glass-opacities-covid-19.
- Oxford Learner’s Dictionaries | Find definitions, translations, and grammar explanations at Oxford Learner’s Dictionaries. (2021). Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/
- Haptoglobin | Lab Tests Online. Labtestsonline.org. (2021). Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://labtestsonline.org/tests/haptoglobin#:~:text=Haptoglobin%20is%20a%20protein%20produced,transports%20oxygen%20throughout%20the%20body
- HDL cholesterol: How to boost your ‘good’ cholesterol. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/hdl-cholesterol/art-20046388
- Vomiting blood (hematemesis). Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/17708-vomiting-blood.
- Hematocrit Ranges and Chart: Test, High, Low, and Normal. (2021). Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://www.medicinenet.com/hematocrit/article.htm.
- haematological. (2021). Retrieved 15 March 2021, from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/haematological
- Tests, M. (2021). Hemoglobin Electrophoresis: MedlinePlus Medical Test. Medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/hemoglobin-electrophoresis/#:~:text=Hemoglobin%20electrophoresis%20is%20a%20test,Hgb)%20F%2C%20fetal%20hemoglobin
- Xu, R., Zhu, X., Yang, Y., Ye, P. (2013). High-sensitive cardiac troponin T. J Geriatr Cardiol, 10(1): 102–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5411.2013.01.015
- Hypertension. (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.who.int/health-topics/hypertension#tab=tab_1
- Hyperthyroidism – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hyperthyroidism/symptoms-causes/syc-20373659#:~:text=Hyperthyroidism%20(overactive%20thyroid)%20occurs%20when,treatments%20are%20available%20for%20hyperthyroidism.
- Encyclopedia, M. (2021). Hypochromia: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003455.htm#:~:text=Hypochromia%20means%20that%20the%20red,in%20the%20red%20blood%20cells.
- Hypoxemia. (2021). Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://www.physio-pedia.com/Hypoxaemia
- Samuel J., ranklin C. (2008) Hypoxemia and Hypoxia. In: Myers J.A., Millikan K.W., Saclarides T.J. (eds) Common Surgical Diseases. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-75246-4_97
- Samuel J., Franklin C. (2008) Hypoxemia and Hypoxia. In: Myers J.A., Millikan K.W., Saclarides T.J. (eds) Common Surgical Diseases. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-75246-4_97
- Vaillant, A., Jamal, Z., & Ramphul, K. (2021). Immunoglobulin. Retrieved 28 May 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513460/
- Herold NC, Mitra P. Immunophenotyping. [Updated 2020 Jul 2]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearlsPublishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558927/
- Infective endocarditis. (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.heartandstroke.ca/heart-disease/conditions/infective-endocarditis#:~:text=Infective%20endocarditis%20is%20an%20inflammation,lead%20to%20life%2Dthreatening%20complications
- Understanding ILD. Interstitial Lung Disease Program. (2021). Retrieved 5 April 2021, from https://med.stanford.edu/ild/patient-resources/understanding-ild.html#:~:text=When%20these%20interstitial%20changes%20occur,the%20x%20ray%20or%20scan.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Social Security Cardiovascular Disability Criteria. Cardiovascular Disability: Updating the Social Security Listings. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2010. 7, Ischemic Heart Disease. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209964/
- Pandey, N., & John, S. (2021). Kayser-Fleischer Ring. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459187/
- MKI67 marker of proliferation Ki-67 [Homo sapiens (human)] – Gene – NCBI. (2021). Retrieved 7 May 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4288
- Doltra, A., Amundsen, B., Gebker, R., Fleck, E., & Kelle, S. (2013). Emerging Concepts for Myocardial Late Gadolinium Enhancement MRI. Current Cardiology Reviews, 9(3), 185-190. doi: 10.2174/1573403×113099990030
- Topics, H. (2021). LDL: The “Bad” Cholesterol: MedlinePlus. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ldlthebadcholesterol.html#:~:text=LDL%20stands%20for%20low%2Ddensity,stands%20for%20high%2Ddensity%20lipoproteins.
