11. The Present Perfect Tense
Learning Outcomes
After completing Chapter 11, students will know how to:
- use the functions of the Present Perfect Tense.
- form the Present Perfect Tense in affirmative statements, negative statements and questions.
- apply the Present Perfect Tense in various situations.
- use appropriate time markers with the Present Perfect Tense.
Functions of the Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is used for
- past actions that happened at an unspecific time.
- repeated past actions at an unspecific time.
- actions that started in the past and are continuing up until now.
Let us discuss these points in detail.
Past actions that happened at an unspecific time:
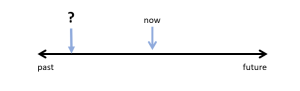
These are actions that finished, but you don’t know when they happened. Some examples are:
- I have seen Niagara Falls.
- Petro has written the test.
- Sari has helped many students.
- We have eaten breakfast.
With this function, the common time markers that are used include already, yet, still, ever, and never. See the table below:
| Time Marker | Definition | Position | Used With | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| already | before now |
|
|
I have already seen Niagara Falls.
Have you seen Jason already? |
| yet | up until now |
|
|
Petro hasn’t written the test yet.
Has John finished his class yet? |
| still | up until now |
|
|
Karen still hasn’t cleaned her room. |
| ever | at any time |
|
|
Stephen hasn’t ever been to Paris.
Have you ever played pickleball? |
| never | not at any time |
|
*the meaning is negative |
Lisa has never ridden a horse. |
Already, Still, Yet, Ever or Never Activity
Already, Still, Yet, Ever or Never (text version)
Which word fits best? Use already, still, yet, ever or never to fill in the blank and complete the sentence.
- I ______[Blank A] haven’t found what I’m looking for.
- She hasn’t done her homework ______[Blank A].
- She has ______[Blank A] seen Niagara Falls.
- Has Debora ______[Blank A] seen Niagara Falls?
- Has Debora seen Niagara Falls ______[Blank A]?
- We haven’t ______[Blank A] been to New York City.
- We ______[Blank A]haven’t been to New York City.
- Yes, Mai has ______[Blank A] seen that movie.
- No, Mai has ______[Blank A] seen that movie.
- Natalie hasn’t ______[Blank A] taught a class online before.
Check your Answers in footnote[1]
Activity source: “Already, Still, Yet, Ever or Never Activity” by Virginia McHardy, CC BY-NC 4.0.
Repeated past actions at an unspecific time:
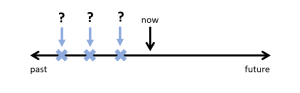
These actions happened repeatedly in the past, but we don’t know when. They are finished actions. Some examples are:
- Sora has seen the movie Titanic three times.
- Gali and Tara have been to Italy several times.
- Zainab has failed her driver’s test twice.
Actions that started in the past and have continued up until now:
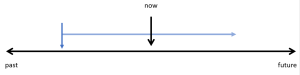
These are actions that started in the past and have continued up until now and might continue into the future. With this function, common time markers used are since and for.
Since is used with a specific time – since 1995, since Tuesday, since childhood
For is used with a duration of time – for 3 years, for 2 days, for a long time
Some examples are:
- I have lived in Barrie for 15 years.
- Mary has worked at Georgian College since 2005.
- Corrine has known me since childhood.
- Mariam has taught ESL for a long time.
Since or For? Activity
Since or For? Activity (Text version)
Complete the sentence by filling in the missing word using either since or for:
- I have lived here _____[Blank A] 8 years.
- I have lived here _____[Blank A] 2018.
- Mariam has been a teacher _____[Blank A] she moved to Barrie.
- Aziz has had a car _____[Blank A] a long time.
- George has had a cold _____[Blank A] Tuesday.
- Carol has been angry _____[Blank A] yesterday.
- The students have known me _____[Blank A] only a short time.
- The students have studied grammar _____[Blank A] 2 hours.
Check your Answers in footnote[2]
Activity source: “Since or For?” by Virginia McHardy, CC BY-NC 4.0.
Forms
Let us now explore how the Present Perfect Tense is formed:
| Subject + | has/have | + past participle |
|---|---|---|
| I | have | studied. |
| Gaelle | has | eaten. |
| Augusta | has | gone. |
| Mary and Alma | have | finished. |
| Subject + | has/have+ | not | + past participle. |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | have | not (haven’t) | taught. |
| Nebrass | has | not (hasn’t) | laughed. |
| Adlet | has | not (hasn’t) | played. |
| You | have | not (haven’t) | arrived. |
| Wang and Shengbo | have | not (haven’t) | decided. |
| Has/Have + | subject | + past participle? | Short Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Have | I | answered? | Yes, you have./No, you haven’t. |
| Has | Stephen | failed? | Yes, he has./No, he hasn’t. |
| Have | the teachers | slept? | Yes, they have./No, they haven’t. |
| Wh ? + | has/have | + subject | past participle? | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | has | Yumi | done? | She has cleaned the kitchen, mopped the floors and dusted. |
| Where | have | they | gone? | They have gone to the dentist. |
| Why | have | you | lied? | I have lied because I didn’t want to get in trouble. |
***Do not use “When” with the Present Perfect Tense questions. Use it with The Simple Past
***For a list of past participles, see Chapter 20.
Present Perfect Form and Function Practice
Watch the video here to review the form and function of Present Perfect. Pay attention to the pop-up messages! There are some practice questions at the end.
Present Perfect Form and Function Review and Practice (Text Version)
Watch the video Present Perfect – Grammar & Verb Tenses (6 minutes)
1:00-1:05 Notice that for actions that started in the past and continue until now, we include a period of time (used with ‘for) or a start time (used with ‘since’).
