Integumentary System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the integumentary system and accessory structures
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the integumentary system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of integumentary system medical terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the integumentary system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic tests and procedures
Key Word Components
Identify meanings of key word components of the integumentary system:
Prefixes
- a- (absence of, meaning)
- bi- (two or both)
- dia- (through, complete)
- dys- (difficult, painful, abnormal, labored)
- epi- (upon, on, over)
- hyper- (above, excessive)
- hypo- (deficient, below, under, incomplete)
- intra- (within, in)
- meta- (change, beyond, after)
- neo- (new)
- para- (beside, around, beyond, abnormal)
- per- (through)
- pro- (before)
- sub- (under, below)
- trans- (through, across, beyond)
- uni- (one)
Combining Forms
- aden/o (gland)
- adip/o (fat)
- albin/o (white)
- aut/o (self)
- bi/o (life)
- coni/o (dust)
- cry/o (cold)
- crypt/o (hidden)
- cutane/o (skin)
- cyan/o (blue)
- derm/o (skin)
- dermat/o (skin)
- erythr/o (red)
- erythemat/o (redness)
- fibr/o (fibrous tissues)
- heter/o (other)
- hidr/o (sweat)
- kerat/o (hard, horny tissue, keratin)
- lei/o (smooth)
- leuk/o (white)
- lip/o, lipid/o (fat)
- melan/o (black)
- myc/o (fungus)
- necr/o (death)
- onych/o (nail)
- pachy/o (thick)
- pil/o (hair)
- py/o (pus)
- rhytid/o (wrinkles)
- sclera/o (hardening)
- seb/o (sebum)
- staphyl/o (grapelike clusters)
- steat/o (fat, sebum)
- strept/o (twisted chains)
- ungu/o (nail)
- xanth/o (yellow)
- xer/o (dryness, dry)
Suffixes
- -a (no meaning, noun ending)
- -al (pertaining to)
- -ad (toward)
- -coccus (berry-shaped)
- -cyte (cell)
- -ectomy (excision)
- -gen (substance that produces/causes, agent that produces/causes)
- -genic (producing, originating, causing)
- -ia (condition of, diseased state, abnormal state)
- -ic (pertaining to)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -ior (pertaining to)
- -logy (study of)
- -logist (specialist who studies and treats)
- -malacia (softening)
- -megaly (enlarged, enlargement)
- -oid (resembling)
- -oma (tumor, swelling)
- -opsy (view of, process of viewing, viewing)
- -orrhea (flow, excessive discharge)
- -osis (abnormal condition, increased numbers relating to blood)
- -ous (pertaining to)
- -pathy (disease)
- -phagia (eating, swallowing)
- -plasia (development, growth, condition of formation)
- -plasm (growth, substance, formation)
- -plasty (surgical repair)
- -rrhea (flow, discharge)
- -sis (state of)
- -stasis (stop, controlling, standing)
- -tome (instrument used to cut)
Integumentary System Words
Integumentary Medical Terms (Text version)
- biopsy (bx)
- BĪ-op-sē
- view of life (removal of living tissue to be viewed under a microscope)
- dermatitis
- dĕr-mă-TĪT-ĭs
- inflammation of the skin
- dermatoautoplasty
- dĕr-mă-tō-AW-tō-plăs-tē
- surgical repair using one’s own skin
- dermatoconiosis
- dĕr-mă-tō-kō-nē-Ō-sĭs
- abnormal condition of the skin caused by dust
- dermatofibroma
- dĕr-mă-tō-fī-BRŌ-mă
- fibrous tumour of the skin
- dermatoheteroplasty
- dĕr-mă-tō-HĔT-ĕr-ō-plăs-tē
- surgical repair using skin from others
- dermatologist
- dĕr-mă-TŎL-ō-jĭst
- Physician who specializes in treating diseases and disorders of the skin
- dermatology (derm)
- dĕr-mă-TŎL-ō-jē
- study of the skin
- dermatome
- DĔR-mă-tōm
- instrument used to cut skin
- dermatoplasty
- DĔR-măt-ō-plas-tē
- get meaning
- epidermal
- ĕp-ĭ-DĔR-mal
- pertaining to upon/on the skin
- erythroderma
- ĕ-rith-rŏ-DĔR-mă
- red skin
- hidradenitis
- hi-dra-ĕn-ĪT-ĭs
