27 Pronouns
Pronouns
A pronoun is a word that can be used in the place of a noun. We use pronouns so we do not have to repeat words. It sounds better if a pronouns are used to replace nouns in the sentence. Knowing just how pronouns work is an important aspect of clear and concise writing.
You must introduce the noun first before using a pronoun to refer to it throughout the rest of the sentence.
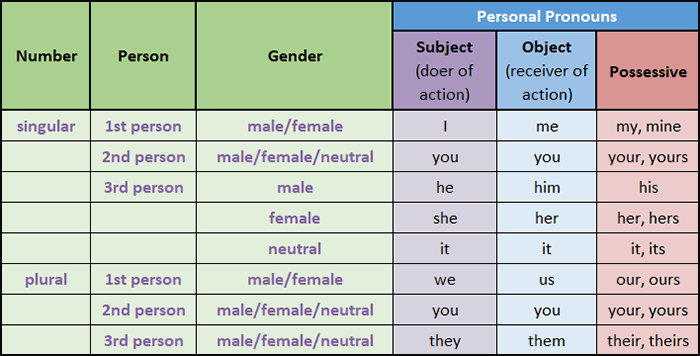
Personal pronouns have the following:

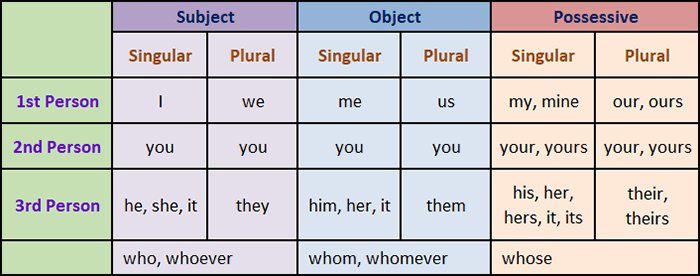
Personal Pronouns: Person
Pronouns can be used in either the first person, second person, or third person.
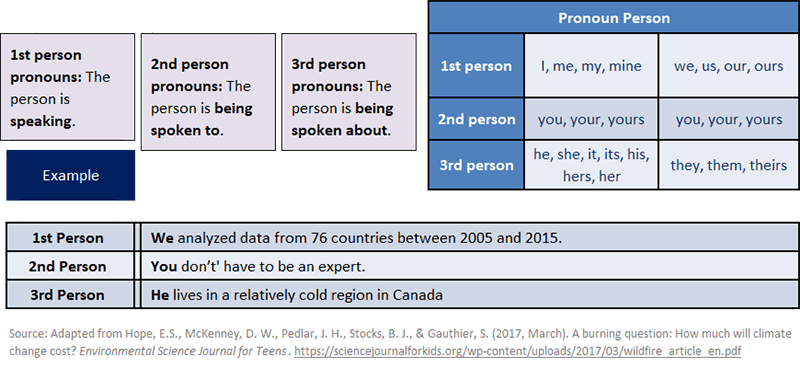
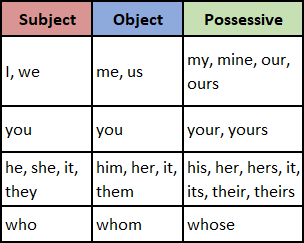
Personal Pronouns: Case
Pronouns can either be subjective, objective, or possessive.
