4.1 – Introduction to the Respiratory System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the respiratory system
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the respiratory system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of respiratory system terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the respiratory system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic testing and procedures related to the respiratory system
Respiratory System Word Parts
Click on prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes to reveal a list of word parts to memorize for the respiratory system
Respiratory System Medical Terms (Text Version)
Prefix
- a- (absence of, without)
- an- (absence of, without)
- dys– (difficult, painful, abnormal, laboured)
- endo– (Gr. within, in )
- eu- (normal, good)
- hyper– (above, excessive)
- hypo– (below, deficient, under)
- intra– (L. within, in)
- poly– (many, much)
- tachy– (fast, rapid)
Combining Form
- adenoid/o (adenoids)
- alveol/o (alveolus)
- atel/o (imperfect, incomplete)
- bronch/o (bronchus)
- bronchi/o (bronchus)
- capn/o (carbon dioxide)
- diaphragmat/o (diaphragm)
- epiglott/o (epiglottis)
- hem/o (blood)
- hemat/o (blood)
- laryng/o (larynx)
- lob/o (lobe)
- muc/o (mucus)
- nas/o (nose)
- orth/o (straight)
- ox/i (oxygen)
- pharyng/o (pharynx)
- phon/o (sound, voice)
- phren/o (diaphragm)
- pleur/o (pleura)
- pneum/o (lung, air)
- pneumon/o (lung, air)
- penumat/o (lung)
- pulmon/o (lung)
- py/o (pus)
- radi/o (x-rays, ionizing radiation)
- respir/o (breath, breathing)
- rhin/o (nose)
- sept/o (septum)
- sinus/o (sinus)
- somn/o (sleep)
- son/o (sound)
- spir/o (breathe, breathing)
- thorac/o (thorax, chest cavity, thoracic cavity)
- tom/o (to cut, section, slice)
- tonsill/o (tonsil)
- trache/o (trachea)
Suffix
- –algia (pain)
- –ar (pertaining to)
- –ary (pertaining to)
- –cele (hernia, protrusion)
- –centesis (surgical puncture to aspirate fluid)
- –eal (pertaining to)
- –ectasis (stretching out, dilation, expansion)
- –emia (in the blood)
- –gram (the record, radiographic image)
- –graph (instrument used to record)
- –graphy (process of recording, radiographic imaging)
- –meter (instrument used to measure)
- –metry (measurement)
- –pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
- –pnea (breathing)
- –rrhagia (rapid flow of blood, excessive bleeding)
- –scope (instrument used for visual examination)
- –scopic (pertaining to visual examination)
- –scopy (process of visually examining, visual examination)
- –spasm (sudden involuntary muscle contraction, spasmodic contraction)
- –stenosis (constriction, narrowing)
- –stomy (creation of an artificial opening)
- –thorax (chest, chest cavity, thoracic cavity)
- –tomy (cut into, incision)
- –itis (inflammation)
- –ectomy (excision, cut out)
- –tome (instrument used to cut)
- –genic (producing, originating, causing)
- –ic (pertaining to)
- –ia (condition, diseased state, abnormal state)
- –plasty (surgical repair)
- –oid (resembling)
- –logy (study of)
- –logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
Activity source: Respiratory System Word Parts by Kimberlee Carter, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Introduction to the Respiratory System
How long you can hold your breath as you continue reading? How long can you do it? Chances are you are feeling uncomfortable already. A typical human cannot survive without breathing for more than three minutes, and even if you wanted to hold your breath longer, your autonomic nervous system would take control. Although oxygen is critical for cells, it is the accumulation of carbon dioxide that primarily drives your need to breathe.
Did You Know?