- inflammation of a sweat gland
- hypodermic
- hī-pō-DĔR-mĭk
- pertaining to below the skin
- intradermal (ID)
- in-tră-DĔR-măl
- pertaining to within the skin
- keratogenic
- kĕr-ă-TŎJ-ĕ-nŭk
- agent that causes growth of horny tissue
- keratosis
- ker-ă-TŌ-sĭs
- abnormal condition of growth of horny tissue
- leiodermia
- lī-ō-DĔR-mē-ă
- condition of smooth skin
- leukoderma
- loo-kŏ-DĔR-mă
- white patches caused by depigmentation
- necrosis
- nĕ-KRŌ-sĭs
- condition of death
- onychocryptosis
- ŏn-ĭ-kō-krip-TŌ-sis
- abnormal condition of a hidden nail
- onychomalacia
- ŏn-ĭ-kō-mă-LĀ-shă
- softening of the nails
- onychomycosis
- on-i-kō-mī-KŌ-sĭs
- abnormal condition of a fungus in the nails
- onychophagia
- ŏn-ĭ-KŎF-ă-jē
- eating the nails (nail biting)
- pachyderma
- pak-ē-DĔR-mă
- thickening of the skin
- paronychia
- păr-ō-NĬK-ē-ă
- diseased state around the nail
- percutaneous
- pĕr-kū-TĀ-nē-ŭs
- pertaining to through the skin
- rhytidectomy
- rit-ĭ-DEK-tŏ-mē
- excision of the wrinkles
- rhytidoplasty
- RĬT-ĭ-dō-plăs-tē
- surgical repair of wrinkles
- seborrhea
-
- sĕb-or-Ē-ă
- discharge (excessive) of sebum
-
- staphylococcus (staph)
- staf-ĭ-lō-KOK-ŭs
- berry-shaped bacterium in grape-like clusters
- streptococcus (strep)
- strep-tŏ-KOK-ŭs
- berry-shaped bacterium in twisted chains
- subcutaneous (subcut, Sub-Q)
- sŭb-kū-TĀ-nē-ŭs
- pertaining to under the skin
- subungual
- sŭb-ŬNG-gwăl
- pertaining to under the nail
- transdermal (TD)
- trănz-DĔRM-ăl
- pertaining to through the skin
- ungual
- ŬNG-gwăl
- pertaining to the nail
- xeroderma
- zer-ŏ-DĔR-mă
- dry skin
- xerosis
- zĕ-RŌ-sĭs
- abnormal condition of dryness
Activity source: Integumentary Medical Terms from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al., licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Integumentary System Medical Terms
Integumentary Medical Terms (Text version)
- abscess
- AB-ses (Original Term)
- localized collection of pus
- abrasion
- ă-BRĀ-zhŏn (Original Term)
- scrape (by injury or mechanical process)
- acne
- AK-nē
- clogging of pores, which can lead to infection and inflammation
- adipocytes
- AD-ĭ-pō-sīts
- Fat cells
- adipose
- AD-ĭ-pōs
- Fat tissue
- albinism
- AL-bĭ-nizm
- genetic disorder that affects the coloring of skin, hair, and eyes.
- apocrine sweat gland
- AP-ŏ-krĕn swet gland
- A type of gland that is found in the skin, breast, eyelid, and ear
- autonomic
- ot-ŏ-NOM-ik
- unconsciously regulates
- bacteria, bacterium
- bak-TĒR-ē, bak-TĒR-ē-ŭm (Original Term)
- single-celled microorganisms that reproduce by cell division and may cause infection by invading body tissue
- basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
- BĀ-săl sel kar-sĭn-Ō-ma
- form of cancer that affects the mitotically active stem cells in the stratum basale of the epidermis
- benign
- bē-NĪN
- Noncancerous, harmless
- cancer
- KAN-sĕr
- A process where abnormal cells in the body divide uncontrollably
- cauterize, cauterization
- KAW-tĕr-īz (Original Term)
- to burn tissues by various means with the intent destroy damaged tissues, prevent infections or coagulate blood vessels
- cellulitis
- sel-yŭ-LĪT-ĭs (Original Term)
- bacterial infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, characterized by redness, pain, heat and swelling
- contusion
- kŏn-TOO-zhŏn (Original Term)
- bruise
- cyanosis
- sī-ă-NŌ-sĭs
- Abnormal condition of blue (bluish colour, lips and nail beds). Typically caused by low oxygenation
- cyst
- sist (Original Term)
- closed sac containing fluid or semisolid material
- debride, debridement
- di-BRĒD, di-BRĒD-mĕnt (Original Term)
- remove damaged tissues and cell debris from a wound or burn to prevent infection and promote healing.
