8.1 – Introduction to Obstetrics
Learning Objectives
- Identify the common processes in obstetrics and explore procedures, diagnostics tests and common complications related to obstetrics
- Describe the specialty of obstetrics and other medical specialties associated with obstetrics
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of obstetrics
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of obstetric terminology
Obstetric Word Parts
Review the list of word parts to memorize for obstetrics:
Prefix
- ante– (before)
- dys– (painful, laboured, difficult)
- micro– (small)
- multi– (many)
- neo– (new)
- nulli– (none)
- post– (after)
- pre– (before)
Combining Form
- amni/o (amnion, amniotic fluid)
- cephal/o (head)
- chori/o (chorion)
- embry/o (embryo)
- esophag/o (esophagus)
- fet/i (fetus, unborn offspring)
- fet/o (fetus, unborn offspring)
- gravid/o (pregnancy)
- lact/o (milk)
- nat/o (birth)
- omphal/o (umbilicus, navel)
- par/o (to bear, labour, childbirth, give birth to)
- part/o (to bear, labour, childbirth, give birth to)
- prim/i (first)
- pseud/o (false)
- puerper/o (childbirth)
- pylor/o (pylorus, pyloric sphincter)
- terat/o (malformations)
Suffix
- –a (no meaning, noun ending)
- –al (pertaining to)
- –amnios (amnion, amniotic fluid)
- –cyesis (pregnancy)
- –e (noun ending, no meaning)
- –gen (substance that produced, agent that produced)
- –genic (producing, originating, causing)
- –graphy (process of recording)
- –ic (pertaining to)
- –is (noun suffix, no meaning)
- –itis (inflammation)
- –logist (specialist who studies and treats, physician who studies and treats)
- –logy (study of)
- –oid (resembling)
- –oma (tumour)
- –rrhea (discharge, flow)
- –rrhexis (rupture)
- –stenosis (constriction, narrowing)
- –tocia (birth, labour)
- –tomy (incision, cut into)
- –um (noun ending, no meaning)
- –us (noun ending, no meaning)
Activity source: Obstetrics Word Parts by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Text version added.
Introduction to Obstetrics
Obstetrics is a specialty that is concerned with the mother and fetus during pregnancy, childbirth, and the immediate postpartum period. Obstetricians study obstetrics and gynecology and are referred to as OB/GYN (Obstetrics and Gynecology).
Media 8.1: CrashCourse. (2015, November 23). Reproductive system, part 4 – Pregnancy & development: Crash Course anatomy & physiology #43 [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/BtsSbZ85yiQ
Obstetrics Medical Terms
Obstetrics Medical Terms (Text version)
Practice the following words related to obstetrics by breaking into word parts and pronouncing. Audio recordings of word pronunciations are available through the online book.
- amnionitis
- amnion/itis
- *rebel does not follow the rules
- inflammation of the amnion
- oligohydramnios
- olig/o/hydr/amnios
- scanty amnion water
- a condition where there is minimal amniotic fluid within the placental sac. This can restrict the fetus from movement and growth
- polyhydramnios
- poly/hydr/amnios
- much amnion water
- amniotomy
- amni/o/tomy
- incision into the amnion to induce labour
- amniocentesis
- amni/o/centesis
- surgical puncture into the amnion to remove a small amount of fluid for testing. The fluid is tested for potential fetal abnormalities
- amniochorial
- amni/o/chori/al
- pertaining to the amnion and chorion
- amniorrhea
- amni/o/rrhea
- discharge (escape) of amniotic fluid
- amniorrhexis
- amni/o/rrhexis
- rupture of the amnion
- microcephalus
- micr/o/cephal/us
- small head
- chorioamnionitis
- chori/o/amnion/itis
- inflammation of the chorion and amnion
- choriocarcinoma
- chori/o/carcinoma
- cancerous tumour of the chorion
- embryogenic
- embry/o/genic
- producing an embryo
- embryoid
- embry/oid
- resembling an embryo
- transesophageal fistula
- trans/esophag/eal fistula
- abnormal passageway between the trachea and esophagus
- fetal
- fet/al
- pertaining to the fetus
- gravida
- gravid/a
- pregnant (woman)
- Note, that this is referring to a woman who is or has been pregnant regardless of outcome
- multigravida
- multi/gravid/a
