14.3 – Physiology (Function) of the Muscular System
The main function of the muscular system is to assist with movement. Muscles work as antagonistic pairs. As one muscle contracts, the other muscle relaxes. This contraction pulls on the bones and assists with movement. Contraction is the shortening of the muscle fibers while relaxation lengthens the fibers. This sequence of relaxation and contraction is influenced by the nervous system.
Muscles also work to keep the posture of the body. This is done through muscle contraction, where the trunk is kept straight either when sitting or standing.
Naming of Muscles
Did You Know?
The tongue is made up of many muscles and muscles work in pairs.
There are many nomenclatures for naming muscles. Some of these include:
- divisions: biceps, triceps, quadriceps
- size: maximus (largest), minimus (smallest)
- shape: deltoid (triangular), trapezious (trapezoid)
- action: flexor (to flex), adductor (towards the midline of the body)
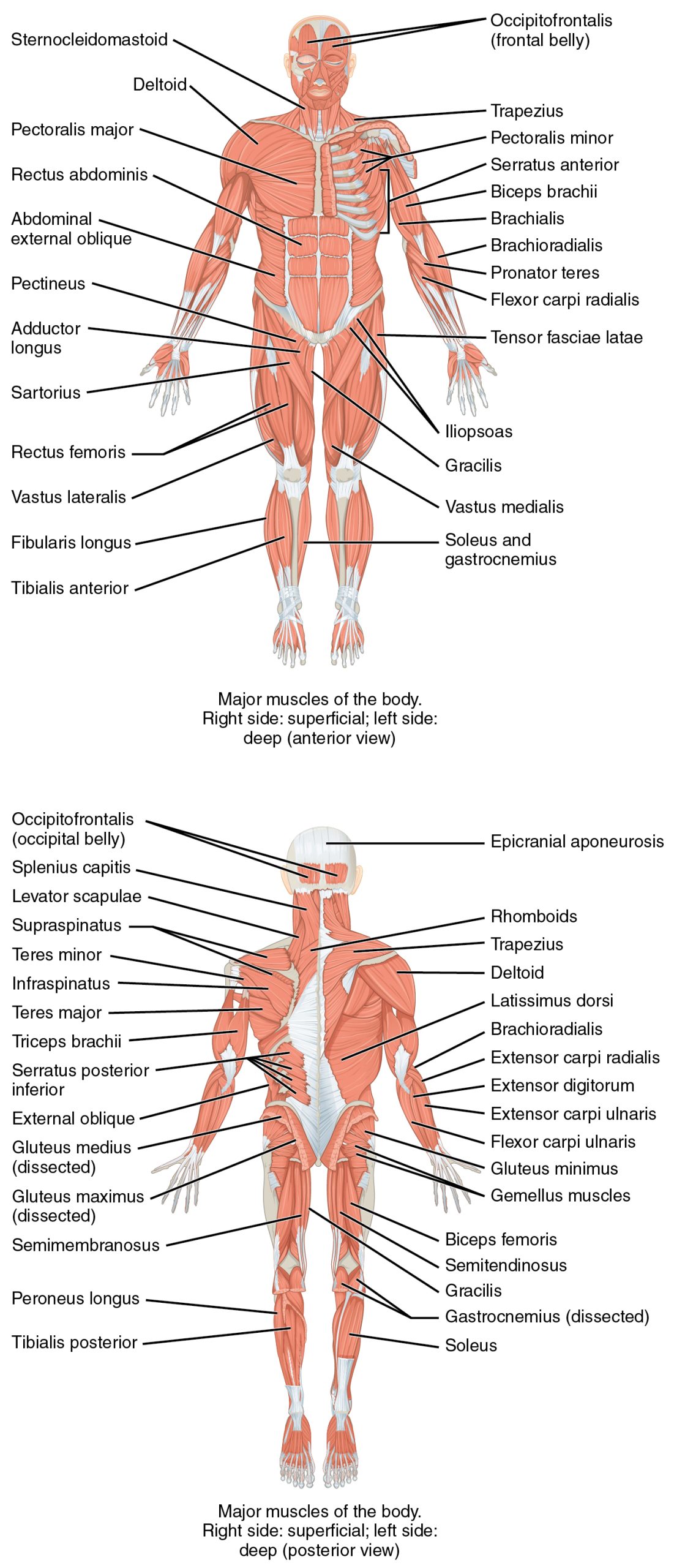
Table 14.1a-b. Understanding a Muscle Name from the Latin. Adapted from Betts et al., 2013. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
| Word | Latin Root 1 | Latin Root 2 | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| abductor | ab = away from | duct = to move | a muscle that moves away from |
| digiti | digitus = digit | n/a | refers to a finger or toe |
| minimi | minimus = mini, tiny | n/a | little |
| Word | Latin Root 1 | Latin Root 2 |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| adductor | ad = to, toward | duct = to move | a muscle that moves towards |
| digiti | digitus = digit | n/a | refers to a finger or toe |
| minimi | minimus = mini, tiny | n/a | little |
Muscular System Medical Abbreviations
Muscular System Abbreviations
- DC (Doctor of Chiropractic)
- DO (Doctor of Osteopathy)
- EMG (Electromyogram)
- MD (Muscular Dystrophy)
- MG (myasthenia gravis)
- Ortho (orthopedics)
Activity source: Muscular System Abbreviations by Kimberlee Carter and Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Converted to text.
Image Descriptions
Figure 14.2 image description: The top panel shows the anterior view of the human body with the major muscles labeled. Labels read (from top, head): occipitofrontalis (frontal belly), sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, deltoid, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, pectoralis major, arm muscles: biceps brachii, brachialis, brachioradialis, pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, abdomnial: rectus abdominis, abdominal external oblique, lower body: tensor fasciae latae, illiopsoas, pectineus, adductor longus, sartorius, gracilis, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vasus medialis, fibularis longus, tibialis anterior. The bottom panel shows the posterior view of the human body with the major muscles labeled. Labels read (from top, head, left side): epicranial aponeurosis, occipitofrontalis, splenius capitis, levator scapulae, rhombus, trapezius, supraspinatus, teras minor, infraspinatus, teres major, triceps brachii, seratus posterior inferior, external oblique, lower body: gluteus medius, gluteus maximus, semimebranosus, peroneus longus, tibialis posterior, (right side, from top) trapezius, deltpid, latissimus dorsi, arm: brachioradialis, extersor carpi radialis, extensor digitorum, extensor carpi ulnaris, flexor carpi ulnaris, lower body: gluteus minimus, gemellus muscles, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, gracilis, gastrocnemius, soleus. [Return to Figure 14.2].
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this chapter is adapted from “Muscular System” in Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / A derivative of Betts et al., which can be accessed for free from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax). Adaptations: dividing Muscular System chapter content into sub-chapters.
in opposition to each other
naming conventions