- dehydration
- dē-hī-DRĀ-shŏn
- Loss of fluids/water is greater than what is taken in.
- dendritic cells
- den-DRIT-ik
- pertaining to dendrites
- dermabrasion
- DĔRM-ă-brā-zhŏn (Original Term)
- procedure to remove superficial scars using sandpaper or revolving wire brushes.
- diaphoresis
- dī-ă-fŏ-RĒ-sĭs (Original Term)
- condition of profuse, excessive sweating
- eccrine sweat gland
- ĔK-rĭn swet gland
- type of gland that produces a hypotonic sweat for thermoregulation
- eczema
- eg-ZĒ-mă (Original Term)
- noninfectious, inflammatory disease presents as redness, blisters, scabs and itching
- edema
- ĕ-DĒ-mă (Original Term)
- puffy swollen tissue due to accumulation of fluid
- excise, excision
- ĕk-SĪZ, ek-SIZH-ŏn (Original Term)
- surgical removal by cutting out
- fascia
- FASH-ē-ă
- Fibrous tissue
- frostbite
- FROST-bīt
- Conservation of core body heat results in the skin actually freezing
- gangrene
- GANG-grēn (Original Term)
- death of tissue due to blood supply loss
- incise, incision
- in-SĪZ, in-SIZH-ŏn (Original Term)
- surgical cut into or wound produced by a sharp instrument
- incision and drainage (I&D)
- in-SIZH-ŏn & DRĀN-ăj
- surgical cut made to allow the free flow of fluids from a lesion, wound, or cavity
- infection
- in-FEK-shŏn (Original Term)
- invasion of pathogens to body tissue
- jaundice, jaundiced
- JON-dĭs, JON-dĭsd (Original Term)
- yellow colouring of the mucous membranes and sclera
- keloid
- (KĒ-loyd)
- Formation of a raised or hypertrophic scar
- keratin
- (KER-ăt-ĭn)
- intracellular fibrous protein that gives hair, nails, and skin their hardness and water-resistant properties
- keratinocyte
- kĕ-RĂT-ĭ-nō-sīt
- Cell that manufactures and stores the protein keratin
- laceration
- las-ĕ-RĀ-shŏn (Original Term)
- torn, ragged-edged wound
- laser surgery
- LĀ-zĕr SŬRJ-ĕ-rē
- A surgical procedure using a powerful beam of light to cut or burn tissue.
- Lesion
- lĒ-zhŏn (Original Term)
- visible change in tissue resulting from injury or disease
- leukoplakia
- loo-kō-PLĀ-kē-ă
- white, thickened patches on mucus membrane tissue of the tongue or cheek
- macule
- MAK-ūl (Original Term)
- flat, coloured spot on the skin
- Meissner corpuscle
- MĪS-nĕr KOR-pŭs-ĕl
- Tactile corpuscle that responds to light and touch, touch receptor
- melanoma
- mel-ă-NŌ-mă
- cancer characterized by uncontrolled growth of melanocytes
- metastasize
- mĕ-TĂS-tă-sīz
- Production of cells that can mobilize and establish tumors in other organs of the body
- nevus
- NĒ-vŭs (Original Term)
- a pigmented skin blemish
- nodule
- NOJ-ool (Original Term)
- a small node-like structure
- Pacinian corpuscle
- pă-SIN-ē-ăn KOR-pŭs-ĕl
- Lamellated corpuscle that responds to vibration
- pallor
- PĂL-or (Original Term)
- paleness
- pathogens
- path-Ŏ-jĕns
- Disease-causing agents
- phagocytes
- făg-ō-SĬTS
- Cells that engulf and absorb bacteria and cell particles
- pruritus
- proo-RĪT-ŭs (Original Term)
- itching
- psoriasis
- sŏ-RĪ-ă-sĭs
- chronic autoimmune disorder that results in patches of thick red skin with the appearance of silvery scales
- pustule
- PŬS-tūl (Original Term)
- small elevation of the skin containing fluid
- reticulated
- rĕ-TIK-yŭ-lāt-ĕd
- constructed, arranged, or marked like a net or network.
