12. The Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Learning Outcomes
After completing Chapter 12, students will know how to:
- use the functions of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
- form the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in affirmative statements, negative statements and questions.
- apply the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in various situations.
- distinguish between stative verbs and continuous verbs.
- use the correct spelling rules for continuous verbs.
Functions
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used for
- actions that started in the past and are continuing up until now (and will probably continue into the future).
- actions that were ongoing in the past, but just recently finished.
Let us discuss this point in detail.
Actions that started in the past and are continuing up until now (and will probably continue into the future)
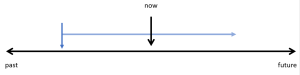
These are actions that started in the past and have continued up until now and might continue into the future. With this function, common time markers used are since and for, or a period of time that has not ended yet (this morning, all year, this week, this summer, etc.).
Since is used with a specific time – since 1995, since Tuesday, since childhood
For is used with a duration of time – for 3 years, for 2 days, for a long time
Some examples are:
- I have been living in Barrie for 15 years.
- Mary has been working at Georgian College since 2005.
- Mariam has been teaching ESL for a long time.
- Mustafa has been coming to class on time all semester.
**This is the same function as the Present Perfect Tense, however do not use stative verbs in this tense. Use the Present Perfect Tense instead. Stative Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses.
Corrine has been knowing me since childhood.
Corinne has known me since childhood.
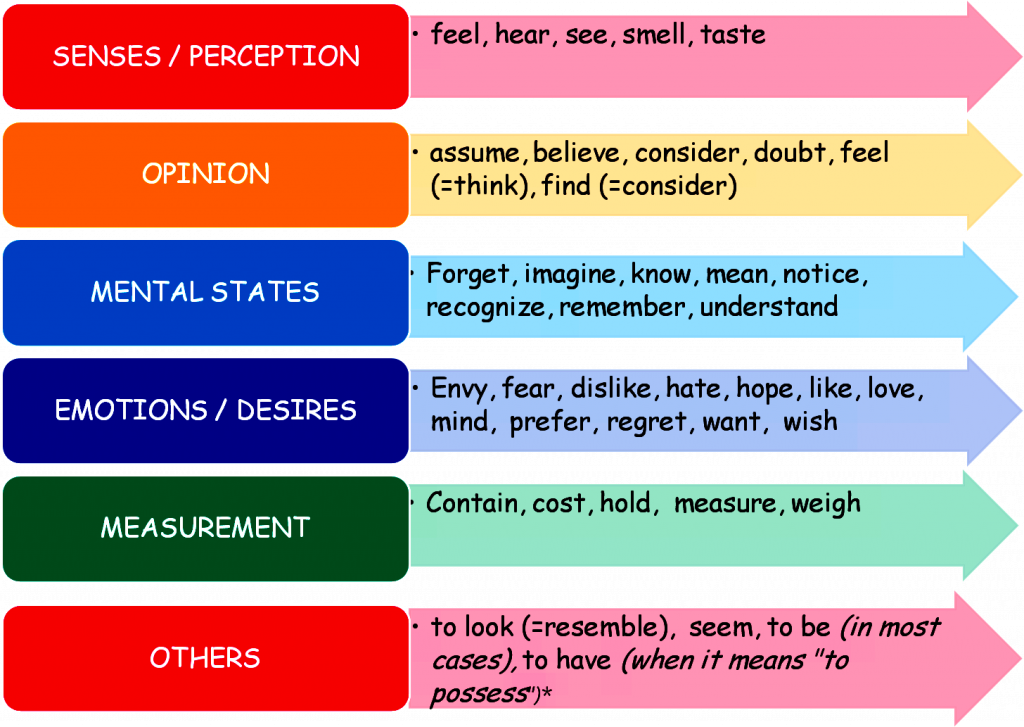
As a review from Chapter 2, here are examples of stative verbs:
Actions that were ongoing in the past, but just recently finished
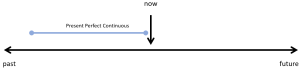
These actions were happening in the past, but were recently completed. Usually there is evidence to support that the action just finished.
Some examples are:
- Have you been smoking? I can smell it on your breath.
- My clothes are dirty because I have been painting all day.
- Celina has been washing the dishes. Look at all the water on the floor!
