Cardiovascular System – Heart
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the heart
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the heart
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of heart terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the heart and explore common diseases, disorders, and diagnostic tests and procedures
Key Word Components
Identify meanings of key word components of the cardiovascular system – heart:
Prefixes
- a- (absence of, without)
- bi- (two)
- brady- (slow)
- dys- (bad, abnormal, painful, difficult)
- endo- (within, in)
- epi- (on, upon, over)
- hypo- (below, deficient)
- hyper- (above, excessive)
- inter- (between)
- pan- (all, total)
- peri- (surrounding, around)
- poly- (excessive, over, many)
- tachy- (fast, rapid)
- tri- (three)
Combining Forms
- angi/o (vessel)
- ather/o (yellowish, fatty plaque)
- arteri/o (artery)
- atri/o (atrium)
- cardi/o/ (heart)
- coron/o (crown or circle, heart)
- ech/o (sound)
- electr/o (electricity)
- isch/o (deficiency, blockage)
- my/o (muscle)
- myos/o (muscle)
- symptomat/o (symptom)
- thromb/o (clot)
- valv/o (valve)
- valvul/o (valve)
- vas/o (vessel)
- ven/o (vein)
- ventricul/o (ventricle)
Suffixes
- -ac (pertaining to)
- -ade (process of)
- -al (pertaining to)
- -apheresis (removal)
- -ar (pertaining to)
- -centesis (surgical puncture to aspirate fluid)
- -dynia (pain)
- -ectomy (excision, surgical removal)
- -emia (condition of blood)
- -genic (producing, originating, causing)
- -gia (pain)
- -gram (record, radiographic image)
- -graph (instrument used to record)
- -graphy (process of recording, radiographic imaging)
- -ia (condition of, diseased state, abnormal state)
- -ic (pertaining to)
- -ion (process)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -lysis (loosening, dissolution, separating)
- -megaly (enlarged, enlargement)
- -logist (specialist, physician who studies and treats)
- -oma (tumor)
- -osis (abnormal condition)
- -ous (pertaining to)
- -pathy (disease)
- -penia (abnormal reduction in number)
- -pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
- -plasty (surgical repair)
- -poiesis (formation)
- -sclerosis (hardening)
- -scope (instrument used to view)
- -scopy (process of viewing)
- -stasis (stop, stopping, controlling)
- -stenosis (narrowing, constriction)
- -tomy (cut into, incision)
Cardiovascular System – Heart Words
Cardiovascular System – Heart Medical Terms (Text Version)
Practice the following cardiovascular system – heart medical terms by breaking into word parts and pronouncing.
- endocarditis
- end/o/card/itis
- Inflammation of the inner (lining) of the heart
- echocardiogram
- ech/o/cardi/o/gram
- a record (using) sound of the heart
- bradycardia
- brady/card/ia
- condition of slow heart (rate)
- electrocardiograph
- electr/o/cardi/o/graph
- instrument used to record the electrical (activity) of the heart
- tachycardia
- tachy/card/ia
- condition of fast/rapid heart (rate)
- pericardiocentesis
- peri/cardi/o/centesis
- Surgical puncture to aspirate fluid from the (sac) surrounding the heart
- electrocardiogram
- electr/o/cardi/o/gram
- a record of electrical (activity) of the heart
- electrocardiography
- electr/o/cardi/o/graphy
- process of recording the electrical (activity) of the heart
- valvulitis
- valvul/itis
- inflammation of a valve
- pericarditis
- peri/card/itis
- inflammation of the (sac) surrounding the heart
- asymptomatic
- a/symptomat/ic
- pertaining to without symptoms
- myocarditis
- my/o/card/itis
- inflammation of the muscle of the heart
- cardiomegaly
- cardi/o/megaly
- enlarged heart
- atherosclerosis
- ather/o/scler/osis
- abnormal condition of plaque (build up) causing constriction
- valvuloplasty
- valvul/o/plasty
- surgical repair of a valve
- Cardiologist
- Cardi/o/logist
- A physician who studies and treats diseases of the heart
- cardiac
- cardi/ac
- pertaining to the heart
- cardiology
- cardi/o/logy
- study of the heart
- atrioventricular
- atri/o/ventricul/ar
- pertaining to the atrium and ventricle
- cardiogenic
- cardi/o/genic
- originating in the heart
- cardiomyopathy
- cardi/o/my/o/pathy
- disease of the heart muscle
Activity source: Cardiovascular System – Heart Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Cardiovascular System – Heart Medical Terms
Cardiovascular System – Heart Terms Not Easily Broken Down (Text Version)
Practice the following cardiovascular system words by breaking into word parts and pronouncing.