- ECG (EKG) Interpretation – Oxford Medical Education. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.oxfordmedicaleducation.com/ecgs/ecg-interpretation/
- Rehman I, Kerndt CC, Rehman A. Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Left Anterior Descending (LAD) Artery. [Updated 2020 Jul 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482375/
- Circumflex Artery | Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from http://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/coronary-arteries/circumflex-artery/index.shtml
- Lesion…What Does The Doctor Mean?. (2021). Retrieved 2 March 2021, from https://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=9695
- Low white blood cell count. (2021). Retrieved 6 May 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/low-white-blood-cell-count/basics/definition/sym-20050615
- Therapeutic Guidelines Limited. (2014). Therapeutic guidelines. West Melbourne, Victoria.
- Paolillo, V., Gastaldo, D., & Vaudano, G. (2006). An unusual course of the ramus intermedius: shown by multislice computed tomographic coronary angiography. Texas Heart Institute journal, 33(3), 406–407.
- Low white blood cell count Causes. (2021). Retrieved 29 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/low-white-blood-cell-count/basics/causes/sym-20050615
- Macroglossia | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. Rarediseases.info.nih.gov. (2021). Retrieved 7 May 2021, from https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/3342/macroglossia.
- Fact Sheets | Testing & Diagnosis | Fact Sheet – Tuberculin Skin Testing | TB | CDC. Cdc.gov. (2021). Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/factsheets/testing/skintesting.htm.
- Nayak, S., & Acharjya, B. (2012). Mantoux test and its interpretation. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 3(1), 2. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.93479
- MCH: High and Low Symptoms and Treatments. Healthline. (2021). Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/mch#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
- Tests, M. (2021). MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume): MedlinePlus Medical Test. Medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/mcv-mean-corpuscular-volume/
- Kurtovic, E., & Limaiem, F. (2021). Mallory Bodies. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 25 March 2021,from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545300/#:~:text=Mallory%20bodies%20(MB)%2C%20also,primary%20biliary%20cirrhosis%20(PBC)%20and.
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (2021). Retrieved 7 May 2021, from https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/metastasis
- What is Metastasis?. (2021). Retrieved 15 March 2021, from https://www.cancer.net/navigating-cancer-care/cancer-basics/what-metastasis
- Jetté, M., Sidney, K., & Blümchen, G. (1990). Metabolic equivalents (METS) in exercise testing, exercise prescription, and evaluation of functional capacity. Clinicalcardiology, 13(8),555–565. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.4960130809
- Pasupathy, S. Tavella, R. & Beltrame, J. F. (2017). Myocardial Infarction With Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA)The Past, Present, and Future Management. Circulation, 135(16), 1490-1493. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027666
- A positive Murphy’s sign is seen in acute cholecystitis.Leith, M. (2021). Murphy’s sign • LITFL • Medical Eponym Library. Life in the Fast Lane • LITFL. Retrieved 5 April 2021, from https://litfl.com/murphys-sign eponymictionary/#:~:text=Murphy’s%20sign%20is%20elicited%20in,hand%2C%20Murphy’s%20sign%20is%20positive.
- Myalgia. (2021). Retrieved 6 May 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/myalgia
- Myelofibrosis; Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention. (2021). Retrieved 15 March 2021, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15672-myelofibrosis
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Stanfordhealthcare.org. (2021). Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/liver-kidneys-and-urinary-system/nonalcoholic-steatohepatitis-nash.html#:~:text=Nonalcoholic%20steatohepatitis%20(NASH)%20is%20liver,called%20nonalcoholic%20fatty%20liver%20disease.
- Nephrectomy (kidney removal) – Mayo Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 15 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/nephrectomy/about/pac-20385165
- Pan, X., & Dylan Wolman, M. (2021). Cardiac risk factors associated with noncalcified plaque burden in asymptomatic patients | 2 Minute Medicine. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.2minutemedicine.com/cardiac-risk-factors-associated-with-noncalcified-plaque-burden-in-asymptomatic-patients/#:~:text=Noncalcified%20plaque%20is%20both%20the,direct%20measure%20for%20patient%20risk
- Morgan, M. (2021). Diagonal branches of the left anterior descending artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://radiopaedia.org/articles/diagonal-branches-of-the-left-anterior-descending-artery#:~:text=Diagonal%20branches%20of%20the%20left%20anterior%20descending%20coronary%20artery%20supply,parent%20vessel%20at%20acute%20angles.
