12.1 – Introduction to the Digestive System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the digestive system and accessory structures
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the digestive system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of digestive system medical terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the digestive system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic tests and procedures
Digestive System Word Parts
Click on prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes to reveal a list of word parts to memorize for the digestive system.
Prefix
- hemi– (half)
- endo– (within, in)
- sub– (under, below)
- dys– (painful, abnormal, difficult, laboured)
Combining Form
- abdomin/o (abdomen, abdominal)
- an/o (anus)
- antr/o (antrum)
- append/o (appendix)
- appendic/o (appendix)
- cec/o (cecum)
- celi/o (abdomen, abdominal cavity)
- cheil/o (lip)
- cholangi/o (bile duct)
- chol/e (gall, bile)
- choledoch/o (common bile duct)
- col/o (colon)
- colon/o (colon)
- diverticul/o (diverticulum)
- duoden/o (duodenum)
- enter/o (intestine)
- esophag/o (esophagus)
- gastr/o (stomach)
- gingiv/o (gum)
- gloss/o (tongue)
- hepat/o (liver)
- herni/o (hernia, protrusion of an organ through a membrane or cavity wall)
- ile/o (ileum)
- jejun/o (jejunum)
- lapar/o (abdomen, abdominal cavity)
- lingu/o (tongue)
- or/o (mouth)
- palat/o (palate)
- pancreat/o (pancreas)
- peritone/o (peritoneum)
- polyp/o (polyp, small growth)
- proct/o (rectum)
- pylor/o (pylorus, pyloric sphincter)
- rect/o (rectum)
- sial/o (saliva, salivary gland)
- sigmoid/o (sigmoid colon)
- steat/o (fat)
- stomat/o (mouth)
- uvul/o (uvula)
Suffix
- -al (pertaining to)
- -cele (hernia, protrusion)
- -centesis (surgical puncture to aspirate fluid)
- -ectomy (excision)
- -gram (the record, radiographic image)
- -graph (instrument used to record)
- -graphy (process of recording)
- -ia (condition of, diseased state, abnormal state)
- -iasis (condition)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
- -logy (study of)
- -malacia (softening)
- -oma (tumour)
- -sis (abnormal condition)
- -pathy (disease)
- -pepsia (digestion)
- -phagia (eating or swallowing)
- -plasty (surgical repair)
- -ptosis (prolapse, drooping)
- -rrhaphy (suturing, repairing)
- -rrhea (flow, discharge)
- -scope (instrument used for visualization)
- -scopy (process of viewing, visualization)
- -stomy (creation of an artificial opening)
- -tomy (incision, cut into)
Activity source: Digestive System Word Parts by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Introduction to the Digestive System
The digestive system is continually at work, yet people seldom appreciate the complex tasks it performs in a choreographed biologic symphony. Consider what happens when you eat an apple. Of course, you enjoy the apple’s taste as you chew it, but in the hours that follow, unless something goes amiss and you get a stomachache, you don’t notice that your digestive system is working. You may be taking a walk or studying or sleeping, having forgotten all about the apple, but your stomach and intestines are busy digesting it and absorbing its vitamins and other nutrients. By the time any waste material is excreted, the body has appropriated all it can use from the apple. In short, whether you pay attention or not, the organs of the digestive system perform their specific functions, allowing you to use the food you eat to keep you going.