- arrhythmia
- deviation in the normal pattern (rhythmn) of a heartbeat
- congenital
- present at birth
- stethoscope
- An instrument used to hear heart and lung sounds
- aneurysm
- localized dilation of the wall of a blood vessel
- diastole
- Phase in the cardiac cycle where heart muscles relax allowing the chambers to fill with blood.
- bruit
- abnormal blowing, swishing heart sound heard on auscultation
- syncope
- brief lapse in consciousness (faint)
- auscultation
- listening to a patient’s heart sounds
- occlude
- block or close tightly
- sphygmomanometer
- instrument used to measure blood pressure
- diaphoresis
- profuse (excessive) sweating
- myocardial infarction (MI)
- heart attack, caused by lack of blood flow and oxygen to the heart
- systole
- Phase in cardiac cycle when ventricles contract and eject blood
Activity source: Cardiovascular System – Heart not easily broken down by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Commonly Abbreviated Cardiovascular System – Heart Terms
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated cardiovascular system – heart terms:
- ACS (acute coronary syndrome)
- AED (automated external defibrillator)
- AFib (atrial fibrillation)
- AI (aortic insufficiency)
- AS (aortic stenosis)
- ASD (atrial septal defect)
- ASHD (arteriosclerotic heart disease)
- AV (atrioventricular)
- BP (blood pressure)
- BPM (beats per minute)
- CABG (coronary artery bypass graft
- CAD (coronary artery disease)
- CCU (coronary care unit, cardiac care unit)
- CHD (coronary heart disease; chronic heart disease)
- CHF (congestive heart failure)
- CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation)
- DVT (deep vein thrombosis)
- ECG, EKG (electrocardiogram)
- ECHO (echocardiogram)
- HF (Heart Failure)
- HHD (hypertensive heart disease)
- HTN (hypertension)
- HR (heart rate)
- ICD (implantable cardioverter defibrillator)
- IV (intravenous)
- MI (Myocardial Infarction)
- PAD (peripheral artery disease)
- PTCA (percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty)
- SPECT (single-photon emission computed tomography)
- TEE (transesophageal echocardiogram)
- VSD (ventricular septal defect)
Sorting Terms
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories:
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Cardiovascular System – Heart Structures
Label the following heart anatomy in the diagram below:
Cardiovascular System: The Heart Anatomy (Text Version)
Label the diagram with correct words listed below:
- Aortic valve
- Mitral (bicuspid) valve
- Aorta
- Pulmonary trunk
- Tricuspid valve
- Interventricular septum
- Inferior vena cava
- Left pulmonary artery
- Right atrium
- Left pulmonary veins
- Left atrium
- Right ventricle
- Right pulmonary veins
- Right pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary valve
- left ventricle
- Superior vena cava
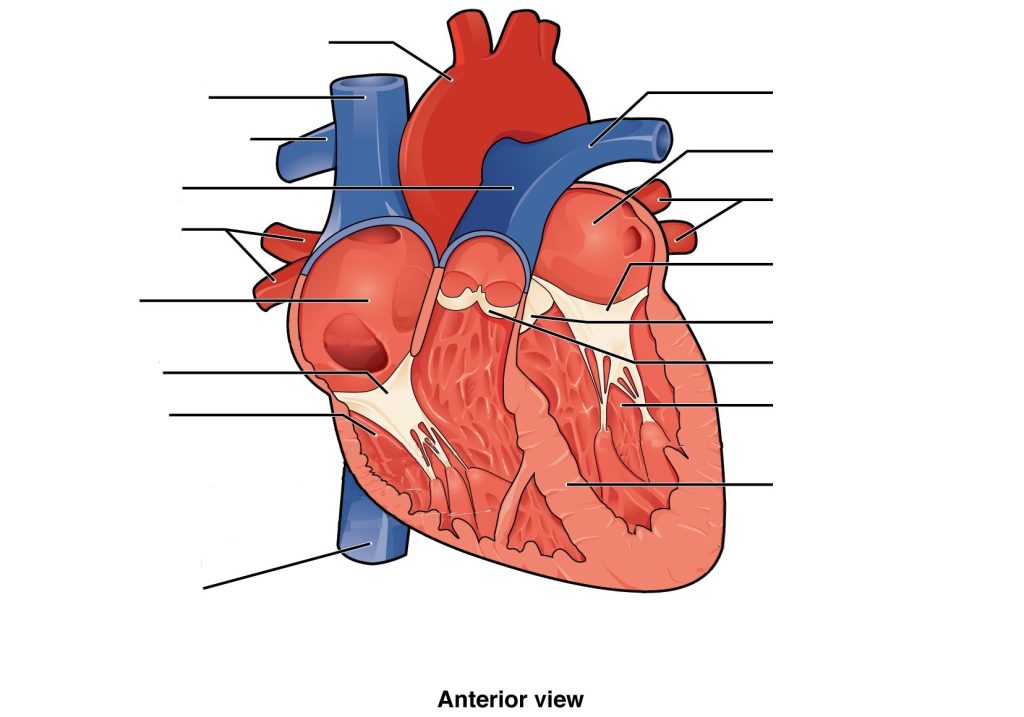
Cardiovascular System: The Heart Anatomy Diagram (Text Version)
This diagram shows the heart with an anterior view. The view shows from (from top, clockwise): the largest artery in the body known as the _______[Blank 1]. The _______[Blank 2] is shown which is the only vein in the body to carry oxygenated blood. The heart is divided into four chambers the_______[Blank 3] is one of the four chambers of the heart it is in the upper left portion of the heart. The _______[Blank 4] also know as the bicuspid valve contains to cusps or flaps and is positioned between the left atrium and lower left ventricle. The _______[Blank 5] is a structure located between the aorta and ______[Blank 6] of the heart which is the left lower chamber of the heart. The ________[Blank 7] is a thick wall of tissue divided the right side of the heart from the left. The _______[Blank 8] lies between the right atrium and pulmonary artery. The ______[Blank 9] is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood to the heart. The ______[Blank 10] is the lower right chamber of the heart. The ________[Blank 11] lies between the right ventricle and the _______[Blank 12] which is the upper right chamber of the heart. The ________[Blank 13] transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The __________[Blank 14] is part of the _________[Blank 15] and transfers deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The _______[Blank 16] a large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart.