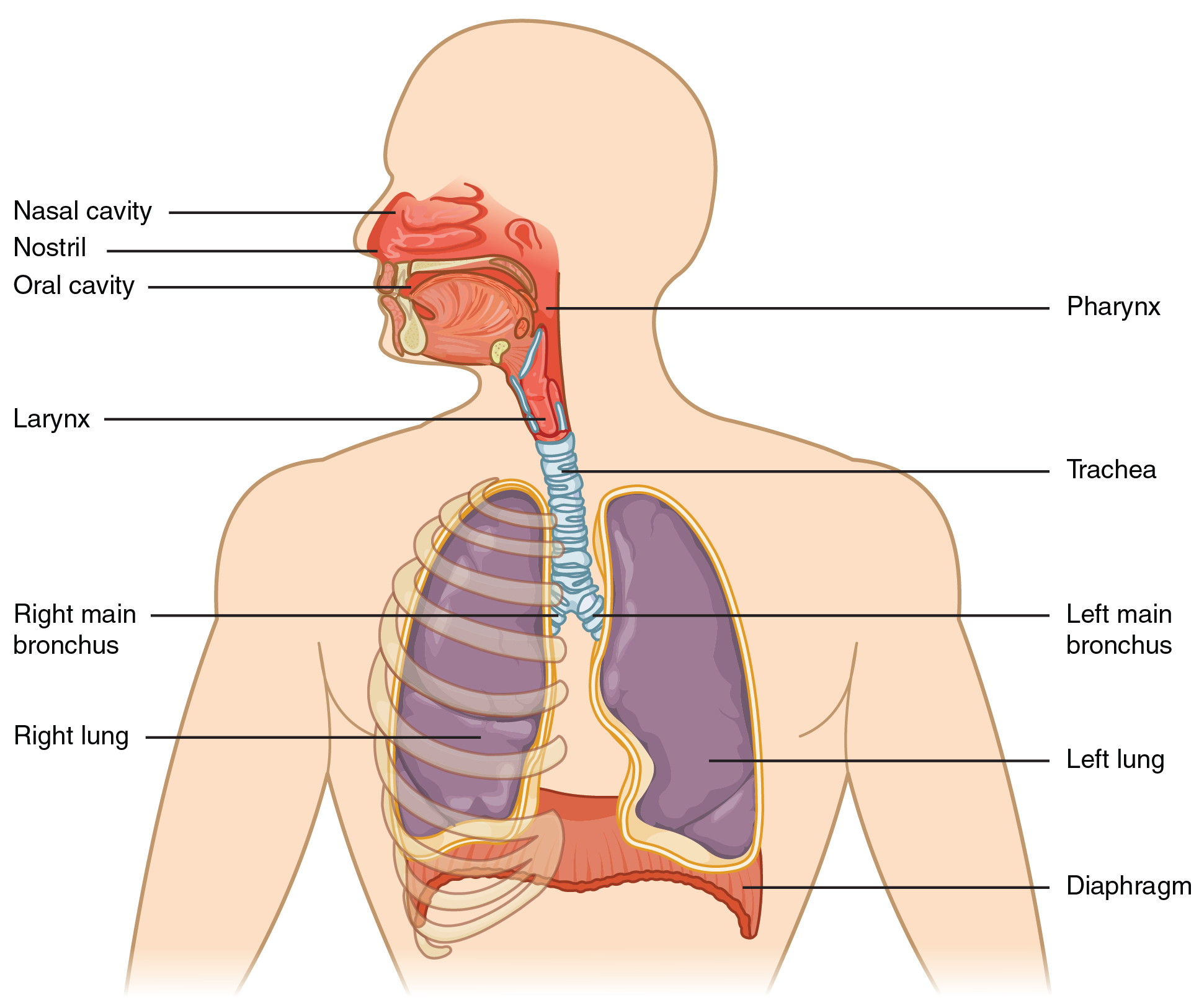
The major structures of the respiratory system function primarily provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help to maintain acid-base balance. Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, speech production, and for straining, such as coughing.