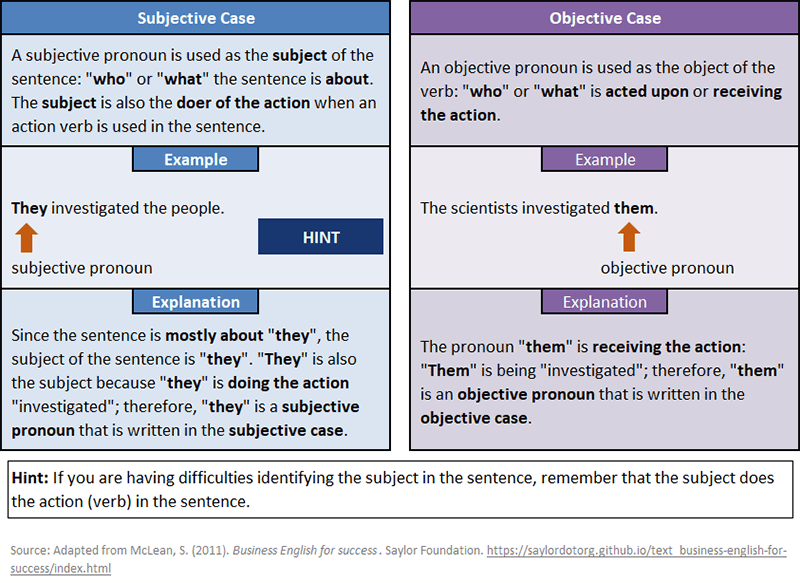
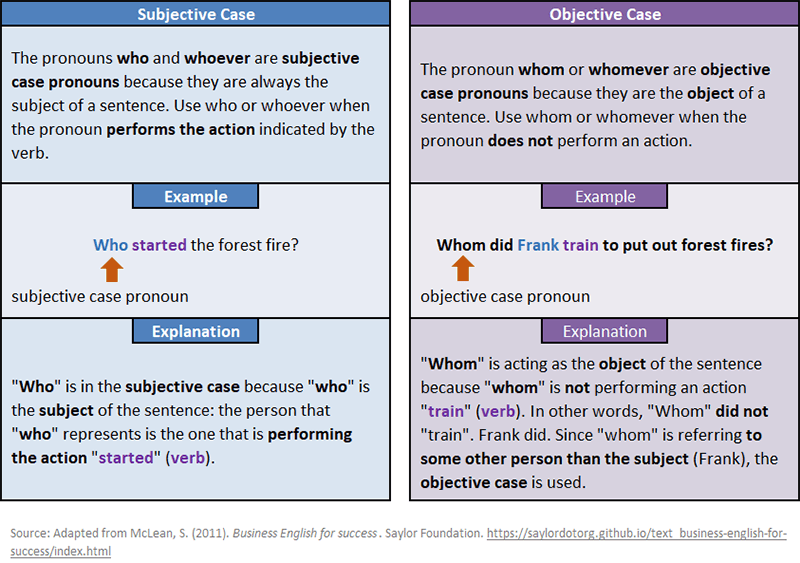
A subjective pronoun is a pronoun that is the subject of the sentence: “who” or “what” the sentence is about. It is also the doer of the action if an action verb is used in the sentence.
An objective pronoun is a pronoun that is the object of the verb: “who” or “what” was acted upon.
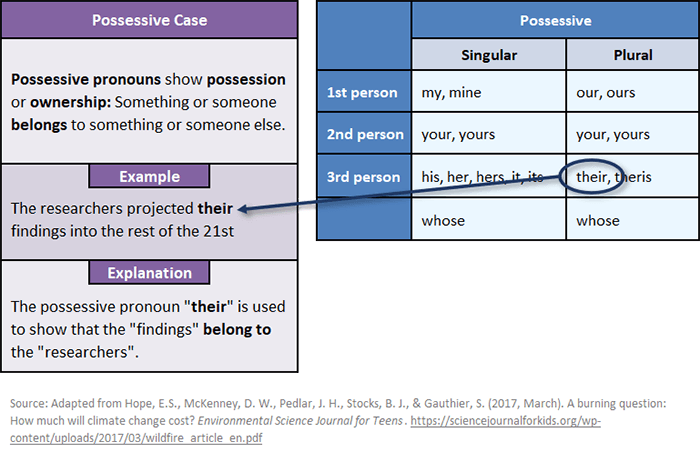
A possessive pronoun is a pronoun that shows possession or ownership.
