1.1: Understanding Technical Communication
Learning Objectives
- Define technical communication
- Examine why technical communication skills are important
- Review a sample of technical communication
What Is Technical Communication?
When you hear the term “technical communication,” what comes to mind? Perhaps you think of scientific reports, specifications, instructions, software documentation, or technical manuals. And you are correct. However, technical communication is so much more than that.
Technical writing is a genre of non-fiction writing that encompasses not only technical materials such as manuals, instructions, specifications, and software documentation, but it also includes writing produced in day-to-day business operations such as correspondence, proposals, internal communications, media releases, and many kinds of reports.
It includes the communication of specialized technical information, whether relating to computers and scientific instruments, or the intricacies of meditation. Since oral and visual presentations are such an important part of professional life, technical communication also encompasses these as well. We might define technical communication, then, as using various modes (oral, written, visual) of communication to manage technical information to analyze a problem, find and evaluate evidence, and draw conclusions in a way that allows people to take action. Thus, technical writing is highly “transactional” as it conveys information to enable specific actions.
Why Are Technical Communication Skills Important?
In a presentation on the topic of Co-op Work Term Reports (McConkey, 2017) the Engineering co-op coordinator for the University of Victoria presented the following statistics regarding the importance of communication skills in the professional world of engineering:
The Reality: Technical Writing and Communication
- How graduate engineers spend their time:
- 25-50% Problem solving of some kind
- 50-75% Communicating (Writing and reading reports, letters, memos, proposals, presentations, discussions w/colleagues, managers, clients)
- Performance evaluations and job advancement usually depend more on communications skills than on technical skills
He added that engineers who are more advanced in their careers spend only 5-10% of their time engaged in problem solving of some kind and 90-95% of their time engaging in related communications tasks: researching, writing and reading reports, proposals, emails, letters, memos; giving or attending presentations; discussing and meeting with colleagues, team mates, managers, clients, and so on.
Technical communication is “transactional”; it entails a purposeful transaction between sender and receiver that provides specific information for practical and specific purposes (informing, instructing, persuading) and is usually geared towards the needs of a specific audience. Technical communicators produce a wide variety of documents and other products:
- Proposals and requests for proposals (RFPs)
- Technical or research reports
- Documentation records and product specifications
- User guides (step-by-step instructions, procedures, manuals)
- Online help, technical support
- Reference information (encyclopedia-style information)
- Consumer literature (information for the public about regulations, safety issues, etc.)
- Marketing literature (product specifications, brochures, promotional literature)
- Technical journalism (found in trade magazines, media releases, etc.)
What Does Technical Writing Look Like?
Technical communications can take many forms, depending on the purpose and intended audience. Consider the following example of technical writing, which is an excerpt adapted from a book called Scientific Sailboat Racing (Wells, 1950, pp. 94-96). From the excerpt in the box below, what can you determine the intended audience?
The most common question asked by skippers wanting to get to the windward mark faster than they have been doing is “How can I make my boat point higher?” Getting to the windward mark first depends primarily on the skill and experience of the skipper; however, having a well-rigged boat will make a significant difference. Look for the following, in order of importance:
- Sails: Have good quality sails, and use the appropriate sails for the wind conditions expected. No one can win races with poor sails, so use the best you can afford. Keep in mind that the leeches of all sails flutter a little, the jib will backwind the luff of the main on any full or medium sail, and in very light wind, even a perfectly cut sail will probably develop a wrinkle along the front of the battens. If the sails are obviously no good, replace them.
- Mast and Centerboard: Ensure that the mast is far enough forward and the centerboard is far enough back so that there is little or no weather helm. Make sure the stiffness of the mast suits the sails.
- Jib Fairleads: Ensure jib fairleads are properly located for the type of jib being used and the strength of wind expected.
- Cleats: Have cleats for both jib and mainsheet; place cleats so that crew can easily make small adjustments for varying wind velocities and hang on the to the jib sheet without having it pop out of the cleat.
- Traveler: Have a mainsheet traveler that allows the main to be pulled down without pulling the boom in too far; it should allow the sail to be pulled down tightly enough so that the leech does not fall off without pulling the boom in any further than it should be.
- Tiller: Have a flexible tiller extension that allows you to sit well forward, but can be adjusted so that it does not get in the way when coming about.
- Boat Weight: Keep the boat as close to minimum weight as possible. Clearly, a lighter boat is easier to handle, but this is not as critical as other factors. If choosing between a lighter crew member with less skill and experience, and a heavier crew member who has greater skill, the latter is usually preferable.