- many pregnancies
- A woman who has been pregnant two or more times regardless of outcome
- lactic
- lact/ic
- pertaining to milk
- lactogenic
- lact/o/genic
- producing milk
- lactorrhea
- lact/o/rrhea
- discharge of milk
- natal
- nat/al
- pertaining to birth
- neonate
- neo/nate
- newborn
- (infant from birth to four weeks of age)
- neonatologist
- neo/nat/o/logist
- physician who studies and treats disorders of the newborn
- neonatology
- neo/nat/o/logy
- study of the newborn
- postnatal
- post/nat/al
- pertaining to after birth
- (reference to the newborn)
- prenatal
- pre/nat/al
- pertaining to before birth
- omphalitis
- omphal/itis
- inflammation of the umbilicus
- omphalocele
- omphal/o/cele
- herniation of the umbilicus
- multipara
- multi/par/a
- many births
- nullipara
- nulli/par/a
- no pregnancies
- a woman who has never been pregnant
- para
- par/a
- a woman who has given birth to an offspring after 20 weeks, live or stillborn
- postpartum
- post/part/um
- after childbirth
- referring to the mother
- antepartum
- ante/part/um
- before childbirth
- referencing the mother
- intrapartum
- intra/part/um
- within (during) labour and delivery
- primigravida
- primi/gravid/a
- first pregnancy
- primipara
- primi/par/a
- first birth
- pseudocyesis
- pseud/o/cyesis
- false pregnancy
- puerperal
- puerper/al
- pertaining to immediately after childbirth
- puerpera
- puerper/a
- childbirth
- pyloric stenosis
- pylor/ic stenosis
- narrowing of the pylorus or pyloric sphincter
- teratogen
- terat/o/gen
- agent producing malformations
- (in a developing embryo)such as chemicals, viruses and environmental factors
- teratogenic
- terat/o/genic
- producing malformations
- teratology
- terat/o/logy
- the study of malformations
- dystocia
- dys/tocia
- labour that is difficult
- hysterorrhexis
- hyster/o/rrhexis
- rupture of the uterus
- episiotomy
- episi/o/tomy
- incision into the vulva
- pelvic sonography
- pelv/ic son/o/graphy
- process of recording sound pertaining to the pelvis
- amenorrhea
- a/men/o/rrhea
- absence of menstrual flow
- hyperemesis gravida
- hyper/emesis gravida
- Excessive vomiting during pregnancy
- neonatal
- neo/nat/al
- pertaining to newborn
- nulligravida
- null/i/gravida
- A woman who has never been pregnant
- episiotomy
- episi/o/tomy
- Incision into the vulva to widen the vaginal opening to prevent ripping or tearing of the perineum during delivery
Activity source: Obstetrics Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Text version added.
Fertilization
Fertilization occurs when a sperm and an oocyte (egg) combine. Each of these reproductive cells is a haploid cell containing half of the genetic material needed to form a human being; their combination forms a single diploid cell. This new single cell is called a zygote.
Most of the time, a woman releases a single egg during an ovulation cycle.
- In approximately 1 percent of ovulation cycles, two eggs are released and both are fertilized.
- Two zygotes form, implant, and develop, resulting in the birth of dizygotic (or fraternal) twins. Because dizygotic twins develop from two eggs fertilized by two sperm, they are no more identical than siblings born at different times.
- Less common, one zygote can divide into two separate offspring during early development. This results in the birth of monozygotic (or identical) twins.
A full-term pregnancy lasts approximately 270 days (approximately 38.5 weeks) from conception to birth. Because it is easier to remember the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP) than to estimate the date of conception, obstetricians set the due date as 284 days (approximately 40.5 weeks) from the LMP. This assumes that conception occurred on day 14 of the woman’s cycle, which is usually a good approximation. The 40 weeks of an average pregnancy are usually discussed in terms of three trimesters, each approximately 13 weeks. During the second and third trimesters, the pre-pregnancy uterus is about the size of a fist and grows dramatically to contain the fetus, causing a number of anatomical changes in the mother.