Subjective vs. Objective Pronouns
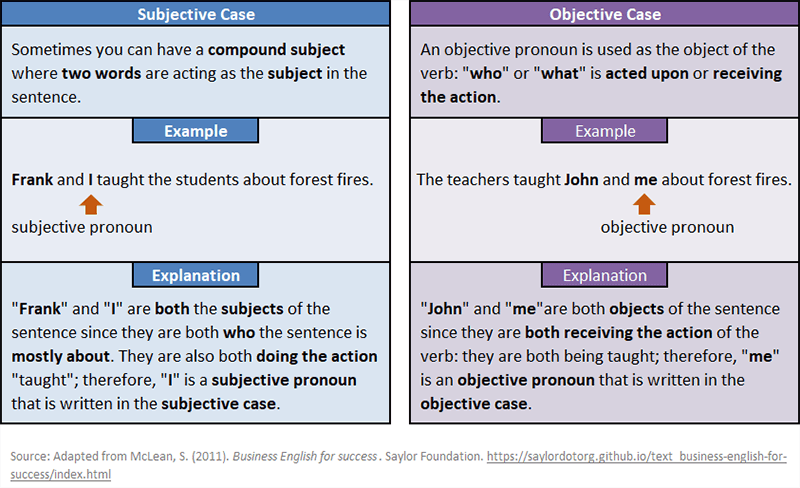
Compound Subjects
Who/Whoever vs. Whom/Whomever as Questions
Possessive Pronoun Case
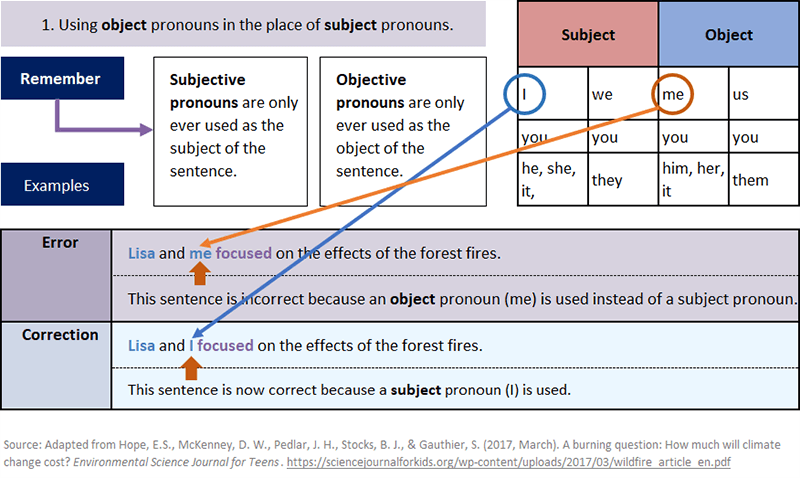
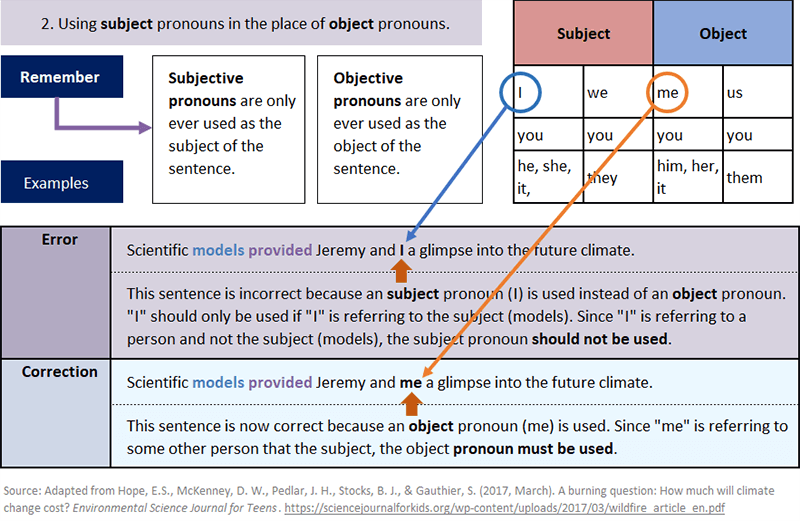
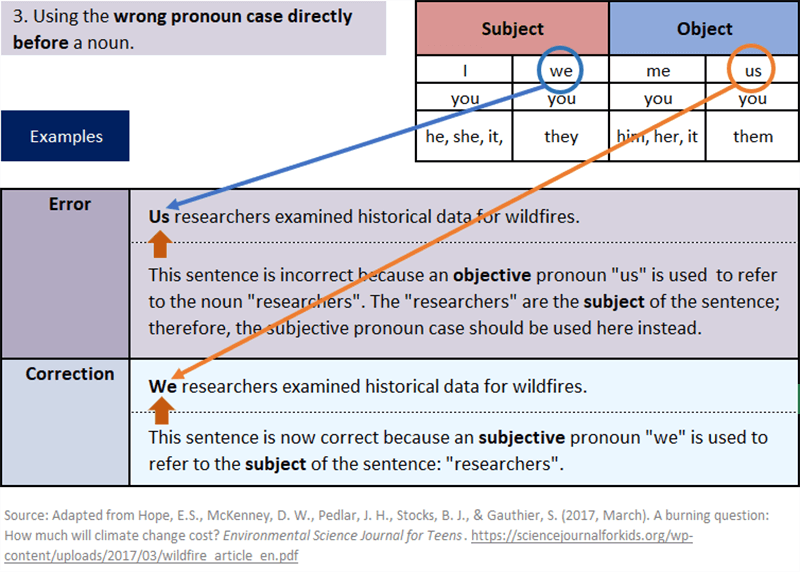
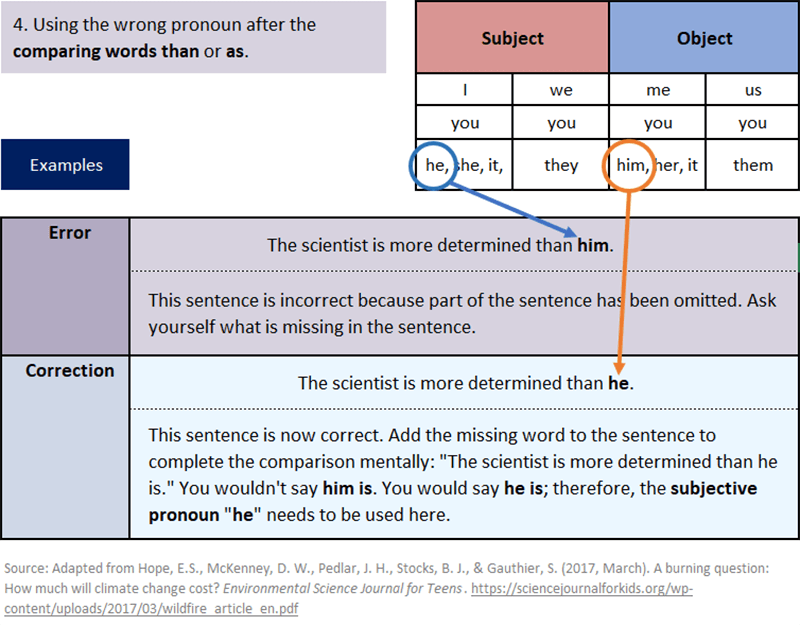
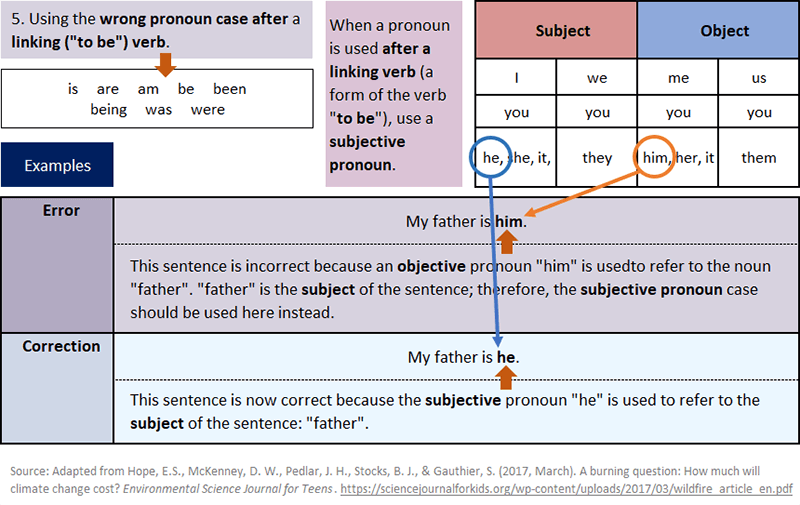
Common Pronoun Errors
Learning Check
Pronoun Antecedents
The noun that pronoun refers to is its antecedent. The antecedent goes before the pronoun in a sentence.

NOTE:
Gender-Neutral Pronouns: Current grammar mechanics have been around for quite some time; however, today’s world has transformed, and gender specific pronouns have been claimed to be restrictive and binary. As a result, there has been a transformation in pronoun use to be more inclusive.