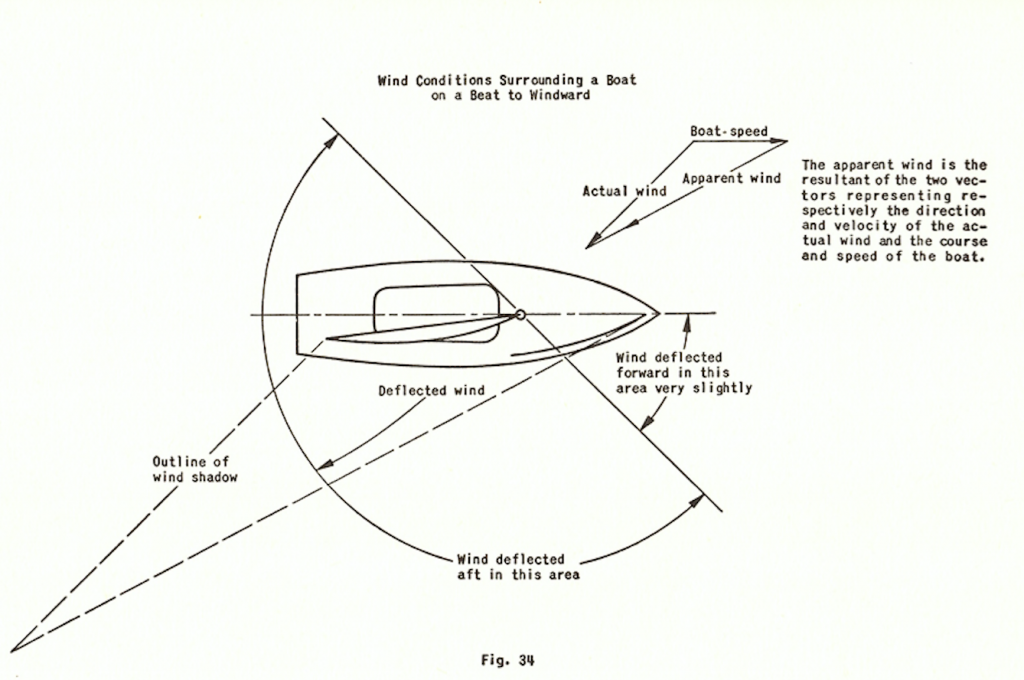
Once the boat is properly set up, a skilled and experienced skipper can point significantly higher than expected by understanding and using wind deflection from other boats. Immediately to leeward of any boat and extending for a distance of about three mast lengths, there is a wind shadow where the wind velocity is greatly decreased. To leeward of the bow of the boat there is a very small region where the direction of the wind is deflected opposite to the normal deflection and where the velocity is accelerated slightly (see Figure 34). Except in the direct wind shadow, the deflection of the wind is more important than the decrease in wind velocity, as the decrease in velocity is very slight except in the immediate shadow of the sails of the windward boat.
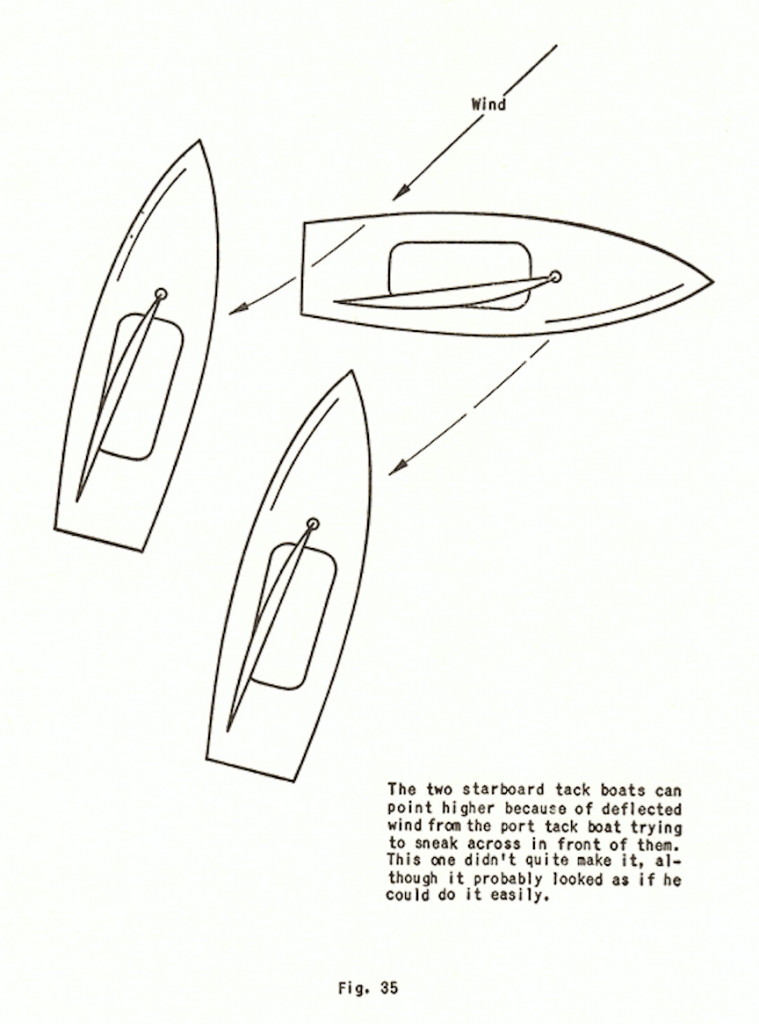
Because of this wind deflection, a boat on the opposite tack cutting behind another boat will be able to point appreciably higher than it normally would. Many skippers on port tacks who thought they could clear starboard tackers have been fooled by not realizing this fact. The deflection of their wind in trying to cross in front of the starboard tacker will enable the starboard tacker to point higher without luffing than he normally would be able to do, and the port tacker who thought he could squeeze by suddenly finds that he cannot (See Figure 35).
TRY IT
Exercise 1.1.A: Draft a Technical Paragraph
Reflect on the description and example of technical writing above and consider your experience professionally, academically, or personally. What kinds of documents have you written that could fall under the genre of technical writing?
Write a paragraph or two on a topic about which you have specialized knowledge and use specialized terminology to explain the idea or instruct the reader. For example, you might write about effective techniques for executing a precision cut using a circular saw or streak-plating bacterial cultures. Consider your audience when choosing how to write this. Will the audience have to be familiar with the terminology used as in the above sailing example? See if you can write a paragraph that can uses technical jargon and then re-write for a general audience, using plain language. Adapting your writing style to your audience and purpose is an important skill for a technical communicator.
References & Attributions
References
McConkey S. (2017, March 3). Writing a work term report. ENGR 120 Plenary Lecture, University of Victoria.
Wells,T. (1950). Scientific sailboat racing. Dodd, Mead, and Co.
Attributions
Content on this page is adapted from Technical Writing Essentials by Suzan Last, which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.