Stages of Childbirth
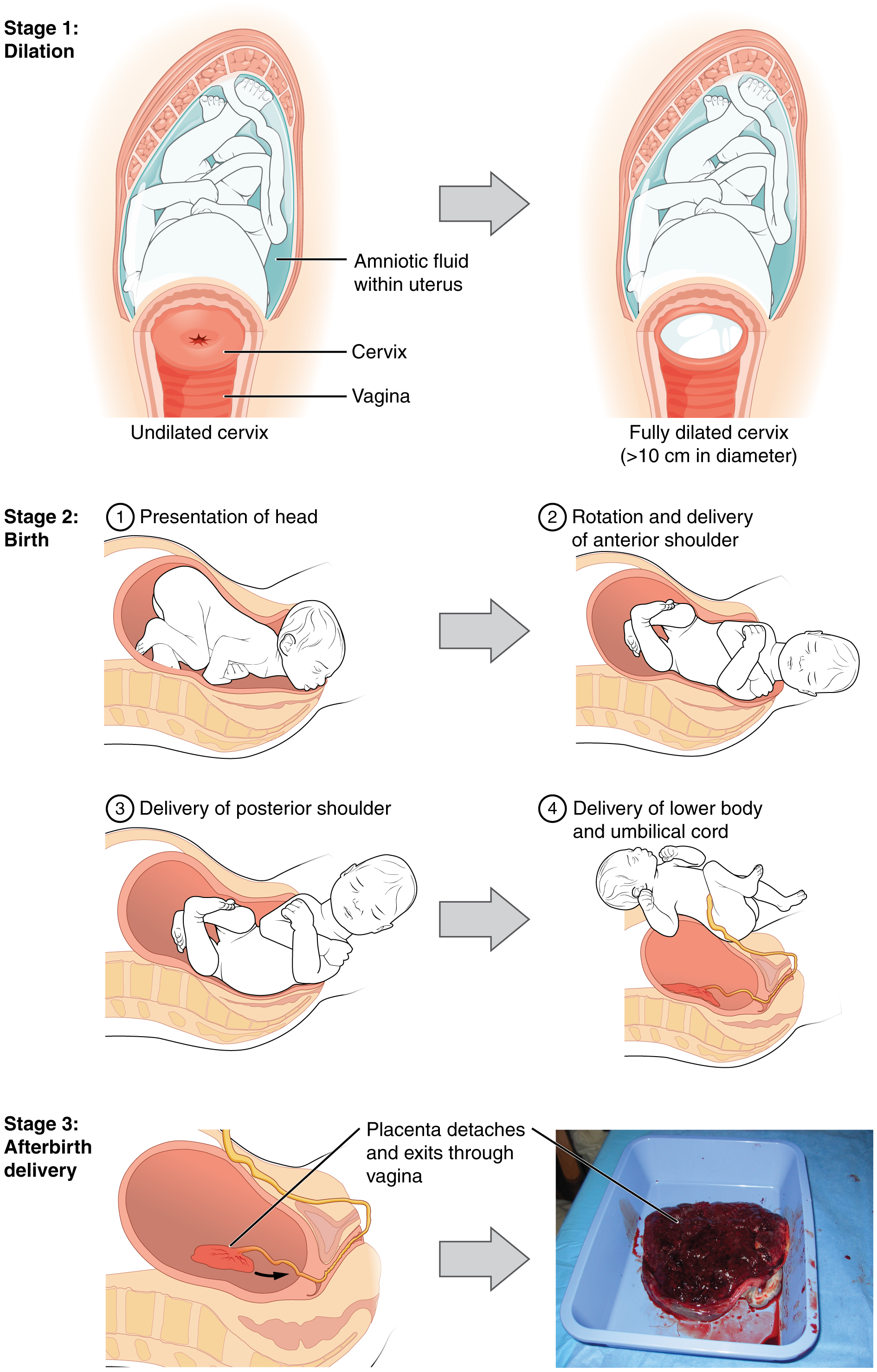
The process of childbirth can be divided into three stages (see Figure 8.1):
- Stage 1: cervical dilation
- Stage 2: expulsion of the newborn
- Stage 3: after birth
For vaginal birth to occur, the cervix must dilate fully to 10 cm in diameter, wide enough to deliver the newborn’s head. The dilation stage is the longest stage of labour and typically takes 6-12 hours. However, it varies widely and may take minutes, hours, or days, depending in part on whether the mother has given birth before. In each subsequent labour, this stage tends to be shorter.
Concept Check
- How is a due date determined?
- Explain the difference between a monozygotic pregnancy and a dizygotic pregnancy.