When writing about a person who uses gender-neutral pronouns, you should refer to the individual’s choice of gender-neutral pronoun. Some of these common gender-neutral pronouns include the following:

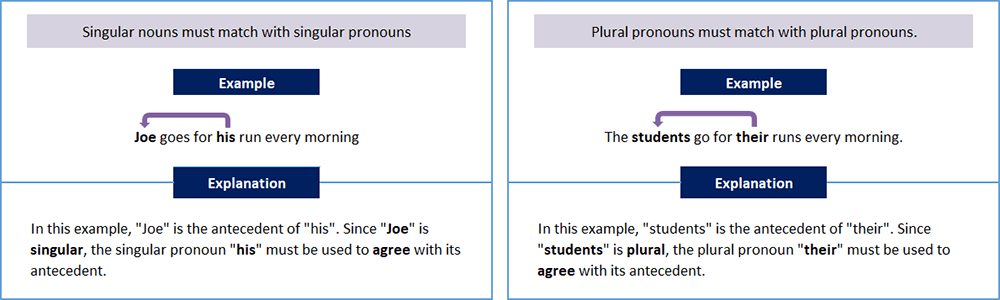
A pronoun must match, or agree, with it antecedent in number, person, and gender.
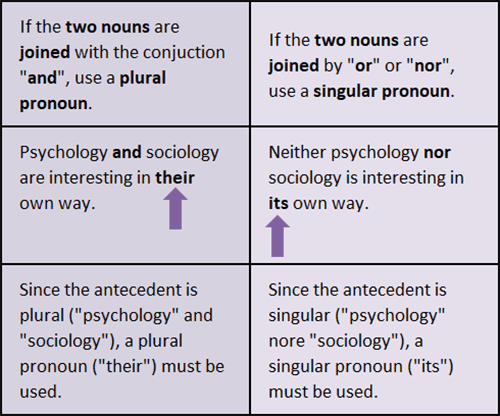
Pronoun Antecedent Agreement: “And”, “Or”, and “Nor”
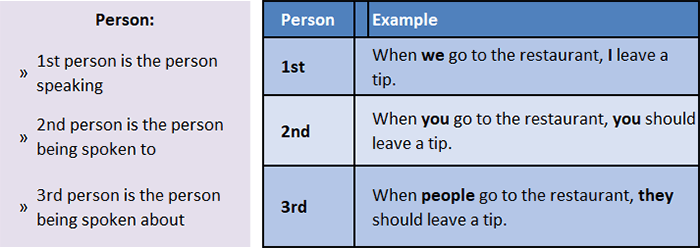
Pronoun Antecedents: Person Agreement
If you begin writing in using a first-person pronoun, be sure to use first-person pronouns throughout your entire written composition.
Pronoun Antecedents: Gender Agreement
When using she or her, use the female pronouns.
When using he or him, use the male pronouns.
If you do not know the gender, use he or she or his or her. In the past, they and their were only used if the antecedent is plural; however, today’s world has transformed, and gender specific pronouns have been claimed to be restrictive and binary. As a result, there has been a transformation in pronoun use to be more inclusive. Nowadays, people will use the pronouns they and their to refer to a singular individual. If you are ever unsure of what pronouns to use, ask the person.
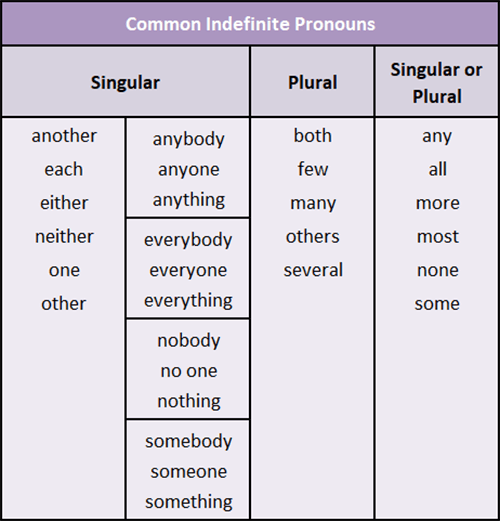
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns are pronouns that do not refer to a specific person or thing.