- rickets
- RIK-ĕts
- A painful condition in children where bones are misshapen due to a lack of calcium, causing bow leggedness
- scar
- skăr
- Collagen-rich skin formed after the process of wound healing that differs from normal skin. Also known as a cicatrix.
- sebaceous gland
- sē-BĀ-shŭs gland
- type of oil gland that is found all over the body and helps to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair.
- squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- SKWĀ-mŭs sel kar-sĭn-Ō-mă
- cancer that affects the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum and presents as lesions commonly found on the scalp, ears, and hands
- stratum basale
- STRĀ-tŭm BĀS-al
- Deepest layer of the epidermal
- suture
- SOO-chŭr
- to stitch the edges of a wound
- sympathetic
- sĭm-pă-THĔT-ĭk
- Flight or fight response
- Sympathetic Nervous System
- sĭm-pă-THĔT-ĭk NĔR-vŭs SIS-tĕm
- Responsible for fight or flight responses
- tinea
- TIN-ē-ă (Original Term)
- A group of fungal skin diseases, charachterized by itching, scaling, and sometimes painful lesions.
- vascularized
- VAS-kyŭ-lă-rīzd
- Has numerous blood vessels
- verruca
- vĕr-ROO-kă
- Also known as a wart. An epidermal growth caused by a virus.
- virus
- VĪ-rŭs (Original Term)
- minute microorganism that may cuase infection by invading body tissue
Activity Source: Integumentary Medical Terms from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al., licensed under CC BY 4.0. /Re-recording of some H5P audio by Tania Deane and David McCuaig and text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Commonly Abbreviated Integumentary System Terms
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated integumentary system terms:
- BCC (basal cell carcinoma)
- bx (biopsy)
- CA-MRSA (community-associated MRSA)
- derm (dermatology)
- HA-MRSA (healthcare-associated MRSA)
- I&D (incision and drainage)
- ID (intradermal)
- MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
- SCC (squamous cell carcinoma)
- SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus)
- staph (staphylococcus)
- strep (streptococcus)
- subcut, Sub-Q (subcutaneous)
- TD (transdermal)
Sorting Terms
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories:
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Layers of the Skin
Practice labeling the layers of the skin:
Layers of the Skin (Text Version)
- Hair Root
- Hair Follicle
- Eccrine Sweat Gland
- Hair shaft
- Adipose tissue
- Hypodermis
- Hair follicle
- dermis
- epidermis
- arrector pili muscle
- pore of sweat gland
- sensory nerve fiber
- sebaceous/oil gland
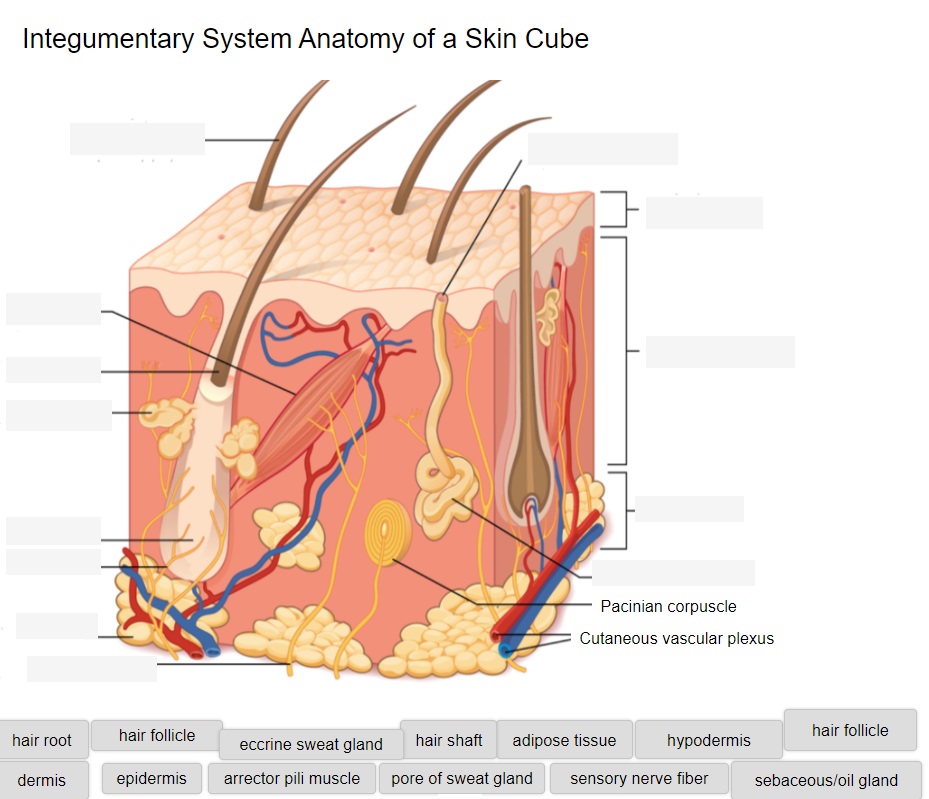
Layers of the Skin Diagram (Text Version)
