Expense Calculations
Overview
The cost of higher education varies depending on many factors. It can differ based on the type of school you choose (college or university), the school’s location, your major, and the amount of funds you may already have. That’s why planning for how to fund your post-secondary education is essential. Knowing the associated costs and how to calculate them can help you create a budget and inform how many scholarships you want to apply to.
Learning Objectives
- Differentiate between the types of costs associated with post-secondary education.
- Learn how to research the various costs of post-secondary education (e.g., your preferred program’s tuition).
- Calculate projected expenses accurately for the duration of a post-secondary education.
Keywords
#Budgeting #FinancialAidDocuments #TimeManagementResources
Types of Expenses
Although students may group their expenses differently based on personal preferences, the following are common categories.
School Expenses
School expenses include all the costs required to fund your education. Although they may be called differently elsewhere, these are some of the main expenses under this category:
Living Expenses
Living expenses include any money you will spend on your needs. Living expenses typically include the cost of:
In first year, many students have the opportunity to live in residence. Each post-secondary institution will have a webpage for students living in residence with detailed information about the cost of different residence rooms, meal plans, and payment schedules. When living in residence, you may still occasionally get groceries to have food in your room, or go out for dinner with friends, so make sure to budget for that as well. Although you likely won’t have to pay for Wi-Fi or utilities in residence, you might have to pay for additional services, like laundry.
Personal Expenses
Personal expenses include any additional costs that are considered “nice to have.” Under our proposed framework, all required, non-school expenses would be considered living expenses.