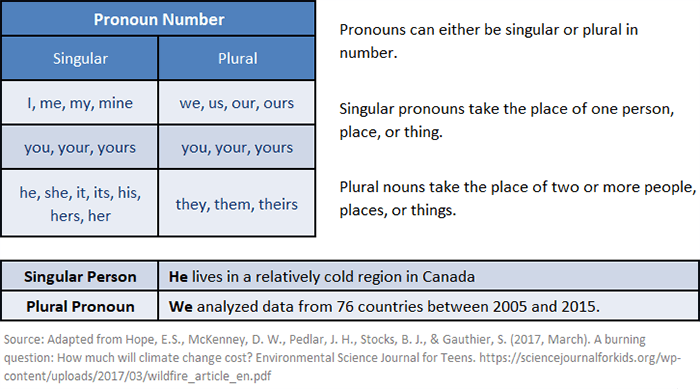
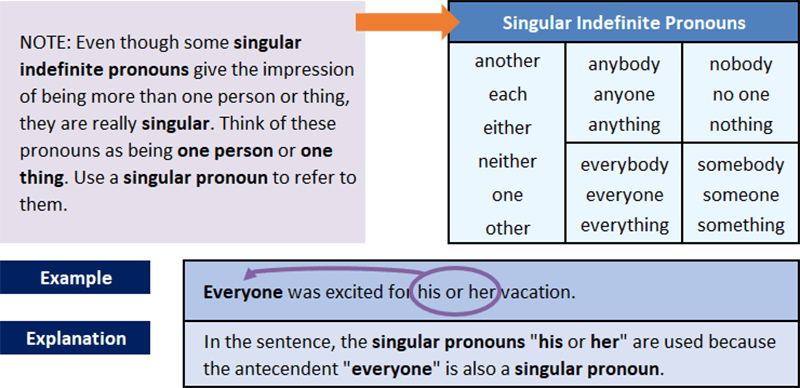
Singular indefinite pronouns refer to or take the place of singular nouns or pronouns. Plural indefinite pronouns refer to or take the place of plural nouns or pronouns.
Learning Check
Common Antecedent Errors
Confusing Pronoun References
Avoid using a pronoun that refers confusingly to two possible antecedents.

Implied Antecedents: They, It, and One
A pronoun must refer to a specific antecedent; however, sometimes confusion occurs when an antecedent has not been clearly stated but instead it has been implied. Avoid using implied antecedents.
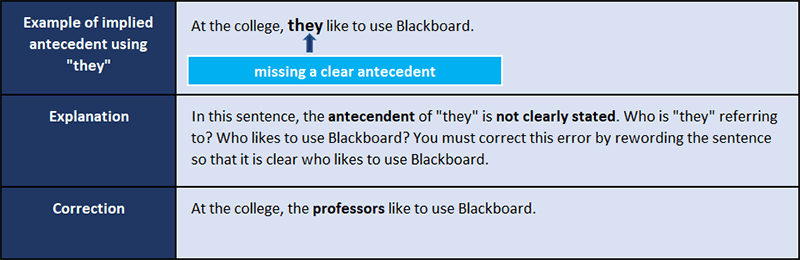
Sometimes the antecedent of one sentence appears in the sentence that came before it. For instance, the sentence used in this example could be preceded by the following sentence:
Professors use web-based software. At the college, they like to use Blackboard.
In this case the antecedent “professors” appears in the first sentence. The pronoun “they” appears in the second sentence. Since the antecedent of “they” (professors) is clearly stated in the previous sentence, there is no need to repeat the antecedent (professors) again, so the pronoun “they” can be used instead.


Repeating a Personal Pronoun Right After its Antecedent
Avoid using a personal pronoun directly after its antecedent in a sentence. When a sentence says the same thing twice, it is redundant. Writers should avoid redundancy.

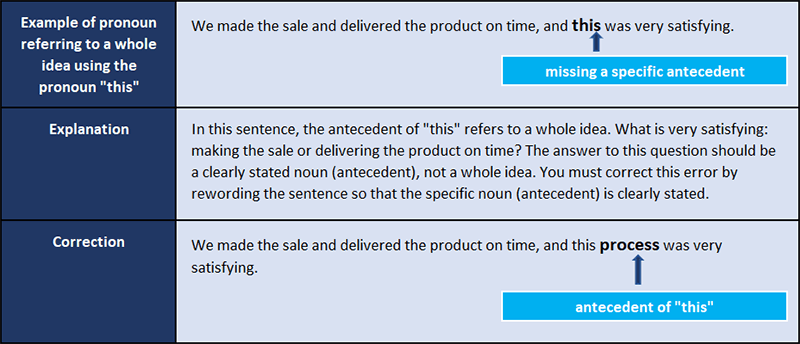
Pronouns “Which” and “This” are Missing Clear Antecedents
Avoid using a pronoun to refer to a whole idea. Pronouns should refer to an antecedent that is specific to a noun and not to a whole idea. The pronouns which and this need clear antecedents. Most of the time, the antecedent of these pronouns needs to be stated right before or after the pronoun.