Watch Respiratory system, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #31 (10 min on YouTube)
Media 4.1: CrashCourse. (2015, August 31). Respiratory system, part 1: Crash Course anatomy & physiology #31. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/bHZsvBdUC2I
Respiratory System Medical Terms
Respiratory System Medical Terms (Text version)
- Adenoiditis
- adenoid/itis
- inflammation of the adenoids
- adenoidectomy
- adenoid/ectomy
- excision of the adenoids
- adenotome
- aden/o/tome
- instrument used to cut the adenoids
- alveolitis
- alveol/itis
- inflammation of the alveoli
- alveolar
- alveol/ar
- pertaining to the alveolus
- atelectasis
- atel/ectasis
- incomplete expansion
- bronchitis
- bronch/itis
- inflammation of the bronchus
- bronchogenic carcinoma
- bronch/o/genic carcin/oma
- cancerous tumour originating in a bronchus
(lung cancer)
- bronchopneumonia
- bronch/o/pneumon/ia
- diseased state of bronchi and lungs
- bronchoplasty
- bronch/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the bronchi
- bronchoscope
- bronch/o/scope
- instrument used for visual examination of the bronchi
- bronchoscopy
- bronch/o/scopy
- visual examination of the bronchi
- bronchoalveolar
- bronch/o/alveol/ar
- pertaining to the bronchi and alveoli
- bronchospasm
- bronch/o/spasm
- spasmodic contraction of the bronchi
- bronchiectasis
- bronchi/ectasis
- dilation of the bronchi
- capnometer
- capn/o/meter
- instrument used to measure carbon dioxide
- acapnia
- a/capn/ia
- condition of absence (less than normal level) of carbon dioxide (in the blood)
- hypercapnia
- hyper/capn/ia
- condition of excessive (greater than normal levels) carbon dioxide (in the blood)
- hypocapnia
- hypo/capn/ia
- condition of deficient (low levels) of carbon dioxide (in the blood)
- diaphragmatocele
- diaphragmat/o/cele
- hernia of the diaphragm
- diaphragmatic
- diaphragmat/ic
- pertaining to the diaphragm
- epiglottitis
- epiglott/itis
- inflammation of the epiglottis
- hemothorax
- hem/o/thorax
- blood in the thoracic cavity
- hematology
- hemat/o/logy
- study of blood
- hematologist
- hemat/o/logist
- specialist in blood and blood disorders
- laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB)
- laryng/o/trache/o/bronch/itis
- inflammation of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi
- laryngoplasty
- laryng/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the larynx
- laryngostomy
- laryng/o/stomy
- creation of an artificial opening into the larynx
- laryngotracheotomy
- laryng/o/trache/o/tomy
- incision into the larynx and trachea
- laryngoscope
- laryng/o/scope
- instrument used for visual examination of the larynx
- laryngoscopy
- laryng/o/scopy
- process of viewing the larynx
- laryngeal
- laryng/eal
- pertaining to the larynx
- laryngospasm
- laryng/o/spasm
- spasmodic contraction of the larynx
- laryngitis
- laryng/itis
- inflammation of the larynx
- lobar pneumonia
- lob/ar pneumon/ia
- disease state of the lung pertaining to the lobe(s)
- lobectomy
- lob/ectomy
- excision of the lobe(s)
- mucoid
- muc/oid
- resembling mucus
- mucous
- muc/ous
- pertaining to mucus
- nasopharyngitis
- nas/o/pharyng/itis
- inflammation of the nose and pharynx
- nasopharyngeal
- nas/o/pharyng/eal
- pertaining to the nose and pharynx
- orthopnea
- orth/o/pnea
- breathing is easier in a straight position
- anoxia
- an/ox/ia
- condition of absence (deficiency) of oxygen
- oximeter
- oxi/meter
- instrument used to measure oxygen
- hypoxemia
- hyp/ox/emia
- condition of deficient oxygen in the blood
- hypoxia
- hyp/ox/ia
- condition of deficient oxygen
- pharyngitis
- pharyng/itis
- inflammation of the pharynx
- aphonia
- a/phon/ia
- condition of absence of voice
- dysphonia
- dys/phon/ia
- condition of difficult speaking (voice)
- phrenalgia
- phren/algia
- pain in the diaphragm
- phrenospasm
- phren/o/spasm
- spasm of the diaphragm
- pleuritic
- pleurit/ic
- pertaining to the pleura
- pleuritis
- pleur/itis
- inflammation of the pleura
- pleuropexy
- pleur/o/pexy
- surgical fixation of the pleura
- interpleural
- inter/pleur/al
