20 Nonlinear Inequations
![]() An inequality for which the side can be written as a product or quotient of linear factors or quadratic factors (that cannot be factored) can be solved through a sign diagram.
An inequality for which the side can be written as a product or quotient of linear factors or quadratic factors (that cannot be factored) can be solved through a sign diagram.
![]() How to solve an inequality ?
How to solve an inequality ?
– determine the points where each factor is 0
– determine the sign of each factor in each interval
– use laws of multiplication or division to determine the sign of the entire quantity.
![]() The set of solution of
The set of solution of ![]() is
is ![]() , since we have
, since we have
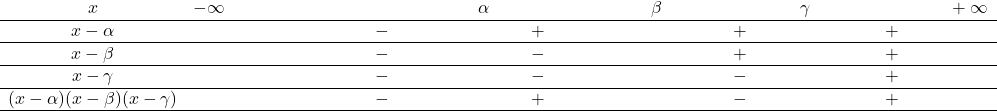
Exercise 1
Show/Hide Solution.
The set of possible solutions is : ![]() .
.
Exercise 2
Show/Hide Solution.
The set of all possible solutions is : ![]() .
.
Exercise 3
Show/Hide Solution.
Note that ![]()
We have
![]()
Now, we have
![]() .
.
Thus, the set of solutions is : ![]() .
.

