2.5 Primary and Secondary Prevention
Primary Prevention
Primary Prevention seeks to prevent health problems before they occur. These prevention efforts look upstream to try to determine the root cause of the problem. Negative health outcomes can be prevented by screening and addressing risk factors and enhancing resistance to those risks (AFMC, 2022). We can prevent unhealthy substance use and substance use disorders, through addressing the community conditions that put people at risk (Saskatoon Health Region, n.d.). For example, in terms of the drug poisoning (overdose) epidemic, primary prevention efforts would focus on preventing poisonings (overdoses) by investigating the community conditions that lead to substance use in the first place (Saskatoon Health Region, n.d.).
VIDEO: Primary Prevention
The following video provides examples of primary prevention efforts.
VIDEO: What is Prevention? – The Role of the Community
The following video provides an illustration of primary prevention efforts.![]() (Some wording used in this video may be considered stigmatizing [i.e., the use of “addiction” instead of “SUD”, “substance misuse” instead of “substance use issues or problems”], does not reflect recommended language, and is not consistent with what you will learn in this course).
(Some wording used in this video may be considered stigmatizing [i.e., the use of “addiction” instead of “SUD”, “substance misuse” instead of “substance use issues or problems”], does not reflect recommended language, and is not consistent with what you will learn in this course).
Secondary Prevention
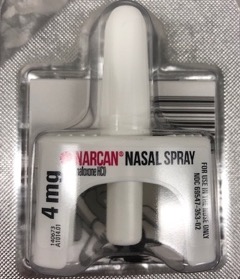
Secondary Prevention seeks to lessen the impact of health problems. Here the focus is on identifying issues and providing interventions and treatment as soon as possible, in order to reverse or slow negative health outcomes (Saskatoon Health Region, n.d.). For people experiencing SUDs, secondary prevention measures can include access to: non-judgemental information and treatment services; availability of clean/sterile equipment (e.g., syringes, pipes); a safe supply of drugs; the provision of naloxone to prevent drug poisoning (overdose) deaths, etc. These types of prevention measures are downstream oriented efforts that are more reactive in nature. They cannot get to the root of the issue/problem that lead to substance use issues in the first place, only proactive primary prevention efforts can achieve this goal.

Click the link below to learn more about substance use prevention and the methods that can be used to support people who use drugs:
Opioids – Social Determinants of Substance Use & Overdose Prevention