This illustration shows a cross section of skin tissue. The outermost layer is called the _______[Blank 1] and occupies one fifth of the cross section. Several hairs are emerging from the surface. The epidermis dives around one of the hairs, forming a ________[Blank 2]. The ________[Blank 3] is located above the hair follicle. Surrounding the base of the hair follicle is the ________[Blank 4] which lubricates the _________ [Blank 5]. Extending the surface of the skin is the ___________[Blank 6]. The middle layer is called the _________[Blank 7], which occupies four fifths of the cross section. The dermis contains an __________[Blank 8] that causes contraction of the hair follicle making the hair stand on end such as when someone experiences goosebumps. The dermis also contains an __________[Blank 9], composed of a bunch of tubules. One tubule travels up from the bunch, through the epidermis, opening onto the surface a __________[Blank 10]. There are two string-like nerves travelling vertically through the dermis. The right nerve is attached to a Pacinian corpuscle, which is a yellow structure consisting of concentric ovals like an onion. The lowest level of the skin, the _________[Blank 11], contains __________[Blank 12], arteries, and veins. Blood vessels travel from the hypodermis and connect to hair follicles and erector pili muscle in the dermis. ____________[Blank 13] located in the hypodermis supports the interpretation of touch.
Check your answers: [1]
Activity source: Layers of the Skin by Kimberlee Carter from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation, illustration from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax), licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Consultation Report (Text Version)
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
Fill in the consultation report with using the following words:
- Excisional
- Lesion
- Asymmetrical
- Mole
- Benign
- Biopsy
- Irregular
PATIENT NAME: Rosemary COOMBS
AGE: 54
Sex: Female
DOB: December 2
DATE OF CONSULTATION: May 29
REQUESTING PHYSICIAN: Trevor Sharpe, MD, Family Medicine
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Donna Brown, MD, Dermatology
HISTORY: This 54-year-old white female, went to her family doctor a year ago when she noticed a dark brown spot on her neck. The spot was a six cm, dark brown, flat ______[Blank 1] with smooth borders that appeared _____[Blank 2] . Ms. Coombs recently went to Dr. Sharpe for a physical and the _____[Blank 3] was examined, it was suggested that Ms. Coombs see me.
PAST HISTORY: No known history of any skin disorders.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Normal except for the lesion on her chest which has grown to 1.3 cm in diameter and ______[Blank 4] in shape. It is mainly dark brown, with regions of darker black. The borders are ______[Blank 5] in outline. There is some blackened areas that are slightly elevated.
PLAN: I have booked a follow up appointment for next week to do an _____[Blank 6] biopsy. I will then send the specimen for a _____[Blank 7]. Another follow up appointment will be made once I receive the results of the biopsy.