Activity source: “Present Perfect Form and Function Review and Practice” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. Video Source: Ellii (formerly ESL Library). (2020, September 14). Present perfect – Grammar & verb tenses [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/553eeL1Dvho
Present Perfect More Practice
Present Perfect is sometimes a difficult tense to understand. This video gives some great examples comparing the Simple Past and Present Perfect to highlight the difference. Watch the video to see the difference between the two tenses. Pay attention to the pop-up messages.
More Present Perfect Practice Interactive Video (Text Version)
Watch the video Introduction to Present Perfect Tense (5 min) on YouTube
1:16-1:20 Remember: The Present Perfect connects the past to the present!
1:32-1:36 Again, a time period connecting the past to now.
Activity source: “Present Perfect Form and Function” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. Video Source: EasyTeaching. (January 2, 2020 ) Introduction to present perfect tense | EasyTeaching [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/LWubbhIr0Og
Present Perfect Form Practice – Affirmative
Present Perfect – Affirmative (Text Version)
Use have/has along with the past participle form of the verb given, to form sentences in present perfect tense:
Example:
The train/leave platform
The train has left the platform.
- Mr. Roy/write a book.
- My father/go to Shanghai.
- I/lose my pencil box
- Rohan/live in this house for five years.
- we/just arrived from Vancouver.
- Children/go to bed.
- Mother/cook soup for lunch today.
- Hannah/just/board the bus.
- we/live here for ten years now.
- the shop/open recently.
Check your Answers [3]
Activity source: “Present Perfect – Affirmative” by Annapurna Madhuri, edited by Sari Martin, from “Simple Present, Present Continuous, and Present Perfect” In Effective English for Teachers by Annapurna Madhuri, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. / Title of activity changed, converted to text and minor edits.
Present Perfect Form Practice – Negative
Present perfect – negative (Text Version)
Rewrite the following sentences in negative form
Example: Svetta has eaten the whole pie.
Negative form: Svetta has NOT eaten the whole pie.
- Qiping has hidden the toys in her shelf.
- Rina and Sheila have reached the school.
- Ms. Kim has given milk to the puppies.
- The cat has caught the mouse.
- Glen has finished his homework.
- The artists have used all the colours.
- She has lived in Jordan for 5 years.
- I have received a parcel from my parents.
Check your answers [4]
Activity source: “Present perfect – negative” by Annapurna Madhuri, edited by Sari Martin, from “Simple Present, Present Continuous, and Present Perfect ” In Effective English for Teachers by Annapurna Madhuri, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. / Converted to text and minor edits.
Present Perfect Form Practice – Interrogative
Present perfect – interrogative (Text Version)
Rewrite the following sentences in interrogative form
Example: Svetta has eaten the whole pie.
Interrogative form: Has Svetta eaten the whole pie?
- Qiping has hidden the toys in her shelf.
- Rina and Sheila have reached the school.
- Ms. Kim has given milk to the puppies.
- The cat has caught the mouse.
- She has lived in Jordan for 5 years.
- The artists have used all the colours.
- His parents have advised him to join a good school.
Check your answers [5]
Activity source: “Present perfect – interrogative” by Annapurna Madhuri, edited by Sari Martin, from “Simple Present, Present Continuous, and Present Perfect ” In Effective English for Teachers by Annapurna Madhuri, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. / Converted to text and minor edits.
Pair Work or Small Groups
Ask and answer the following questions in partners or a small group:
- Who is the most interesting person you have ever met?
- Where is the most interesting place you have ever been?
- What is the most unusual thing you have ever eaten?
- What is the funniest thing that has ever happened to you?
- How many times have you gone to a concert?
- How many times have you flown in an airplane?
- How long have you known me?
- How long have you lived in your home?
Communicative Activity – “Never Have I Ever” Game
- Prepare 2-3 statements; Think of things that you’ve never done, but which you think your classmates have.
- The first student says one of their statements. If someone else has done it, they put up their hand to signify this and they get one point. Students keep track of the points themselves or appoint a captain to do this.
- The next person can say their statement and you follow the same procedure, until everyone has said at least one statement. You can also continue until you’ve done two or three rounds, depending on your class size.
- The person with the most points has had the most interesting life.
Verb Tenses in Music
For a fun activity, listen to the following songs:
- I Still Haven’t Found What I’m Looking For by U2
- In My Life by The Beatles
Can you hear the Present Perfect Tense in the lyrics?

Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, “The Present Perfect Tense” by Sari Martin & Virginia McHardy is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
- 1. still, 2. yet, 3. already, 4. already, 5. yet, 6. ever, 7. still, 8. already, 9. never, 10. ever. ↵
- 1. for, 2. since, 3. since, 4. for, 5. since, 6. since, 7. for, 8, for. ↵
-
- Mr. Roy has written a book.
- My father has gone to Shanghai.
- I have lost my pencil box.
- Rohan has lived in this house for five years.
- We have just arrived from Vancouver.
- Children have gone to bed.
- Mother has cooked soup for lunch today.
- Hannah has just boarded the bus.
- We have lived here for 10 years now.
- The shop has opened recently.
-
- Qiping has not hidden the toys in her shelf.
- Rina and Sheila have not reached the school.
- Ms. Kim has not given milk to the puppies.
- The cat has not caught the mouse.
- Glen has not finished his homework.
- The artists have not used all the colours.
- She has not lived in Jordan for 5 years.
- I have received a parcel from my parents.
-
- Has Qiping hidden the toys in her shelf?
- Have Rina and Sheila reached the school?
- Has Ms. Kim given milk to the puppies?
- Has the cat caught the mouse?
- Has she lived in Jordan for 5 years?
- Have the artists used all the colours?
- Have his parents advised him to join a good school?