A work-life balance is important to your overall well-being, so there’s nothing wrong with having non-essential expenses – it’s totally normal. Rather, this category provides another way to track and manage your spending.
Some examples of this type of expense might include:
- Concert tickets.
- Going out with friends.
- Streaming service subscriptions (e.g., Netflix, Spotify).
- Workout supplements (e.g., protein powder).
- Non-essential meal delivery services (e.g., Uber Eats, InstaCart).
- Going on vacation.
How Expense Tracking Helps with Financial Aid Applications
Tracking your expenses helps you manage the amount of money you’re spending, and also helps you budget the amount of money needed to fund a post-secondary education. Expense tracking is a great way to plan your post-secondary education, by determining how much you will likely spend over the next few years. This can help you decide for which scholarship brackets to apply (e.g., $100-1,000 dollars or $1,000-$5,000). The better you track your expenses, the better you can plan your financial aid applications.
The amount of expenses you need to track can be overwhelming. Use our Notion database to easily calculate your projected expenses. In use, your Projected Expense Calculator might look something like this:
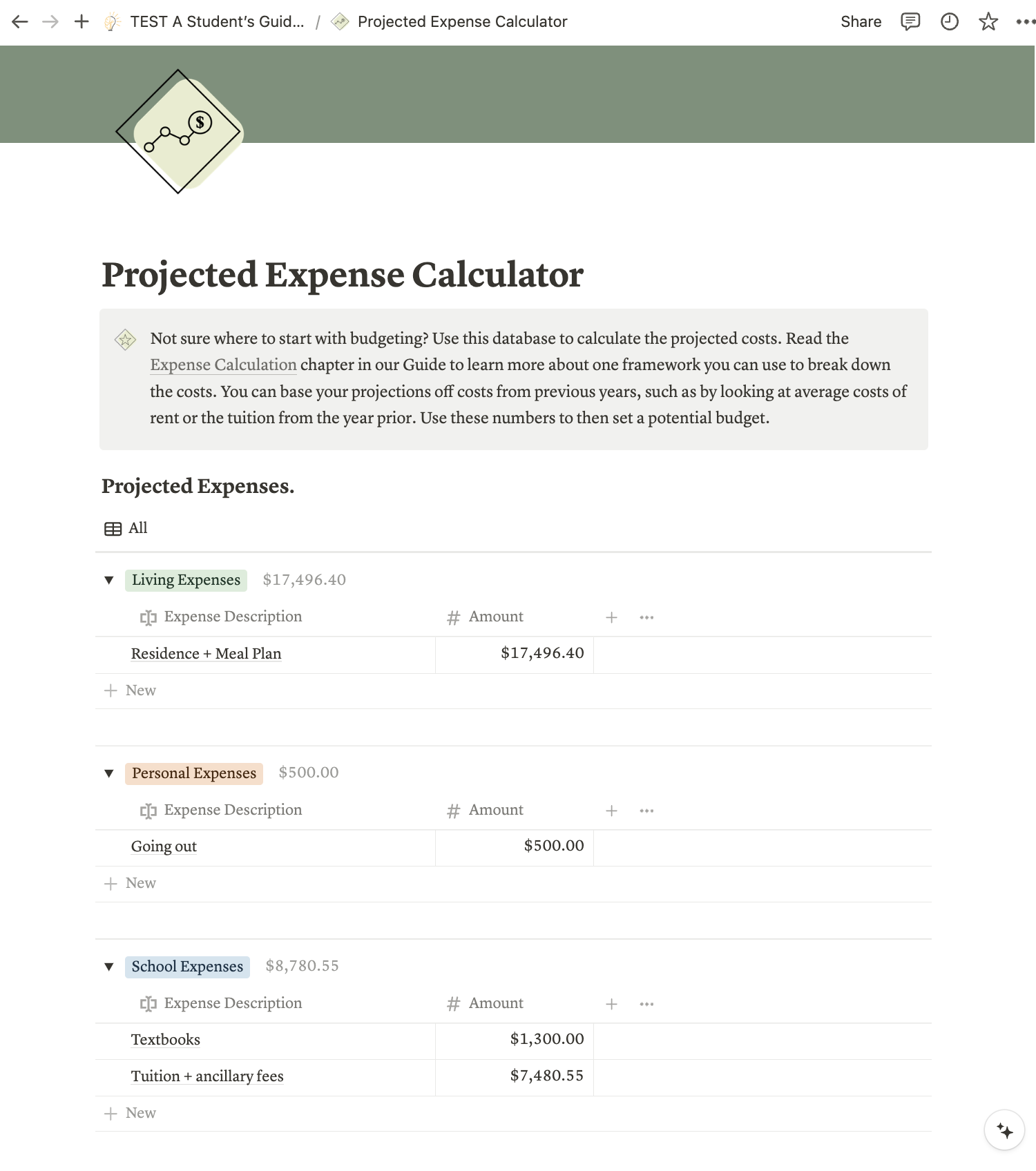
Tracking Your Monthly Expenses
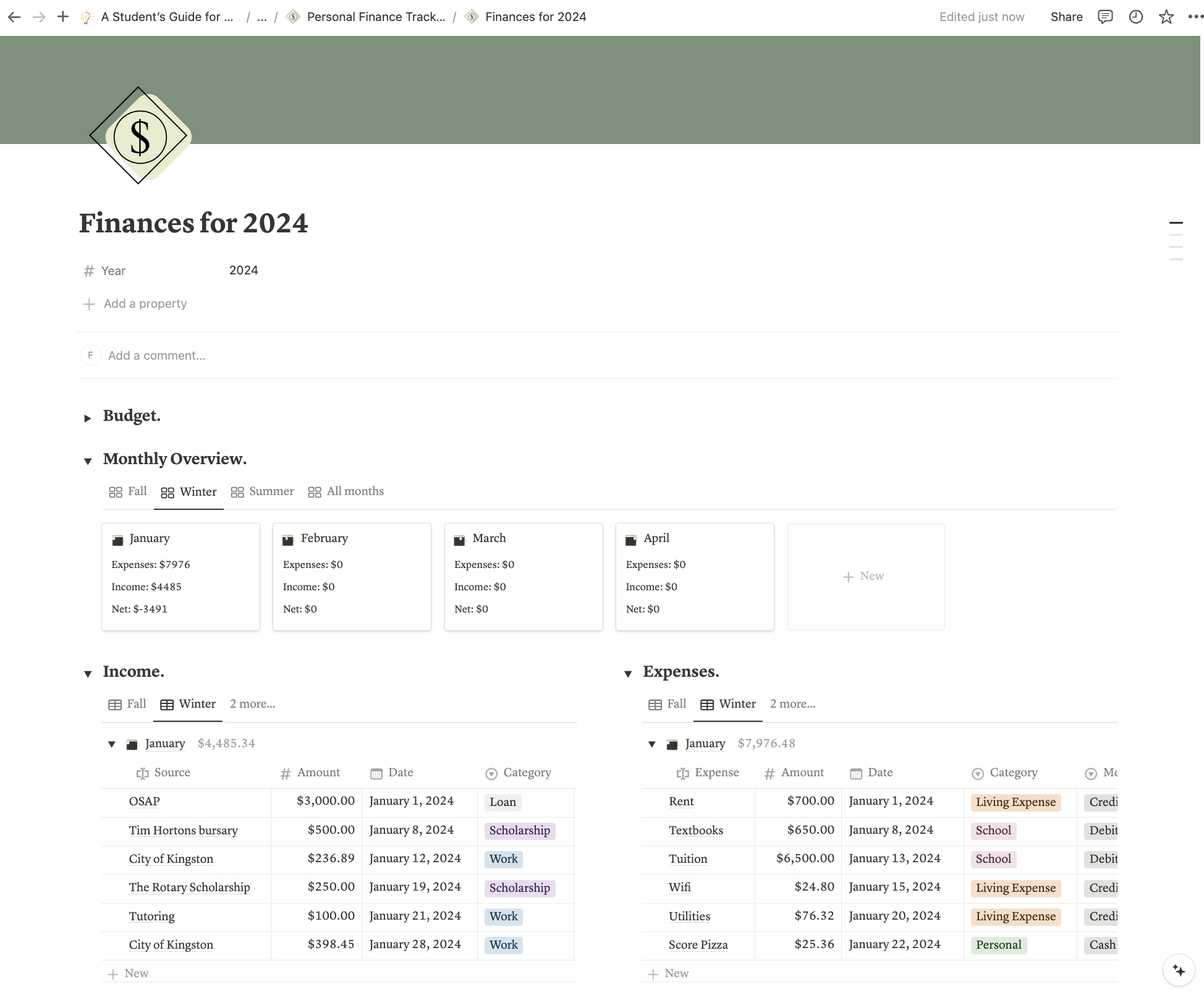
Tracking your monthly expenses throughout your higher-education experience is important to ensure you stay within your budget. This provides a clear overview of how you’re spending your money ,and will help you stay accountable.
Use our Notion database to track your monthly expenses and help you better manage your finances. In use, your Personal Finance Tracker might look something like this:
Check Your Learning
Before you proceed, take a moment to review some of the content you’ve learned so far.
Glossary
Ancillary fees
Fees you pay in addition to your tuition to support your life at school (e.g., athletic facility membership).