Check your answers: [1]
Activity source: Cardiovascular System: The Heart Anatomy by Gisele Tuzon, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation, illustration from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax), licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Cardiovascular System – Consultation Report (Text version)
Fill in the consultation report with the words listed below:
- shortness
- ECG
- implant
- embolism
- BP
- venous
- CBC and Diff
- hypercholesterolemia
- cardiovascular
- hypertension,
- WBC
- bradycardia
- intravenous
PATIENT NAME: Lorna GILBERT
AGE: 52
SEX: Female
DOB: February 27
DATE OF CONSULTATION: June 12
REQUESTING PHYSICIAN: Trevor Sharpe, MD, Family Medicine
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Kevin Palmer, MD, Cardiology
HISTORY: This 52-year-old female was referred to our cardiology clinic by her family physician Dr. Trevor Sharpe. She had visited her physician last month with complaints of persistent fatigue, dizziness, light-headedness, fainting, and an inability to exercise without experiencing ________[Blank 1] of breath. She claims that she is otherwise healthy; however, there is a history of ___________[Blank 2] diseases in her family. Her father had developed DVT during a long flight and subsequently suffered from pulmonary ___________[Blank 3]. Her mother had idiopathic intracranial _________[Blank 4] and died from MI at a relatively young age. The patient has 3 siblings, 2 of them suffering from hypertension and ______________[Blank 5].
LABORATORY DATA: The laboratory results show normal ____________[Blank 6]. Hemoglobin, Hct, __________[Blank 7] count, and platelet count are within normal range. The patient’s PT and partial thromboplastin time are normal.
ALLERGIES: She is not allergic to any medications.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Today the patient is alert and oriented but feels completely exhausted. She is also complaining of a mild chest pain. Her ________[Blank 8]- is 180/110. Heart rate is in the high 50s with irregular rate and rhythm. NECK: is supple, without jugular ___________[Blank 9] distention or bruits. LUNGS: are clear, without wheezing, rhonchi, or rales.
IMPRESSION: I suspect the patient suffers from _________[Blank 10] and needs a pacemaker to regulate her heart rhythms. However, given the significant history of cardiovascular disorders in her family, I will order more tests before making a definite diagnosis.
PLAN: I will admit the patient to a telemetry bed and monitor her for 48 hours. If her chest pain worsens, she will be moved to CCU and will be treated with ____________[Blank 11] nitroglycerin. An __________[Blank 12] has also been ordered to confirm bradycardia. If the ECG results confirm my speculations, the patient will be scheduled for a pacemaker __________[Blank 13] as soon as possible.
_____________________________________
Kevin Palmer, MD, Cardiology
Check your answers: [2]
Activity source: Cardiovascular System – Consultation Report by Seedah Akram & Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Test Your Knowledge
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below:
Cardiovascular System – Heart Glossary Reinforcement Activity (Text version)
- ____[Blank 1] is the ability of the blood vessels to dilate and constrict as needed.