Homeostasis in the Newborn: Apgar Score
In the minutes following birth, a newborn must undergo dramatic systemic changes to be able to survive outside the womb. An obstetrician, midwife, or nurse can estimate how well a newborn is doing by obtaining an Apgar score. The Apgar score was introduced in 1952 by the anesthesiologist Dr. Virginia Apgar as a method to assess the effects on the newborn of anesthesia given to the labouring mother. Healthcare providers now use it to assess the general well-being of the newborn, whether or not analgesics or anesthetics were used.
The five criteria for the Apgar score (skin colour, heart rate, reflex, muscle tone, and respiration) are assessed and each criterion is assigned a score of 0, 1, or 2. Scores are taken at 1 minute after birth and again at 5 minutes after birth. Each time scores are taken, the five scores are added together. High scores (out of a possible 10) indicate the baby has made the transition from the womb well, whereas lower scores indicate that the baby may be in distress.
The technique for determining an Apgar score is quick and easy, painless for the newborn, and does not require any instruments except for a stethoscope. A convenient way to remember the five scoring criteria is to apply the mnemonic APGAR:
- Appearance (skin colour)
- Pulse (heart rate)
- Grimace (reflex)
- Activity (muscle tone)
- Respiration
Of the five Apgar criteria, heart rate and respiration are the most critical. Poor scores for either of these measurements may indicate the need for immediate medical attention to resuscitate or stabilize the newborn. In general, any score lower than 7 at the 5-minute mark indicates that medical assistance may be needed. A total score below 5 indicates an emergency situation. Normally, a newborn will get an intermediate score of 1 for some of the Apgar criteria and will progress to a 2 by the 5-minute assessment. Scores of 8 or above are normal.
Check Your Knowledge of Obstetrics Medical Terms and Abbreviations
Obstetrics Medical Terms Not Easily Broken into Word Parts
Obstetrics Words Not Easily Broken into Word Parts (Text version)
- abortion (AB) (ă-BOR-shŏn)
- termination of the pregnancy before the fetus is viable
- abruptio placentae (ă-BRŬP-shē-ō plă-SENT-ā)
- pre-mature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall
- Apgar score (AP-gar skōr)
- Evaluation of a newborn’s physical condition within one to five minutes after birth, which was developed by and named for Virginia Apgar (making this an eponym).
- Breech (brēch)
- The position of the fetus is feet first. Ideally, the position of the fetus should be head first.
- Cesarean section (CS, C-section) (si-ZAR-ē-ăn SEK-shŏn)
- Delivery of the fetus through an abdominal incision
- cephalic presentation (sĕ-FAL-ĭk prē-zen-TĀ-shŏn)
- birth position in which any part of the head emerges first
- Cephalic version (sĕ-FAL-ĭk VĔR-zhŏn)
- pertaining to turning the head; this procedure is done on the fetus when they are in the head-down position.
- cerclage (sĕr-KLĂZH)
- Suturing of the cervix to prevent dilation and premature delivery
- colostrum (kŏ-LOS-trŭm)
- thin, milky fluid secreted by the breast during pregnancy and the first few days after delivery
- congenital anomaly (kŏn-JĔN-ĭ-tăl ă-NOM-ă-lē)
- abnormality present at birth
- eclampsia (e-KLAMP-sē-ă)
- a serious condition in pregnancy with hypertension; patients are at risk of coma, convulsions and even death.
- Ectopic pregnancy (ek-TOP-ik PREG-năn-sē)
- Pregnancy occurring outside the uterus, commonly in the fallopian tube.
- Induction (in-DŬK-shŏn)
- The process of bringing on or starting labour. This may be done with a membrane sweep or through the use of IV oxytocin
- in vitro fertilization (IVF) (in VĒ-trō fĕrt-ĭl-ĭ-ZĀ-shŏn)
- method of fertilizing human ova outside the body and placing the zygote in the uterus
- lactation (lak-TĀ-shŏn)
- secretion of milk
- lochia (LŌ-kē-ă)
- vaginal discharge after birth
- meconium (mē-KŌ-nē-ŭm)
- first stool of the newborn
- midwife (MĬD-wīf)
- individual who practices midwifery
- craniocerebral
- practice of assisting in childbirth
- Obstetrician (ob-stĕ-TRISH-ăn)
- Physician who specializes in obstetrics
- Obstetrics (OB) (ŏb-STE-triks)
- medical specialty dealing with pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium
- parturition (păr-tū-RĬSH-ŭn)
- act of giving birth
- placenta previa (plă-SENT-ā PRĒ-vē-ă)
- abnormally low implantation of the placenta on the uterine wall, can result in hemorrhage and a c- section
- preeclampsia (prē-ĕ-KLAMP-sē-ă)
- The abnormal condition in pregnancy where the patient experiences hypertension, edema and proteinuria is called, but with no convulsions. Can progress to eclampsia.
