18 3.7 A Very Interesting Transgenic Mouse for Neuroscience
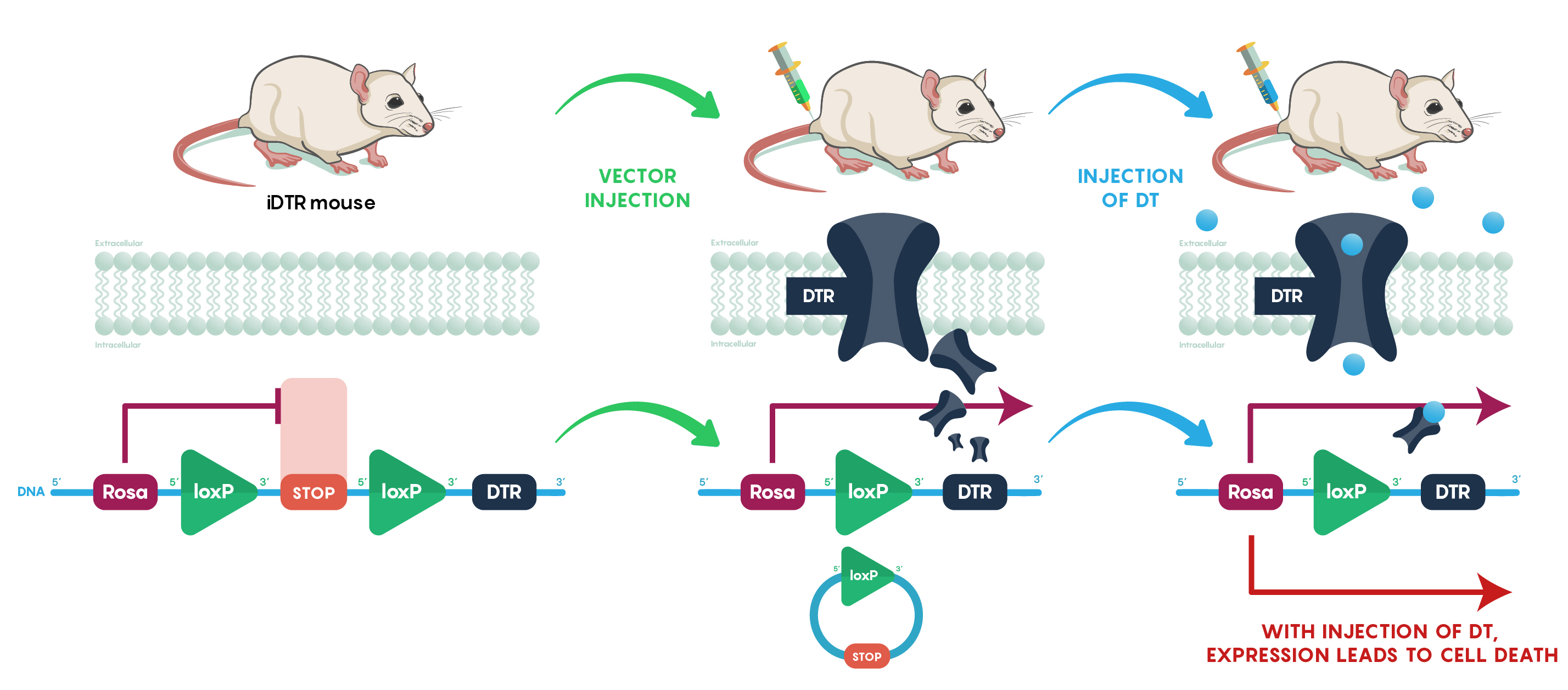
One of the very exciting aspects of neuroscience is the use of transgenic mice to aid in our understanding of behaviour. One particular mouse, not originally intended for use in neuroscience was the Rosa or iDTR mouse. The Rosa or iDTR (for inducible Diphtheria Toxin Receptor) mouse utilizes a transgene very similar to the Cre-driver lines. In this mouse (shown in Figure 1 below) all cells throughout the mouse’s body carries the DNA sequence for the Diphtheria Toxin Receptor DTR). Note that this DTR DNA sequence is preceded by a STOP codon that is flanked by loxP sites. If Cre-recombinase was introduced by vector injection then the STOP codon is removed and the DTR is now transcribed and translated in the area or tissue where the Cre-recombinase was injected. Normally this does not present a problem as the mouse has had no exposure to diphtheria toxin. However, we can inject the toxin systemically into the mouse and only those cells expressing the receptor will undergo apoptotic cell death.