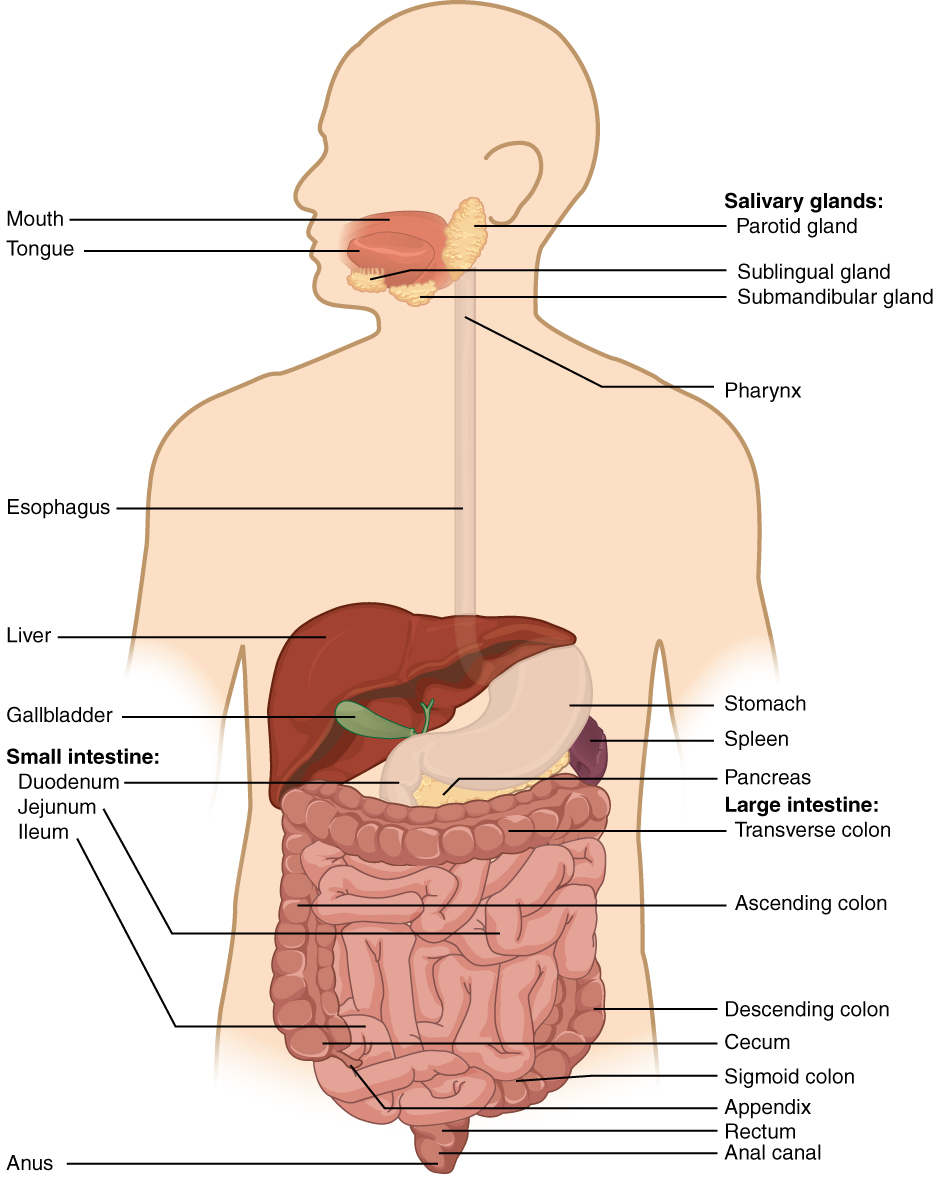
This chapter examines the structure and functions of these organs, and explores the mechanics and chemistry of the digestive processes. The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although the small intestine is the workhorse of the system, where the majority of digestion occurs, and where most of the released nutrients are absorbed into the blood or lymph, each of the digestive system organs makes a vital contribution to this process (see Figure 12.1).
Watch Digestive System, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #33 (11 min)
Media 12.1: CrashCourse. (2015, September 7). Digestive system, part 1: Crash Course anatomy & physiology #33 [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/yIoTRGfcMqM
Digestive System Medical Terms
Now that you have memorized the word parts, see if you can break down the following digestive terms and define them.
Digestive System Medical Terms (Text Version)
Practice the following digestive system words by breaking into word parts and pronouncing.