Form
Let us now explore how the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is formed:
| Subject + | + has/have been | + verb + ing. |
|---|---|---|
| I | have been | studying. |
| He | has been | eating. |
| She | has been | watching. |
| They | have been | playing. |
| Subject + | has/have + not | + been | + verb + ing. |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | have not (haven’t) | been | studying. |
| She | has not (hasn’t) | been | waiting. |
| Lisa | has not (hasn’t) | been | teaching. |
| Corinne and Hannah | have not (haven’t) | been | working. |
| Has/Have+ | subject | been + verb + ing? | Short Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Have | I | been helping? | Yes, you have./No, you haven’t. |
| Has | Catherine | been teaching? | Yes, she has./No, she hasn’t. |
| Have | the children | been working? | Yes, they have./No, they haven’t. |
| Wh ? + | has/have | + subject | been + verb + ing | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | have | I | been doing? | You have been procrastinating. |
| Where | has | she | been studying? | She has been studying at Georgian College. |
| When | have | you | been going there? | I have been going there every Tuesday. |
Present Perfect Continuous Form and Function Review
Watch this short video to review the function and form of Present Perfect Continuous. Pay attention to the contractions and their pronunciation, and don’t forget to do the practice activities at the end! Remember that the Present Perfect Continuous is also sometimes called the Present Perfect Progressive.
Watch the video Present Perfect Progressive – Grammar & Verb Tenses (5 mins) on YouTube
Video Source: Ellii (formerly ESL Library). (2020, September 14). Present perfect progressive – Grammar & verb tenses [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/iCzJN0g5NHQ
The Present Perfect vs The Present Perfect Continuous
The Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous are two tricky tenses to learn and use. This video compares these two tenses and when to use them. You will see examples using Present Perfect with stative verbs that are still true and including an amount of time, or with actions that have ended at some point in the past, while comparing the use of Present Perfect Continuous for action verbs (non-stative verbs) that started in the past and continued until now or just now. Watch the video carefully, take notes, and don’t forget to pause and answer the questions!
Present Perfect vs Present Perfect Continuous (Text Version)
Watch the video Explained! I have LIVED v I have been LIVING // Present Perfect v Present Perfect Continuous (11 min) on YouTube
Pause at 2:18: Again, the present perfect connects the past to now either with time (today, this year, ever) or with actions that affect the present.
Pause at 3:05: My whole life
- Pause at 6:50: Select all the stative verbs from the verbs below:
- think
- believe
- taste
- look
- listen
- see
- watch
- hear
- be
- own
- say
- hate
- show
- understand
- touch
- know
- fall
- want
- change
- hope
- wish
- need
- plan
| Possession | Sense | Emotion | Mental State | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| have | hear | love/like | know | weigh |
| own | sound | hate/dislike | believe | owe |
| possess | smell | adore | disagree | seem |
| consist | see | prefer | agree | fit |
| contain | taste | need | recognize | cost |
| – | – | desire | promise | – |
| – | – | wish | understand | – |
| – | – | value | mean | – |
| – | – | appreciate | – | – |
- Pause at 8:02. True or false: These two sentences mean the same thing:
- I have lived in Amsterdam for many years.
- I have been living in Amsterdam for many years.
- Pause at 8:40. True or false: These two sentences mean the same thing:
- I have lived in Halifax.
- I have been living in Halifax.
- Pause at 9:20. Which action has ended?
- I have lived in Seoul for 1 year.
- I have been living in Seoul for 1 year.
- I have lived in Seoul.
Pause at 9:24: So if we use the present perfect or the present perfect continuous with an amount of time, it means the action is still continuing. We can use ‘live’ and ‘work’ with both tenses and it means the same thing, but stative verbs must be used with present perfect only – they cannot be continuous.
Check your Answers in footnote[1]
Activity source: “Present Perfect vs Present Perfect Continuous Interactive Video” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. Video Source: English with Greg. (2021, March 19). EXPLAINED! I have LIVED v I have been LIVING // Present perfect v present perfect continuous [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/oLDpZ8W-P8Y
Present Perfect Continuous Function Practice
Present Perfect Continuous Function Practice (Text Version)
Read each present perfect continuous sentence and guess the function. Turn the card to see the answer. The functions you can choose from are:
- Actions that started in the past and continuing until now (and may continue into the future)
- Actions that were ongoing in the past but just recently finished (and with present evidence or effect)
- He’s been checking his email all morning.
- The car is all wet. It’s been raining.