____________________________
Donna Brown, MD, Dermatology
Note: Report samples (H5P and Pressbooks) are to encourage learners to identify correct medical terminology and do not represent the Association for Health Documentation Integrity (AHDI) formatting standards.
Check your answers: [2]
Activity source: Integumentary system – consultation report by Heather Scudder, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Fill in the Blanks
Practice filling in the blanks with the correct word parts.
Medical Terminology (Text version)
Fill in the spaces below with the following terms:
- Xero
- o
- hidr
- rhytid
- ous
- genic
- logist
- o
- ectomy
- derma
- cutane
- itis
- ous
- o
- al
- necr
- o
- o
- plasty
- sis
- phagia
- tone
- trans
- sub
- cutane
- dermat
- derma
- kerat
- aden
- auto
- derm
- per
- onych
- dermat
____[Blank 1a] / ____ [Blank 2a]/ ____[Blank 3a] / ____[Blank 4a] refers to the surgical repair of one’s own skin.
Something that generates the production of epidermal tissues might be called ____[Blank 2a] / ____[Blank 2b] /____[Blank 2b].
____[Blank 3a] / ____[Blank 3b] / ____[Blank 3c] refers to something in state of death.
____[Blank 4a] /____[Blank 4b] /____[Blank 4c] is a technical name for finger-biting.
____[Blank 5a] / ____[Blank 5b] / ____[Blank 5c] means pertaining to through the skin.
____[Blank 6a] / ____[Blank 6b] / ____[Blank 6c] injection is given under the skin.
During the winter months many people complain of ____[Blank 7a] / ____[Blank 7b] and use extra lotion.
A patch filled with medication, applied to the skin so that medication goes through the skin is referred to as a ____[Blank 8a] / ____[Blank 8b] / ____[Blank 8c] patch.
An instrument use to cut the skin for biopsy is referred to as a ____[Blank 9a] / ____[Blank 9b].
A specialist who studies and treats disorders and diseases of the skin is referred to as a ____[Blank 10a] / ____[Blank 10b] / ____[Blank 10b]/
The medical term that means a sweat gland is inflamed is ____[Blank 11a] / ____[Blank 11b] / ____[Blank 11c].
The medical term to excise wrinkles or commonly referred to as a facelift is ____[Blank 12a] / ____[Blank 12b].
Check your answers: [3]
Activity source: Integumentary Medical Terms by Jesslyn Wilkinson, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Test Your Knowledge
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below:
Integumentary System Glossary Reinforcement Activity (Text version)
- Cells that manufacture and store the protein keratin are called ______[Blank 1].
- Scar
- Vascularized
- Keratinocytes
- The outer layer of skin, made of closely packed epithelial cells are called____[Blank 2].
- Fascia
- Adipocytes
- Epidermis
- Specialized cells that produce melanin which is a dark pigment responsible for the colouration of skin and hair are called____[Blank 3].
- Necrosis
- Melanocytes
- Keloid
- Deepest layer of the epidermal is the _____[Blank 4].
- Dermis
- Fascia
- Stratum Basale
- Production of cells that can mobilize and establish tumors in other organs of the body are called _____[Blank 5].
- Pathogens
- Debridement
- Metastasize
Check your answers: [4]
Activity source: Integumentary System Glossary Reinforcement Activity by Gisele Tuzon and Kimberlee Carter, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Downloadable Worksheets
View or download & print the PDF or Word format worksheets below
Worksheet – Integumentary System – Chapter 3 [Word]
3. Integumentary – Scenario [Word]
3. Integumentary – Abbreviations [Word]
3. Integumentary – Definitions Using Word Parts [Word]
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this book is adapted from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al. (2022), Nicolet College, CC BY 4.0 International. / A derivative of Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Carter & Rutherford (2020), and Anatomy and Physiology by Betts, et al., CC BY 4.0, which can be accessed for free at OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology.