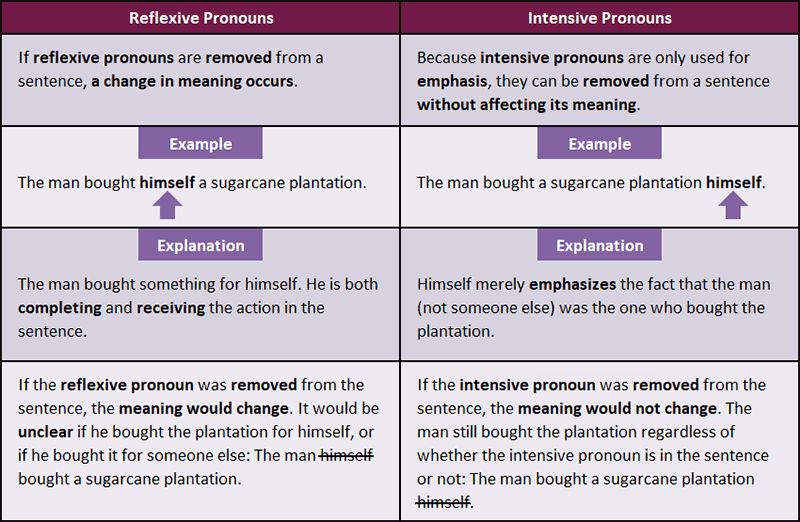
Reflexive Pronouns
Tips to Remember
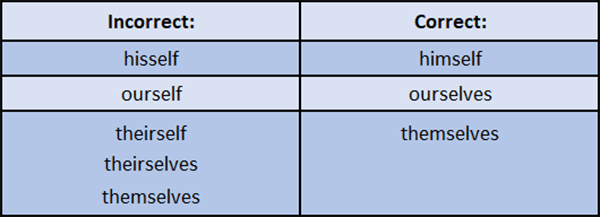
Do not use reflexive pronouns instead of subject or object pronouns.

The following reflexives do not actually exist even though people commonly use them:
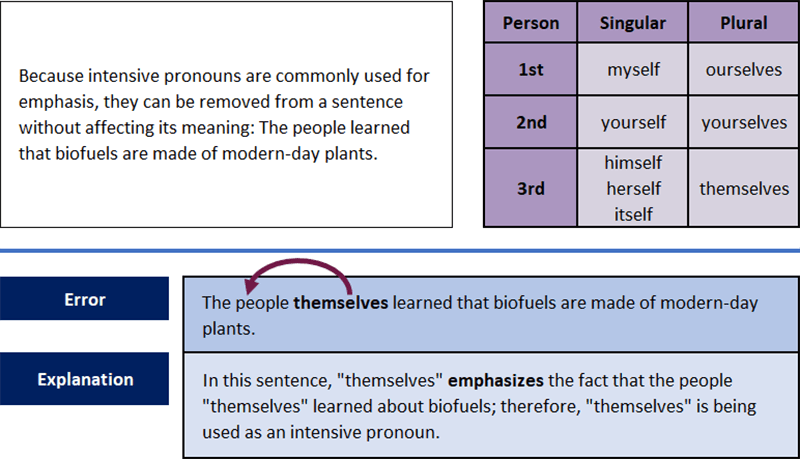
Intensive Pronouns
Intensive pronouns are the same words as reflexive pronouns; however, intensive pronouns are only used to emphasize a noun. Often this noun comes immediately before the intensive pronoun.
Intensive vs Reflexive Pronouns
Learning Check
Additional Resources
To learn more about pronouns:
- Watch this video
- Read Chapter 5.4 of Writing for Success [1]
- Writing for Success is adapted from a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-SA) in 2011 by a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution. This adapted edition is produced by the University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing through the eLearning Support Initiative. ↵