- Smith, A. (2018, January 31). Odynophagia: Symptoms, causes
- Knott, D. (2021). Oedema | Fluid & Water Retention. Patient.info. Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://patient.info/signs-symptoms/oedema-swelling#:~:text=Oedema%20is%20fluid%20retention.,make%20you%20short%20of%20breath
- Tidy, D. (2021). Oliguria. Professional reference for Oliguria.Patient.info. Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://patient.info/doctor/oliguria.
- Appleby, M.A., Michaels, A.D., Chen, M. et al.Importance of the TIMI frame count: implications for future trials. Trials1, 31 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1186/cvm-1-1-031
- Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) Test | Michigan Medicine. (2021). Retrieved 27 April 2021, fromhttps://www.uofmhealth.org/healthlibrary/hw203152#:~:text=Partial%20thromboplastin%20time%20(PTT)%20is,blood%20to%20clot%20(coagulation).
- Huang, I., Pranata, R., Lim, M., Oehadian, A., & Alisjahbana, B. (2020). C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, D-dimer, and ferritin in severe coronavirus disease-2019: a meta-analysis. Therapeutic Advances In Respiratory Disease, 14, 175346662093717. doi: 10.1177/1753466620937175
- Periorbital Edema: Pictures, Causes, and Treatments and More. (2021). Retrieved 26 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/periorbital-edema
- Platelet Function Assay (PFA) Epinephrine/Collagen -Bloodworks Northwest. (2021). Retrieved 29 April 2021, from https://www.bloodworksnw.org/lab-test/pfa-epinephrine-collagen
- Portal Hypertension: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatments. Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Retrieved 25 March 2021, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4912-portal-hypertension#:~:text=Portal%20hypertension%20is%20an%20increase,might%20also%20be%20the%20cause.
- Pressure Bandage: How and When to Apply & Precautions. (2021). Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/pressure-bandage
- Pretibial Myxedema: Background, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1103765-overview#:~:text=Pretibial%20myxedema%20(PTM)%20or%2C,Thyroid%20dermopathy%20occurs%20rarely.
- NT-proB-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP). (2021). Retrieved 29 April 2021, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/16814-nt-prob-type-natriuretic-peptide-bnp
- Procalcitonin Test – Understand the Test & Your Results. Labtestsonline.org. (2021). Retrieved 5 April 2021, from https://labtestsonline.org/tests/procalcitonin#:~:text=Procalcitonin%20is%20a%20substance%20produced,systemic%20bacterial%20infections%20and%20sepsis.
- Prognathism Information | Mount Sinai – New York. Mount Sinai Health System. (2021). Retrieved 7 May 2021, from https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/symptoms/prognathism#:~:text=Prognathism%20is%20an%20extension%20or,the%20plane%20of%20the%20face.
- van den Berg, R., Jongbloed, E., de Schepper, E., Bierma-Zeinstra, S., Koes, B., & Luijsterburg, P. (2018). The association between pro-inflammatory biomarkers and nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review. The Spine Journal, 18(11), 2140-2151. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.06.349
- Prothrombin time test – Mayo Clinic. Mayoclinic.org. (2021). Retrieved 14 May 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/prothrombin-time/about/pac-20384661.
- Bamford, P., Soni, R., Bassin, L. et al.Delayed diagnosis of right-sided valve endocarditis causing recurrent pulmonary abscesses: a case report. J Med Case Reports13, 97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-2034-7
- Knipe, H. (2021). Ramus intermedius artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ramus-intermedius-artery
- Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) Test. Healthline. (2021). Retrieved 30 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/rdw-blood-test
- Reach for relief from a runny nose. (2021). Retrieved 6 May 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/runny-nose/basics/definition/sym-20050640
- Anatomy and Function of the Coronary Arteries. (2021). Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/anatomy-and-function-of-the-coronary-arteries
- Sepsis – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sepsis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351214#:~:text=Sepsis%20is%20a%20potentially%20life,may%20progress%20to%20septic%20shock.
- van Domburg, R. T., Cobbaert, C., Kimman, G. J., Zerback, R., & Simoons, M. L. (2000). Long-term prognostic value of serial troponin T bedside tests in patients with acute coronary syndromes. The American journal of cardiology, 86(6), 623–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9149(00)01040-7
- Porter, D. (2018). What is a Slit Lamp?American Academy of Ophthalmology. Retrieved 8 April 2021, from https://www.aao.org/eye-health/treatments/what-is-slit-lamp.
