2. The Simple Present Tense
Learning Outcomes
After completing Chapter 2, students will know how to:
- use the functions of the Simple Present Tense.
- form the Simple Present Tense in affirmative statements, negative statements and questions.
- apply the Simple Present Tense in various situations.
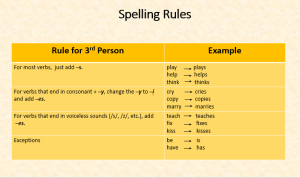
- use the correct spelling rules for 3rd person singular verbs in the Simple Present Tense.
Functions of The Simple Present Tense
Simple present tense is used for
- general truths
- actions happening at the moment (stative verbs)
- routines, habits, and schedules
- future appointments or future schedules
Let us discuss all these points in detail.
General Truths:
General truths can include facts or something that exists and is always true. These can be scientific facts, preferences, likes, dislikes, descriptions, or general states, for instance. Some examples are:
- I like pizza.
- I don’t like coffee.
- Erin works really hard.
- The sun rises in the east.
- That store doesn’t open early in the morning.
- He has brown hair and brown eyes.
- She owns a car.
Actions Happening at the Moment:
We usually use the Present Continuous Tense when we want to express actions happening at the moment. However, some verbs cannot be put in a continuous tense, so they are called stative verbs. Stative verbs include verbs like feel, understand, have, etc. This is when we use The Simple Present Tense. Some examples are:
- I have a headache at the moment.
- I see my teacher at the water fountain.
- He feels jealous.
- I don’t understand this lesson.
- She doesn’t appear happy right now.
Below are some examples of stative verbs:
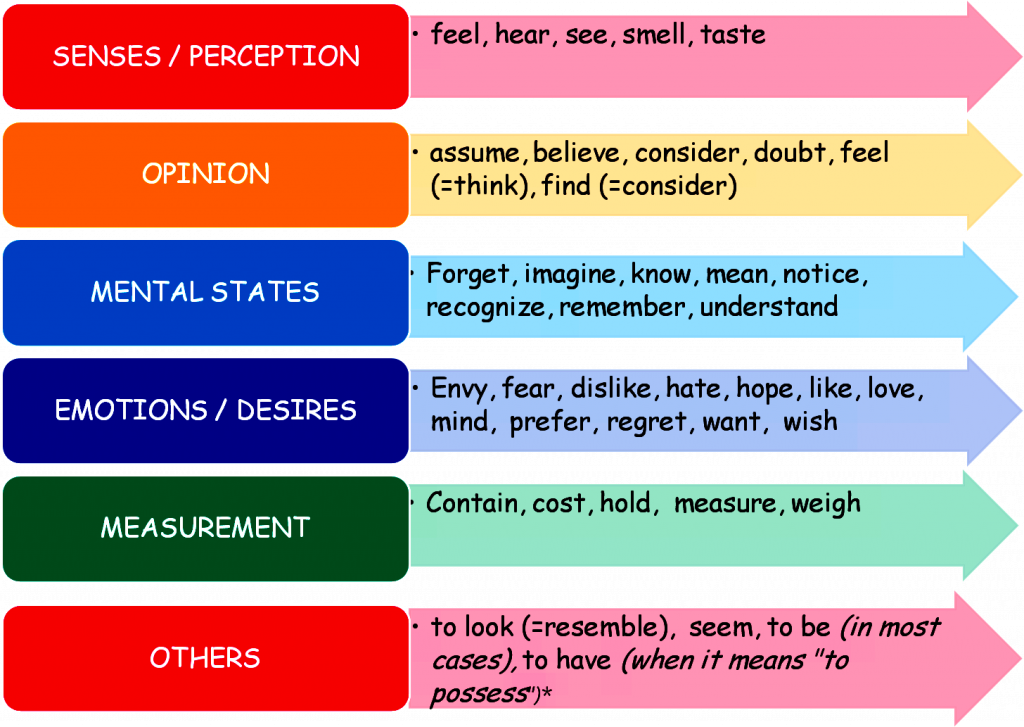
Routines, Habits, and Schedules:
The Simple Present Tense is used to express regular habits, routines, schedules, and repeated actions. Some examples are:
- I take a shower every morning.
- I turn off all the lights before I leave the house.
- Samir plays basketball on Saturday afternoons.
- We visit the dentist twice a year.
- The class doesn’t meet on Wednesdays.
- I don’t watch TV in the evening.
With this function, frequency adverbs can be used, including always, never, sometimes, usually, often, rarely, hardly ever, etc. These adverbs come before the main verb, or after the verb “to be”. Some examples are:
- I usually wake up at 7am.
- I don’t often have a cup of coffee in the afternoon.
- They rarely visit us in the winter.
