14. The Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Learning Outcomes
After completing Chapter 14, students will know how to:
- use the functions of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense.
- form the Past Perfect Continuous Tense in affirmative statements, negative statements and questions.
- apply the Past Perfect Continuous Tense in various situations.
- use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense with the Simple Past and appropriate time markers.
- distinguish between stative verbs and continuous verbs.
- use the correct spelling rules for continuous verbs.
Functions of the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used for actions that were ongoing up until another past action happened.
Let us discuss this point in detail.
The Past Perfect Continuous is usually used together with the Simple Past Tense. We use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense to describe an action that was ongoing until another action happened. The Simple Past Tense is used for the second past action. Notice the timeline below:
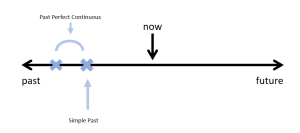
Common Time Markers used with The Past Perfect Continuous Tense and the Simple Past (see Chapter 11):
- when
- by the time
- before
- ***since and for are also used to show the length of the first action
Some examples are:
- I had been painting for three hours by the time the paint ran out.
- Carolina had been doing her homework since 4pm when the power went out.
- Hannah had been making dinner before her kids got home.
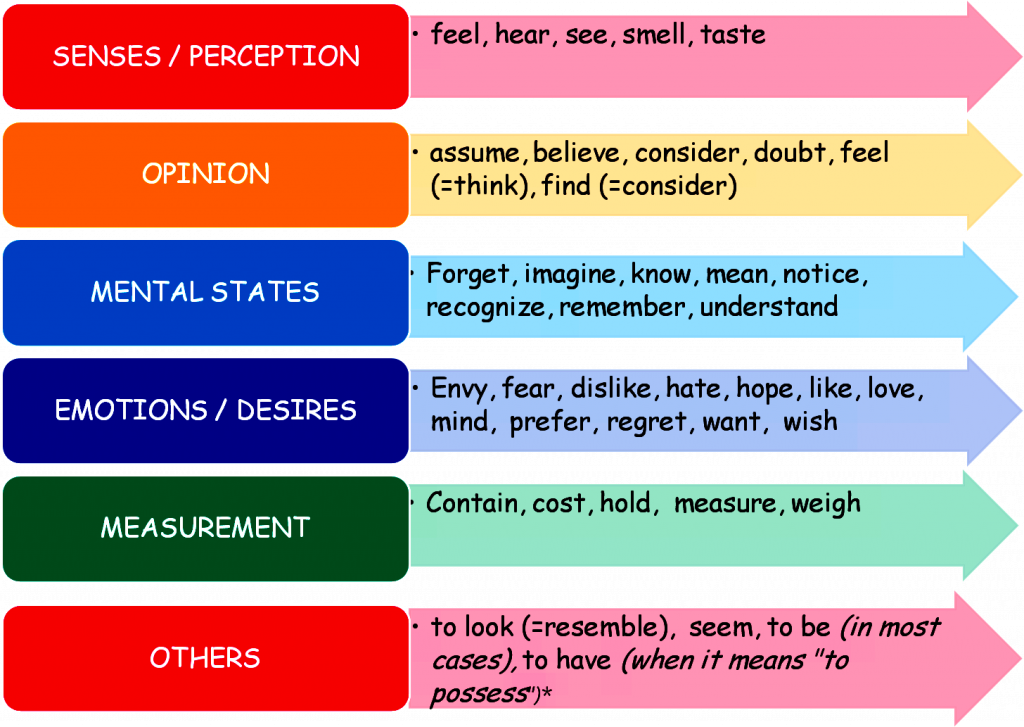
**Just as a reminder, Stative Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses.
Donna had been knowing me since childhood when we stopped talking to each other.
Donna had known me since childhood when we stopped talking to each other.
As a review from Chapter 2, here are examples of stative verbs:
Forms of The Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Let us now explore how the Past Perfect Continuous Tense is formed:
| Subject + | + had been | + verb + ing. |
|---|---|---|
| I | had been | studying. |
| He | had been | eating. |
| She | had been | watching. |
| They | had been | playing. |
| Subject + | had+ not | + been | + verb + ing. |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | had not * | been | studying. |
| She | had not | been | waiting. |
| Lisa | had not | been | teaching. |
| Corinne and Hannah | had not | been | working. |
| *had not = hadn’t |
| Had+ | subject | been + verb + ing? | Short Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Had | I | been helping? | Yes, you had./No, you hadn’t. |
| Had | Catherine | been teaching? | Yes, she had./No, she hadn’t. |
| Had | the children | been working? | Yes, they had./No, they hadn’t. |
| Wh ? + | had | + subject | been + verb + ing | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | had | I | been doing? | You had been procrastinating by the time our mother got home. |
| Where | had | she | been studying? | She had been studying at Georgian College when she got a job. |
| Why | had | you | been going there? | I had been going there before classes to get help with grammar. |
Past Perfect Continuous – Some Uses and Comparisons
Past Perfect Continuous can be a tricky tense to understand, especially because English has so many past tenses that seem similar. In this video, the speaker, Greg, makes comparisons between the Past Perfect Continuous, the Past Perfect, and the Past Continuous and some of their differences. Take notes if you need to and don’t forget to pause to answer the pop-up questions!