Financial aid
Funds from the government, private organizations and/or from an educational institution to help students pay for their education.
Higher Education
Schooling that happens after high school (i.e., University or College). Also known as post-secondary education.
Living expenses
Money that you will spend on your needs (e.g., housing, food, clothing, transportation, healthcare plans etc.).
Personal expenses
Money that you will spend on items that are typically for fun or related to personal interests and hobbies.
Projected expenses
The total amount of money you expect to spend on your various expenses.
School expenses
All the costs associated with funding your education.
Tuition fees
The fees that you pay your educational institution for the schooling that you receive.
References
Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities. (2013). Tuition and ancillary fees [PDF]. https://www.tcu.gov.on.ca/pepg/documents/TuitionandAncillaryFees.pdf
How to Cite this Chapter Using APA Style
*Nusselder, F., *Burrows, H. M. R., Giovannangeli, A. J., Armstrong, A. M., & Xu, Y. (2024). Expense calculation. In Pay for post-secondary: A student’s guide for securing financial aid. Queen’s University, eCampus Ontario. Licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/payforpostsecondary/part/expense-calculations/
*denotes equal contributions as first authors
Schooling that happens after high school (i.e., University or College). Also known as post-secondary education.
The fees that you pay your educational institution for the schooling that you receive.
All the costs associated with funding your education.
Money that you will spend on your needs (e.g., housing, food, clothing, transportation, healthcare plans, etc.).
Money that you will spend on items that are typically for fun or related to personal interests and hobbies.
Funds from the government, private organizations, and/or an educational institution to help students pay for their schooling.
The total amount of money you expect to spend on your various expenses.