- He is never late to class in the mornings.
Future Appointments or Schedules:
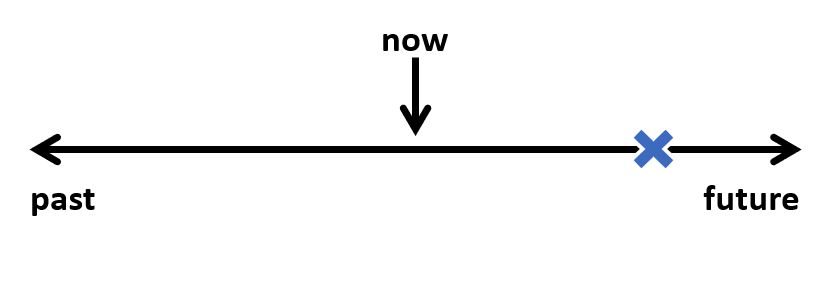
We sometimes use The Simple Present Tense for future appointments or meetings. This is especially true for public transportation and formal appointments with a scheduled time. Some examples are:
- We have a test next Friday.
- She sees the doctor in 2 days.
- The bus leaves at 7am tomorrow.
- The train leaves in one hour.
**Time Markers Used with The Simple Present Tense
Some common time markers used with The Simple Present Tense are:
- every day/night/week/month/year
- in the morning/afternoon/evening
- once a day/week/month/year
- on Mondays/Tuesdays/Wednesdays etc…
Form of The Simple Present Tense
Let us now explore how the Simple Present Tense is formed:
| Subject + | base verb (s) + | every day. |
|---|---|---|
| I | swim | every day. |
| He | swims | every day. |
| She | swims | every day. |
| They | swim | every day. |
| Subject + | do/does+ | not + | base verb |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | do | not (don’t) | swim. |
| He | does | not (doesn’t) | swim. |
| Do/Does + | subject+ | base verb? | Short Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do | you | swim? | Yes, I do./ No, I don’t. |
| Does | he | swim? | Yes, he does./ No, he doesn’t. |
| Wh ? + | do/does+ | subject | + base verb? | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Where | do | you | swim? | I swim in my friend’s pool. |
| When | does | he | swim? | He swims every Saturday. |
Watch It!
Watch the video: Forming the Present Simple tense in English (5 minutes)
Video Source: GoEnglish. (2014, November 07). Forming the present simple tense in English [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/BNv44tAt9PA
Simple Present Functions Practice
Read each sentence and guess the function. Click ‘turn’ to see the answer.
Simple Present Tense Functions (Text Version)
Read each simple present sentence and guess the function. The functions are: General truth (preference); General truth (fact); General truth (states); actions happening at the time of speaking (stative verbs); routines/habits; and future schedules.
- She earns a lot of money.
- The bus leaves at 3:00pm.
- The moon revolves around the earth.
- The baby drinks a glass of milk every morning.
- Neelu likes chocolate.
- Wood always floats on water.
- Lions hunt at night.
- She leaves for Mexico in two days.
- I have a really bad stomachache.
- I feel nervous.
- I own a car and a bicycle.
- He occasionally drinks coffee in the morning.
- Richard does not take care of his pets.
- The students do not have a test tomorrow.
- The flowers do not bloom until late spring.
- I play the piano.
- I do not like broccoli.
- He works out on the weekends mostly.
- I don’t understand what he’s saying.
Check your Answers in footnote[1]
Activity source: “Simple Present Tense Functions” by Sari Martin, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Simple Present Form Practice – Affirmative
Simple Present form quiz (Text version)
Fill in the given blanks with the correct form of verb listed below each question
- She ________[Blank 1] a lot of money.
- earns
- earn
- Mona’s dress ________[Blank 1] beautiful.
- to be
- is
- The bus ________[Blank 1] at 3.00 pm.
- leave
- leaves
- The moon ________[Blank 1] round the earth.
- revolve
- revolves
- The baby ________[Blank 1] a glass of milk every morning.
- drink
- drinks
- Aurora ________[Blank 1] chocolates.
- like
- likes
- Wood always ________[Blank 1] on water.
- float
- floats
- Lions ________[Blank 1] at night.
- hunt
- hunts
- There ________[Blank 1] many books in the library.
- is
- are
- She ________[Blank 1] for Mexico in two days .
- leave
- leaves
Check your Answers in footnote[2]
Activity source: “Simple Present form quiz” by Annapurna Madhuri, edited by Sari Martin, from “2 Simple present” In Effective English for Teachers by Annapurna Madhuri, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. / Converted to Text and some examples edited and added.
Simple Present Tense Form Practice – Negative and Interrogative
Simple Present Tense Functions (Text Version)
Fill in the blanks with the words in correct boxes using: do, does, do not :
- Neelu ________[Blank 1] walk to school in the morning.