Past Perfect Continuous – Some Uses and Comparisons (Text Version)
Watch EXPLAINED! Past Continuous and Past Perfect Continuous Tenses (8 mins) on YouTube & pause to answer the questions.
- Pause at 3:27: Clarification: The rain didn’t stop falling from the sky when I left the house. It continued. Past Continuous shows two closely connected actions: (one long, continuous one) and one short one that ends the continuous one, or happens during the ongoing action.
- Pause at 3:54: Past Perfect Continuous IS NOT closely related to the second action. They do not connect, crossover, or happen at the same time (but only when there’s no time clause/time marker)
- Pause at 5:21: Remember: an amount of time, like 2 hours, is a completed amount, which is why we use the Past Perfect Continuous when followed by a short action.
- Pause at 6:33: Is the following statement correct? I was eating my dinner for 1 hour when I choked on broccoli.
- Pause at 7:12: Which action was NOT completed when the phone rang?
- I was studying all night last night when the phone rang.
- I had been studying for 4 hours last night when the phone rang.
- I had studied all night last night when the phone rang.
- I had been studying all night last night when the phone rang.
- Pause at 7:19: Which action happened closer in time to the second action “before we watched a movie”?
- We had been painting the walls before we watched a movie.
- We had painted the walls yesterday before we watched a movie.
- We had been painting the walls for 2 hours before we watched a movie.
Check your Answers in footnote[1]
Past Perfect Continuous – A Sample Conversation
Watch the dramatic cartoon conversation We’d been hoping for a romantic trip – Past perfect continuous (7 mins) on YouTube, and especially focus on the Past Perfect Continuous examples!
Video Source: Easy English. (2020, September 23). We’d been hoping for a romantic trip – Past perfect continuous [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/qvIZ204JorM
Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Affirmative
Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Affirmative (Text Version)
Fill in the missing words (marked with the letters a-f) using affirmative past perfect continuous and the verb in brackets (listed first). Spelling and punctuation count!
- I _______ [Blank 1 – work] all day so I didn’t want to go out.
- Ayo _______ [Blank 1 – sleep] for 10 hours when I woke him up.
- Dimitri and Athena _______ [Blank 1 – live] in Beijing for 3 years when he lost his job.
- We felt a bit ill because we _______ [Blank 1 – eat] all day.
- It _______ [Blank 1 – rain] as the road was covered in water.
- It _______ [Blank 1 – snow] for 3 days.
Check your Answers in footnote[2]
Activity source: “Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Affirmative”, by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Negative
Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Negative (Text Version)
Fill in the missing words (marked with the letters a-e) using the negative form of Past Perfect Continuous and the verb in brackets (listed first). Use the contraction when possible. Spelling and punctuation count!
- I _______ [Blank 1 – work] there long when Minh quit.
- Even though JinAe _______ [Blank 1 – do] anything, she was still too tired to go out.
- Hussein was in trouble with the teacher because he _______ [Blank 1 – go] to classes.
- Rania _______ [Blank 1 – sleep] long when there was a knock at the door.
- Ravi didn’t feel healthy because he _______ [Blank 1 – go] to the gym.
Check your Answers in footnote[3]
Activity source: “Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Negative” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative
Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative (Text Version)
Fill in the missing words (marked with letters a-e) by forming the interrogative form of Past Perfect Continuous using the verb and subject in brackets (listed first). Spelling and punctuation count!
- When you got sick, _______ [Blank 1 – you/eat] enough?
- There was water everywhere inside. What _______ [Blank 1 – the children/do] ?
- _______ [Blank 1 – it/rain] when you left the restaurant?
- How long _______ [Blank 1 – Julia/live] in Brazil when she found that job?
- How long _______ [Blank 1 – we/wait] when the bus finally arrived?
Check your Answers in footnote[4]
Activity source: “Past Perfect Continuous Form Practice – Interrogative” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Verb Tenses in Music
For a fun activity, listen to the following song:
- I’ll Never Forget You by Birdy
Can you hear the Past Perfect Continuous Tense in the lyrics?

Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, “The Past Perfect Continuous Tense” by Sari Martin & Virginia McHardy is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
-
- False. "One hour" is a COMPLETED amount of time, so we cannot use Past Continuous. Past Continuous actions are not completed actions when followed by Simple Past. Only Past Perfect Continuous are completed actions followed by Simple Past.
- (a) I was studying all night last night when the phone rang.
- (c) We had been painting the walls for 2 hours before we watched a movie.
-
- I had been working all day so I didn't want to go out.
- Ayo had been sleeping for 10 hours when I woke him up.
- Dimitri and Athena had been living in Beijing for 3 years when he lost his job.
- We felt a bit ill because we had been eating all day.
- It had been raining as the road was covered in water.
- It had been snowing for 3 days.
-
- I hadn't been working there long when Minh quit.
- Even though JinAe hadn't been doing anything, she was still too tired to go out.
- Hussein was in trouble with the teacher because he hadn't been going to class.
- Rania hadn't been sleeping long when there was a knock at the door.
- Ravi didn't feel healthy because he hadn't been going to the gym.
-
- When you got sick, had you been eating enough?
- There was water everywhere inside. What had the children been doing?
- Had it been raining when you left the restaurant?
- How long had Julia been living in Brazil when she found that job?
- How long had we been waiting when the bus finally arrived?