- Goel, M., Dhillon, S., Kumar, S., & Tegeltija, V. (2021). Clinical judgement in chest pain: a case report. Journal Of Medical Case Reports, 15(1). doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02666-z
- Pulmonary Stenosis | Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/pulmonary-stenosis#:~:text=Pulmonary%20stenosis%20can%20be%20mild,this%20is%20called%20subpulmonic%20stenosis
- subepithelial. (2021). Retrieved 7 May 2021, from https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/subepithelial
- Heart Murmurs. (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.utmb.edu/pedi_ed/CoreV2/Cardiology/cardiologyV2/cardiologyV24.html#:~:text=a)%20Systolic%20ejection%20murmurs%20(SEM,shortly%20after%20S1%20(pulse).
- Goel, M., Dhillon, S., Kumar, S., & Tegeltija, V. (2021). Clinical judgement in chest pain: a case report. Journal Of Medical Case Reports, 15(1). doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02666-z
- Yingchoncharoen, T., Jellis, C., Popovic, Z., Flamm, S., & Kwon, D. (2014). Reproducibility of multiple T1 Mapping techniques and to ECV quantification. Journal Of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 16(S1). doi: 10.1186/1532-429x-16-s1-p18
- Tachycardia – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 26 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tachycardia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355127
- Jadidi, J., Sigari, M., Efendizade, A., Grigorian, A., Lehto, S. A., & Kolla, S. (2019). Thyroid acropachy: A rare skeletal manifestation of autoimmune thyroid disease. Radiology case reports, 14(8), 917–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2019.04.021
- Dhali, T. K., & Chahar, M. (2015). Thyroid dermopathy-a diagnostic clue of hidden hyperthyroidism. Dermato-endocrinology, 6(1), e981078. https://doi.org/10.4161/19381980.2014.981078
- Tests, M. (2021). TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) Test: MedlinePlus Medical Test. Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/tsh-thyroid-stimulating-hormone-test/
- Thyrotoxicosis – Thyroid Disorders | Virginia Mason, Seattle. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://www.virginiamason.org/thyrotoxicosis#:~:text=Thyrotoxicosis%20means%20an%20excess%20of,have%20%E2%80%9Cenough%E2%80%9D%20thyroid%20hormone.
- Appleby, M.A., Michaels, A.D., Chen, M. et al.Importance of the TIMI frame count: implications for future trials. Trials1, 31 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1186/cvm-1-1-031
- Sharma, S. (2004). Cardiac troponins. Journal Of Clinical Pathology, 57(10), 1025-1026. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2003.015420
- Schleicher, G. K., Lowman, W. & Richards, G. A. Case Study: A Patient with Asthma, COVID-19 Pneumonia and Cytokine Release Syndrome Treated with Corticosteroids and Tocilizumab. Wits J. Clin. Med.2, 47 (2020).
- Prophylactic Antiobiotics: Types, Uses, and Administration. (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/prophylactic-antibiotic-premedication
- Toxic Granulation – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Sciencedirect.com. (2021). Retrieved 5 April 2021, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/toxic-granulation#:~:text=Toxic%20granulations%20are%20purple%20or,toxic%20vacuolizations%20are%20vacuoles%20representing.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE). (2021). Retrieved 23 March 2021, from https://www.heartandstroke.ca/heart-disease/tests/transesophageal-echocardiogram-tee#:~:text=A%20transesophageal%20echocardiogram%20(TEE)%20is,the%20structures%20of%20the%20heart
- Can triglycerides affect my heart health?. (2021).Retrieved 30 April 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/triglycerides/art-20048186#:~:text=Triglycerides%20are%20a%20type%20of,triglycerides%20for%20energy%20between%20meals
- Congenital Heart Defects – Facts about Ventricular Septal Defect | CDC. (2021). Retrieved 22 March 2021,
- Baronciani, L., & Peyvandi, F. (2020). How we make an accurate diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Thrombosis Research, 196, 579-589. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2019.07.010
- NCI Dictionary of Genetics Terms. (2021). Retrieved 27 May 2021, from https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/genetics-dictionary/def/x-linked-recessive-inheritance
- Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) – Symptoms and causes. (2021). Retrieved 15 March 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/enlarged-spleen/symptoms-causes/syc-20354326#:~:text=Your%20spleen%20is%20an%20organ,during%20a%20routine%20physical%20exam