- gastroenterology (gastr/o/enter/o/logy)
- study of the stomach and intestines
- cholecystitis (chol/e/cyst/itis)
- inflammation of the gallbladder
- proctoscope (proct/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the rectum
- pyloroplasty (pylor/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the pylorus
- hepatomegaly (hepat/o/megaly)
- enlarged liver
- gastric (gastr/ic)
- pertaining to the stomach
- cholangiography (cholangi/o/graphy)
- radiographic imaging of the bile duct
- gastroenterologist (gastr/o/enter/o/logist)
- specialist who studies and treats stomach and intestines
- cholangiogram (cholangi/o/gram)
- radiographic image of the bile duct
- hepatoma (hepat/oma)
- tumour of the liver
- pancreatitis (pancreat/itis)
- inflammation of the pancreas
- esophagogram (esophag/o/gram)
- radiographic image of the esophagus
- steatosis (steat/osis)
- abnormal condition of fat
- rectocele (rect/o/cele)
- protrusion of the rectum
- endoscope (endo/scope )
- instrument used to view within (hollow organs)
- abdominal (abdomin/al)
- pertaining to the abdomen
- proctoptosis (proct/o/ptosis)
- condition of prolapse of the rectum
- diverticulitis (diverticul/itis)
- inflammation of the diverticulum
- oral (or/al)
- pertaining to the mouth
- appendectomy (append/ectomy)
- excision of the appendix
- esophagoscopy (esophag/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the esophagus
- cheilorrhaphy (cheil/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of the lip
- glossorrhaphy (gloss/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of the tongue
- pyloromyotomy (pylor/o/my/o/tomy)
- incision into the pyloric muscle
- gastroplasty (gastr/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the stomach
- colectomy (col/ectomy)
- excision of the colon
- sigmoidoscopy (sigmoid/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the sigmoid colon
- palatitis (palat/itis)
- inflammation of the palate
- esophageal (esophag/eal)
- pertaining to the esophagus
- colitis (col/itis)
- inflammation of the colon
- ileocecal (ile/o/cec/al)
- pertaining to the ileum and cecum
- gastrectomy (gastr/ectomy)
- excision of the stomach
- anoplasty (an/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the anus
- cholelithiasis (chole/lith/iasis)
- condition of gallstones
- gastroscopy (gastr/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the stomach
- colostomy(col/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening in the colon
- polyposis (polyp/osis)
- abnormal condition of (multiple) polyps
- laparoscopy (lapar/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the abdominal cavity
- cholecystectomy (chole/cyst/ectomy)
- excision of the gallbladder to remove stones
- glossitis (gloss/itis)
- inflammation of the tongue
- cholangioma (cholangi/oma)
- tumour of the bile duct
- pancreatic (pancreat/ic)
- pertaining to the pancreas
- stomatitis (stomat/itis)
- inflammation of the mouth
- ileocecal (ile/o/cec/al)
- pertaining to the ileum and cecum
- nasogastric (nas/o/gastr/ic)
- pertaining to the nose and stomach
- proctoscopy (proct/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the rectum
- herniorrhaphy (herni/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of a hernia
- appendicitis (appendic/itis)
- inflammation of the appendix
- gingivectomy (gingiv/ectomy)
- excision of the gums
- gastroenterocolitis (gastr/o/enter/o/col/itis)
- inflammation of the stomach, intestines, and colon
- choledocholithotomy (choledoch/o/lith/o/tomy)
- incision into the common bile duct to remove stones
- gastroscope (gastr/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the stomach
- diverticulosis (diverticul/osis)
- abnormal condition of having diverticula
- uvulitis (uvul/itis)
- inflammation of the uvula
- dysphagia (dys/phagia)
- difficult swallowing
- gastrostomy (gastr/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening in the stomach
- hemicolectomy (hemi/col/ectomy)
- excision of half of the colon
- choledocholithiasis (choledoch/o/lith/iasis)
- condition of stones in the common bile duct
- uvulectomy (uvul/ectomy)
- excision of the uvula
- peritoneal (periton/eal)
- pertaining to the peritoneum
- ileostomy (ile/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening in the ileum
- steatorrhea (steat/o/rrhea)
- discharge of fat
- sialolith (sial/o/lith)
- stone in the salivary gland
- proctology (proct/o/logy)
- study of disease and disorders of the rectum
- gastrojejunostomy (gastr/o/jejun/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening between the stomach and the jejunum
- rectal (rect/al)
- pertaining to the rectum
- gingivitis (gingiv/itis)
- inflammation of the gums
- colonoscopy (colon/o/scopy)
- process of viewing the colon
- colorectal (col/o/rect/al)
- pertaining to the colon and rectum
- anal (an/al)
- pertaining to the anus
- duodenal (duoden/al)
- pertaining to the duodenum
- abdominocentesis (abdomin/o/centesis)
- surgical puncture to aspirate fluid from the abdomen
- hepatitis (hepat/itis)
- inflammation of the liver
- laparoscope (lapar/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the abdominal cavity