- Cassandra has been working on her research for her Masters degree and now it’s finally done!
- There’s no way I can let the dog inside the house like that! He’s been rolling around in fresh mud!
- Tyler hasn’t been studying at all this evening.
- Sarit has been working from home because she hasn’t been feeling well.
Check your Answers in footnote[2]
Activity source: “Present Perfect Continuous Form and Function Interactive Video” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Affirmative
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Affirmative (Text Version)
Using the verb in brackets, fill in the blanksusing the affirmative form of present perfect continuous. Spelling and punctuation count! You do not need to use the contraction, but if you do, give yourself a point.
- His pants are so dirty. He _______ [Blank 1 – paint] all day.
- Reza _______ [Blank 1 – run] around doing errands all morning.
- Yuki _______ [Blank 1 – bake] for 3 hours. I hope she’s almost done.
- Sabrina and Junyoung _______ [Blank 1 – attend] classes regularly.
- We _______ [Blank 1 – discuss] this problem since 9am. Let’s take a break.
Check your Answers in footnote[3]
Activity source: “Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Affirmative” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Negative
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Negative (Text Version)
Fill in blank (marked with letters a-e) with the negative form of the tense Present Perfect Continuous. Use the verb in brackets (listed first). Spelling and punctuation count! USE THE CONTRACTION whenever possible.
- Leah _______ [Blank 1 – come] to work lately.
- The students _______ [Blank 1 – achieve] high scores on their tests lately.
- My mom and dad _______ [Blank 1 – make] as much homemade food this month. They’ve been enjoying dining at restaurants.
- The dog _______ [Blank 1 – play] as much as he usually does. I wonder if she’s sick.
- We _______ [Blank 1 – shop] yet this month. We’ve been saving our money.
Check your Answers in footnote[4]
Activity source: “Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Negative” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative 1 (Text version)
Put the words in order to make a question using the Present Perfect Continuous. There is one extra word you don’t need. Put this extra word in the blank space at the end.
the/been/through/flowed/?/water/the/has/flowing/dam/
Check your Answers in footnote[5]
Activity source: “Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative 1” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative 2 (Text version)
Put the words in order to make a question using the Present Perfect Continuous. There is one extra word you don’t need. Put this extra word in the blank space at the end.
studying/has/textbooks/been/sisters/this/the/?/have/their/from/week
Check your Answers in footnote[6]
Activity source: “Present Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative 2” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Communicative Activity – Discussion Questions
- How long have you been studying English?
- What have you been reading lately?
- Have you been watching any interesting TV shows or movies?
- What has been the most challenging thing you’ve been working on at school or work?
- Have you been learning any new hobbies or skills recently?
- How long have you been living in your current city?
- What have you been doing to stay healthy?
- Have you been spending more time with family or friends lately?
- What have you been doing to improve your English skills?
- Have you been experiencing any interesting weather recently?
Verb Tenses in Music
For a fun activity, listen to the following songs:
- I’ve Been Waiting for a Girl Like You by Foreigner
- In View by The Tragically Hip
Can you hear the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in the lyrics?

Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, “The Past Perfect Continuous Tense” by Sari Martin & Virginia McHardy is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
-
- believe, taste, see, hear, be, own, know, hate, understand, want, wish, need.
- True.
- False.
- c) I have lived in Seoul.
-
- Actions that started in the past and continuing until now (and may continue into the future)
- Actions that were ongoing in the past but just recently finished (and with present evidence or effect)
- Actions that were ongoing in the past but just recently finished (and with present evidence or effect)
- Actions that were ongoing in the past but just recently finished (and with present evidence or effect)
- Actions that started in the past and continuing until now (and may continue into the future)
- Actions that started in the past and continuing until now (and may continue into the future)
-
- He has been painting all day.
- Reza has been running around doing errands all morning.
- Yuki has been baking for 3 hours.
- Sabrina and Junyoung have been attending classes regularly.
- We have been discussing this problem since 9am.
-
- Leah hasn't been coming to work lately.
- The students haven't been achieving high scores on their tests lately.
- My mom and dad haven't been making as much homemade food this month. They've been enjoying dining at restaurants.
- The dog hasn't been playing as much as he usually does. I wonder if she's sick.
- We haven't been shopping yet this month. We've been saving our money.
- Has the water been flowing through the dam? flowed ↵
- Have the sisters been studying from their textbooks this week? has ↵