- ________[Blank 1] Sheela paint?
- The students ________[Blank 1] have a test tomorrow.
- ________[Blank 1] Mr. and Mrs. Murty work in the same school?
- ________[Blank 1] the woman work at the college?
- The boy ________[Blank 1] does not study hard for his exams.
- The flowers ________[Blank 1] bloom until late spring.
- ________[Blank 1] the play begin at 9 O’ clock?
- ________[Blank 1] the children play in the park every evening?
- They ________[Blank 1] earn a lot of money.
- Richard ________[Blank 1] take care of his pets.
Check your Answers in footnote[3]
Activity source: “Simple Present – Negative and Interrogative form practice” by Annapurna Madhuri, edited by Sari Martin, from “2 Simple present” In Effective English for Teachers by Annapurna Madhuri, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0. / Converted to Text and some examples edited.
Fill in the Blanks with the Simple Present Tense (text version)
- (like) I ____ [Blank A] ice cream very much.
- (like/not) Stephen isn’t good at speaking in front of others, so he ____ [Blank A] presentations.
- (play) ____ [Blank A] you ____ [Blank B] a lot of sports?
- (carry) Natalie ____ [Blank A] 3 bags: one for her books, one for her shoes and one for her lunch.
- (go) Where ____ [Blank A] Amanda ____ [Blank B] every weekend?
- (use/not) We ____ [Blank A] our phones in the classroom.
- (open) The Last Class ____ [Blank A] at 8:00am for students who want a quick breakfast.
- (stay) ____ [Blank A] the library ____ [Blank B] open on the weekends in the summer? No, it ____ [Blank C].
- (have) Corinne ____ [Blank A] a great parking spot in the summer because most students (have/not) ____ [Blank B] classes.
- (be) ____ [Blank A] you hungry? No, I ____ [Blank B]. I ____ [Blank C] full from last night’s dinner.
Check your Answers in footnote[4]
Activity source: Fill in the Blanks with the Simple Present Tense by Virginia McHardy, licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0.
Communicative Activities
1. What Does This Person Do? – Job Guessing Game
-
Prepare job cards with pictures (doctor, teacher, chef, etc.).
-
One student picks a card and describes the job without saying it:
-
“This person helps sick people. This person works in a hospital.”
-
-
Others guess: “Is it a doctor?”
Variation: Use real people you know (famous or personal).
2. Discussion Questions
Ask and answer the questions in partners or a small group:
-
What time do you wake up?
-
What do you eat for breakfast?
-
Where do you live?
-
Do you like pizza? Why or why not?
-
What do you do on the weekend?
-
Do you play any sports or games?
-
What music do you listen to?
-
What do you do after school (or work)?
-
Do you have any brothers or sisters? What do they do?
-
What do you do in your free time?
Verb Tenses in Music
For a fun activity, listen to the following songs:
- You Belong with Me (Taylor’s Version) by Taylor Swift
- Don’t Worry, Be Happy by Bobby McFerrin
Can you hear the Simple Present Tense in the lyrics?

Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, “The Simple Present Tense” by Sari Martin & Virginia McHardy is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
-
- general truth (fact)
- general truth (state or preference)
- future schedule
- general truth (fact)
- routine/habit
- general truth (preference)
- general truth (fact)
- general truth (fact)
- general truth (fact)
- future schedule
- actions happening at the time of speaking (stative verbs)
- actions happening at the time of speaking (stative verbs)
- general truth (state)
- routine/habit
- general truth (fact)
- future schedule
- general truth (fact)
- general truth (state)
- general truth (preference)
- routine/habit
- actions happening at the time of speaking (stative verbs)
-
- She earns a lot of money.
- Mona's dress is beautiful.
- The bus leaves at 3.00 pm.
- The moon revolves round the earth.
- The baby drinks a glass of milk every morning.
- Neelu linkes chocolates.
- Wood always floats on water.
- Lions hunt at night.
- There are many books in the library.
- She leaves for Mexico in two days.
-
- Neelu does not walk to school in the morning.
- Does Sheela paint?
- The students do not have a test tomorrow.
- Do Mr. and Mrs. Murty work in the same school?
- Does the woman work at the college?
- The boy does not study hard for his exams.
- The flowers do not bloom until late spring.
- Does the play begin at 9 O' clock?
- Do the children play in the park every evening?
- They do not earn a lot of money.
- Richard does not take care of his pets.
- 1. like, 2. does not/doesn't like, 3. Play, 4. carries, 5. does / go, 6. do not/don't use, 7. opens, 8. Does / does not/doesn't, 9. has / do not/don't have, 10. Are / I'm/am not / am ↵