- pertaining to between the pleura (space between the pleural membranes)
- pneumoconiosis
- pneum/o/coni/osis
- abnormal condition of dust in the lungs
- pneumonia
- pneumon/ia
- diseased state of lung
- pneumonitis
- pneumon/itis
- inflammation of the lung
- pneumothorax
- pneum/o/thorax
- air in the thoracic cavity
- pneumonectomy
- pneumon/ectomy
- excision of the lung
- pneumatocele
- pneumat/o/cele
- hernia of the lung
- pulmonary
- pulmon/ary
- pertaining to the lung(s)
- pyothorax
- py/o/thorax
- pus in the thoracic cavity
- radiography
- radi/o/graphy
- process of recording x-rays
- radiologist
- radi/o/logist
- physician who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of disease using medical imaging
- radiology
- radi/o/logy
- study of the use of radiant energy in diagnosing disease
- respirologist
- respir/o/logist
- specialist who studies and treats disease and disorders related to breathing
- respirology
- respir/o/logy
- the study of breathing disorders and disease
- rhinitis
- rhin/itis
- inflammation of the nose
- rhinomycosis
- rhin/o/myc/osis
- abnormal condition of fungus in the nose
- rhinorrhagia
- rhin/o/rrhagia
- rapid flow of blood from the nose
- rhinoplasty
- rhin/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the nose
- rhinorrhea
- rhin/o/rrhea
- discharge from the nose
- septoplasty
- sept/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the septum
- septotomy
- sept/o/tomy
- incision into the (nasal) septum
- sinusitis
- sinus/itis
- inflammation of a sinus
- polysomnography (PSG)
- poly/somn/o/graphy
- process of recording many (test) during sleep
- sonogram
- son/o/gram
- the record of sound
- sonography
- son/o/graphy
- process of recording sound
- spirometer
- spir/o/meter
- instrument used to measure breathing (lung volume)
- spirometry
- spir/o/metry
- measuring breathing (air flow)
- thoracalgia
- thorac/algia
- pain in the chest, thorax
- thoracocentesis
- thorac/o/centesis
- surgical puncture to aspirate fluid (from the thoracic cavity)
- thoracentesis
- thora/centesis
- surgical puncture to aspirate fluid from thoracic cavity
- thoracotomy
- thorac/o/tomy
- incision into the thoracic cavity
- thoracoscopy
- thorac/o/scopy
- visual examination of the thoracic cavity
- thoracic
- thorac/ic
- pertaining to the chest, thorax
- thoracoscope
- thorac/o/scope
- instrument used to visualize the thoracic cavity
- tomography
- tom/o/graphy
- process of recording slices
- tonsillitis
- tonsill/itis
- inflammation of the tonsils
- tonsillectomy
- tonsill/ectomy
- excision of the tonsils
- tracheitis
- trache/itis
- inflammation of the trachea
- tracheoplasty
- trache/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the trachea
- tracheostomy
- trache/o/stomy
- creation of an artificial opening into the trachea
- tracheotomy
- trache/o/tomy
- incision into the trachea
- endotracheal
- endo/trach/eal
- pertaining to within the trachea
- tracheostenosis
- trache/o/stenosis
- narrowing of the trachea
- endoscope
- endo/scope
- instrument used to view within
(a hollow organ or cavity)
- endoscopic
- endo/scopic
- pertaining to view within
(a hollow organ or cavity)
- endoscopy
- endo/scopy
- visual examination within
(a hollow organ or cavity)
- apnea
- a/pnea
- absence of breathing
- dyspnea
- dys/pnea
- breathing that is difficult
- eupnea
- eu/pnea
- normal breathing
- hypopnea
- hypo/pnea
- deficient breathing
- tachypnea
- tachy/pnea
- rapid breathing
Activity Source: Respiratory System Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Image Descriptions
Figure 4.1 image description: This figure shows the upper half of the human body. The major organs in the respiratory system are labeled. [Return to Figure 4.1].
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this chapter is adapted from “Respiratory System” in Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford licensed under CC BY 4.0. / A derivative of Betts et al., which can be accessed for free from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax). Adaptations: dividing Respiratory System chapter content into sub-chapters.
unconsciously regulates