- Compliance
- LDL
- Syncope
- A disorder in which too many red blood cells are produced is called ______[Blank 2].
- Mitral valve
- Polycythemia
- Great vessels
- ____[Blank 3] is difficult breathing.
- Dyspnea
- Pacemaker
- Roots of the Great Vessels
- A condition in which cells receive insufficient amounts of blood and oxygen is called ______[Blank 4].
- Diaphoresis
- Ischemic
- Serous
- Using extreme heat or extreme cold to destroy cells in part of the heart which were causing abnormal rhythms is called _____[Blank 5].
- Congenital
- Ablation
- Cyanosis
Check your Answers: [3]
Activity source: Cardiovascular System – Heart Glossary Reinforcement Activity by Gisele Tuzon, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Downloadable Worksheets
View or download & print the PDF or Word format worksheet below:
Worksheet – Cardiovascular System – Chapter 9-10 [Word]
9. Cardiovascular – Heart – Definitions [Word]
9. Cardiovascular – Heart – Words Not Easily Broken [Word]
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this book is adapted from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al. (2022), Nicolet College, CC BY 4.0 International. / A derivative of Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Carter & Rutherford (2020), and Anatomy and Physiology by Betts, et al., CC BY 4.0, which can be accessed for free at OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology.
-
↵
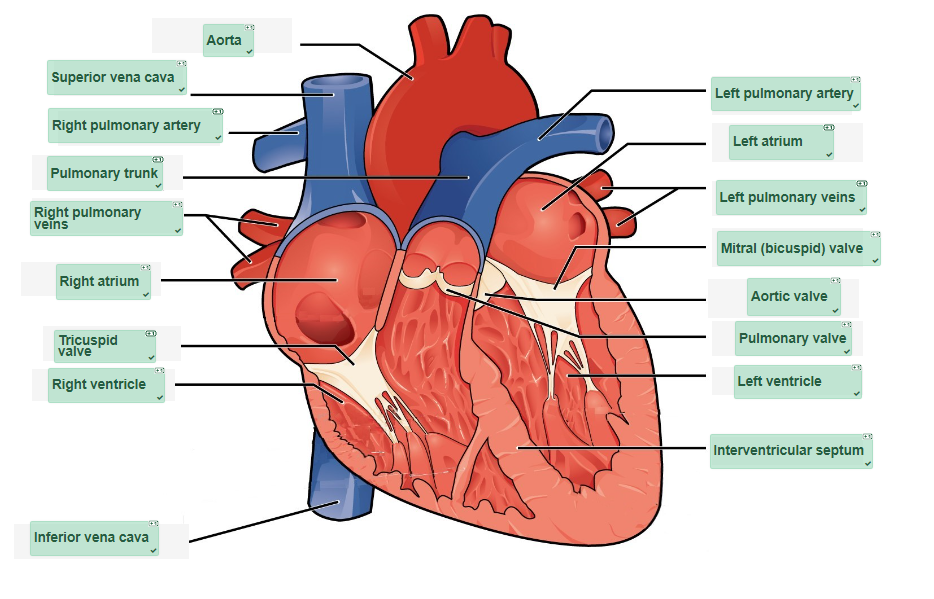
Check your answers: Cardiovascular System: The Heart Anatomy Diagram (Text Version)
This diagram shows the heart with an anterior view. The view shows from (from top, clockwise): the largest artery in the body known as the aorta. The left pulmonary vein is shown which is the only vein in the body to carry oxygenated blood. The heart is divided into four chambers the left atrium is one of the four chambers of the heart it is in the upper left portion of the heart. The mitral valve also know as the bicuspid valve contains to cusps or flaps and is positioned between the left atrium and lower left ventricle. The aortic valve is a structure located between the aorta and left ventricle of the heart which is the left lower chamber of the heart. The interventricular septum is a thick wall of tissue divided the right side of the heart from the left. The pulmonary valve lies between the right atrium and pulmonary artery. The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood to the heart. The right ventricle is the lower right chamber of the heart. The tricuspid valve lies between the right ventricle and the right atrium which is the upper right chamber of the heart. The right pulmonary veins transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The pulmonary trunk is part of the right pulmonary artery and transfers deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The superior vena cava a large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. - 1. shortness 2. cardiovascular 3. embolism 4. hypertension 5. hypercholesterolemia 6. CBC and Diff 7. WBC 8. BP 9. venous 10. bradycardia 11. intravenous 12. ECG 13. implant ↵
- 1. Compliance, 2. Polycythemia, 3. Dyspnea, 4. Ischemic, 5. Ablation ↵