-
↵
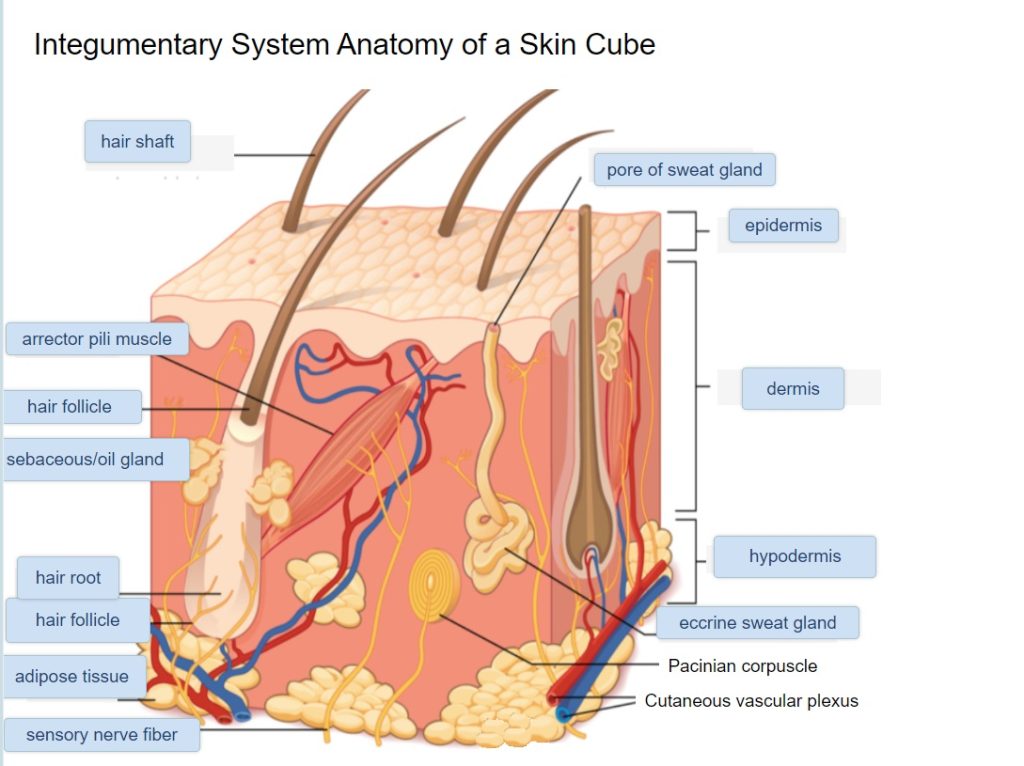
Check your answers: Layers of the Skin Diagram (Text Version)
This illustration shows a cross section of skin tissue. The outermost layer is called the epidermis and occupies one fifth of the cross section. Several hairs are emerging from the surface. The epidermis dives around one of the hairs, forming a hair follicle. The hair root is located above the hair follicle. Surrounding the base of the hair follicle is the sebaceous/oil gland which lubricates the hair follicle. Extending the surface of the skin is the hair shaft. The middle layer is called the dermis, which occupies four fifths of the cross section. The dermis contains an arrector pili muscle that causes contraction of the hair follicle making the hair stand on end such as when someone experiences goosebumps. The dermis also contains an eccrine sweat gland, composed of a bunch of tubules. One tubule travels up from the bunch, through the epidermis, opening onto the surface a pore of sweat gland. There are two string-like nerves travelling vertically through the dermis. The right nerve is attached to a Pacinian corpuscle, which is a yellow structure consisting of concentric ovals like an onion. The lowest level of the skin, the hypodermis, contains adipose tissue, arteries, and veins. Blood vessels travel from the hypodermis and connect to hair follicles and erector pili muscle in the dermis. Sensory nerve fibers located in the hypodermis supports the interpretation of touch. - 1. Mole, 2. Benign, 3. Lesion, 4. Asymmetrical, 5. Irregular, 6. Excisional, 7. Biopsy ↵
- 1. Dermat /o /auto /plasty. 2. Kerat /o /genic. 3. Necr /o /sis. 4. Onych /o /phagia. 5. Per /cutane /ous. 6. Sub /cutane /ous. 7. Xero /derma. 8. Trans /derm /al. 9. Derma /tone. 10. Dermat /o /logist. 11. Hidr /aden /itis. 12. Rhytid /ectomy. ↵
- 1. Keratinocytes, 2. Epidermis, 3. Melanocytes, 4. Stratum Basale, 5. Metastasize ↵