- premature infant (prē-mă-CHŪR IN-fănt)
- infant born before completing 37 weeks of gestation (also called preterm infant)
- puerperium (pū-ĕr-PĒ-rē-ŭm)
- period from delivery until the reproductive organs return to normal (approximately six weeks)
- quickening (KWĬK-ĕn-ĭng)
- first feeling of movement of the fetus in utero by the pregnant woman
- stillborn (STIL-bōrn)
- an infant that is born dead
Activity source: Obstetrics Words Not Built From Word Parts from Medical Terminology. by Grimm et al., licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Some H5P audio re-recorded by Tania Deane and David McCuaig and text version added.
Obstetrics Abbreviations
Review the list of common abbreviates below.
Obstetrics Common Abbreviations
- AB (abortion)
- AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein test)
- AI (artificial insemination)
- CS, C-section (cesarean section)
- CVS (chorionic villus sampling)
- DOB (date of birth)
- EDD (expected or estimated date of delivery)
- FAS (fetal alcohol syndrome)
- IVF (in vitro fertilization)
- LMP (last menstrual period)
- multip (multipara)
- NB (newborn)
- OB (obstetrics)
- primip (primipara)
- RDS (respiratory distress syndrome)
- VBAC (vaginal birth after cesarean section)
- ZIFT (Zygote intrafallopian transfer)
Activity Source: Obstetrics Common Abbreviations by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Text version added.
Obstetrics Pathology Report
Obstetrics- Pathology Report (Text version)
Use the words below to fill in the pathology report:
- salpingectomy
- ectopic
- ultrasound
- fallopian
- tube
- clots
- cassettes
- microscopic
- pregnancy
OBSTETRICS – PATHOLOGY REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Bonnie PERRY
AGE: 34
SEX: Female
DOB: May 3
PATIENT ID: 900132
DATE OF ADMISSION AND SURGERY: June 14
ADMITTING DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic pregnancy
SURGEON: Adam Vance, MD, OB/GYN
PATHOLOGY ID: Specimen No. 05-S-899
SPECIMEN RECEIVED: June 14 Specimen Reported: June 18
SURGICAL PROCEDURE: Right partial _______[Blank 1].
CLINICAL HISTORY: This 34-year-old white female had an __________[Blank 2] pregnancy as
proven by pelvic ________[Blank 3].
TISSUE RECEIVED: Right fallopian tube.
GROSS DESCRIPTION: The specimen designated right _______[Blank 4] tube was examined
reveals the presence of a fallopian tube measuring 5.9 cm in length and 2.3 cm in average diameter. Sectioning of the _________[Blank 5] shows it to be distended with blood __________[Blank 6] and possible field tissue. The sections were taken, and placed in three _________[Blank 7], A through C, for embedding.
MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: __________[Blank 8] examination performed.
MICROSCOPIC DIAGNOSIS: Ruptured tubal ___________[Blank 9].
___________________________________________
Joseph Gibbs, MD, Anatomic & Clinical Pathology
Check your Answers: [1]
Activity source: Obstetrics- Pathology Report by Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. / Text version added.
Image Descriptions
Figure 8.1 image description: This multi-part figure shows the different stages of childbirth. The top panel shows dilation of the cervix (undilated vs fully dilated), the middle panel shows birth (presentation of the head, rotation and delivery of anterior shoulder, delivery of posterior shoulder, delivery of lower body and umbilical cord), and the bottom panel shows afterbirth delivery. [Return to Figure 8.1].
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this chapter is adapted from “Obstetrics” in Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / A derivative of Betts et al., which can be accessed for free from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax). Adaptations: dividing Obstetrics chapter content into sub-chapters.
- 1.salpingectomy, 2.ectopic, 3.ultrasound, 4.fallopian, 5.tube, 6. clots, 7.cassettes, 8. Microscopic, 9.pregnancy ↵
male gamete (spermatozoon)
female gamete
Process of fertilization is complete and results in a single-celled diploid zygote with all the genetic instructions it needs to develop into a human.