- antrectomy (antr/ectomy)
- excision of the antrum (of the stomach)
- enterorrhaphy (enter/o/rrhaphy)
- suturing of the intestine
- esophagitis (esophag/itis)
- inflammation of the esophagus
- uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
- uvul/o/palat/o/pharyng/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the uvula, palate, and pharynx
- peritonitis (periton/itis)
- inflammation of the peritoneum
- diverticulectomy (diverticul/ectomy)
- excision of the diverticula
- enteropathy (enter/o/pathy)
- disease of the intestines
- proctologist (proct/o/logist)
- Specialist who studies and treats diseases of the rectum
- gastritis (gastr/itis)
- inflammation of the stomach
- abdominoplasty (abdomin/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the abdomen
- celiotomy (celi/o/tomy)
- incision into the abdominal cavity
- gastroenteritis (gastr/o/enter/itis)
- inflammation of the stomach and intestines
- endoscopy (endo/scopy)
- process of viewing within (hollow organs)
- palatoplasty (palat/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the palate
- laparotomy (lapar/o/tomy)
- incision into the abdominal cavity
- colonoscope (colon/o/scope)
- instrument used to view the colon
- polypectomy (polyp/ectomy)
- excision of polyps
- gastrojejunostomy (gastr/o/jejun/o/stomy)
- creation of an artificial opening between the stomach and the jejunum
- CT colonography (CT colon/o/graphy)
- radiographic imaging of the colon using computed tomography
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- esophag/o/gastr/o/duoden/o/scopy
- process of viewing the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
- stomatogastric (stomat/o/gastr/ic)
- pertaining to the mouth and stomach
- celiac (celi/ac)
- pertaining to the abdomen
- gastromalacia (gastr/o/malacia)
- softening of the stomach
- dyspepsia (dys/pepsia)
- difficult digestion
- esophagogastroplasty (esophag/o/gastr/o/plasty)
- surgical repair of the esophagus and stomach
- sublingual (sub/lingu/al)
- pertaining to under the tongue
- steatohepatitis (steat/o/hepat/itis)
- inflammation of liver associated with fat
Activity source: Digestive System Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Digestive System
Practice with this activity:
Digestive System(Text version)
Fill in the blanks using the following list of words:
- polyp
- palpate
- obesity
- hemorrhoids
- emesis
- melena
- flatus
- ascites
- feces
- reflux
- nausea
- cirrhosis
- dysentery
- adhesion
- stoma
The Physician during an examination will ________[Blank 1] to feel for texture, size, consistency and location of body parts with hands.
A _______[Blank 2] is a small tumour-like growth that extend from the surface of a mucous membrane.
___________[Blank 3] is an abnormal increase in the proportion of fat cells resulting in excess body weight for height.
Distended and swollen veins in the rectum and anus are called ___________[Blank 4].
The medical term for vomiting is ____________[Blank 5].
__________[Blank 6] is black tarry stool that contains blood from the gastrointestinal tract.
_________[Blank 7] is the medical term for gas in the gastrointestinal tract.
Abnormal intraperitoneal accumulation of fluid with large amount of proteins and electrolytes is _________[Blank 8].
____________ is fecal matter.
Abnormal backward flow is called ____________[Blank 10].
The urge to vomit is __________[Blank 11].
__________[Blank 12] is a chronic degenerative disease of the liver due to alcohol abuse.
___________[Blank 13] is an inflammation of the intestine presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea.
A band of scar tissue that binds anatomic surfaces to each other is called an ___________[Blank 14].
The surgical opening between an organ and the surface of the body is called a ___________[Blank 15].
Check your answers: [1]
Activity source: Digestive System by Alyssa Arsenault, licensed under CC BY- 4.0 from “Digestive System” in Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Converted to Text.
Image Descriptions
Figure 12.1 image description: This diagram shows the digestive system of a human being, with the major organs labeled. Labels read (clockwise, from top): salivary glands: parotid gland, sublingual gland, submandibular gland; pharynx, stomach, spleen, pancreas, large intestine: transverse colon, ascending colon, descending colon, cecum, sigmoid colon, appendix, rectum, anal canal, anus; small intestine: duodenum, jejunum, ileum, gall bladder, liver, esophagus, tongue, mouth. [Return to Figure 12.1].
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this chapter is adapted from “Digestive System” in Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / A derivative of Betts et al., which can be accessed for free from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax). Adaptations: dividing Digestive System chapter content into sub-chapters.
- 1. palpate, 2. polyp, 3. obesity, 4. hemorrhoids, 5. emesis, 6. melena, 7. flatus, 8.ascites, 9. feces, 10. reflux, 11. nausea, 12. cirrhosis, 13. dysentery, 14. adhesion, 15. stoma ↵

