Calculating the Rate, i
Note that due to the placement of ![]() in the PV & FV formulas for ordinary annuities, it is not possible to solve for
in the PV & FV formulas for ordinary annuities, it is not possible to solve for ![]() algebraically. Excel has a function we can use to solve for
algebraically. Excel has a function we can use to solve for ![]() .
.
where:
- Nper is the total number of payment periods in an annuity.
- Pmt is the payment made each period
- If pmt is omitted, you must include the fv argument.
- Pv is the present value
- Fv is the future value,
- If fv is omitted, it is assumed to be 0 and you must include the pmt argument.
- Type is the number 0 or 1 and indicates when payments are due.
- 0 indicates at the end of the period
- 1 indicates at the beginning of the period
- If type is omitted, it is assumed to be 0
Example 1
A life insurance company advertises that $50,000 will purchase a 20-year annuity paying $341.13 at the end of each month. What nominal rate of return and effective rate of return does the annuity investment earn? (Source: Jerome & Worswick, 2020, Example 12.3A).
For this example we are given:
- Compounding/payment frequency = 12
- PMT = $341.13
- PV = $50,000
- FV = 0
- Type = 0
- Number of years: 20
We can set up our spreadsheet to calculate the nominal and effective rates.
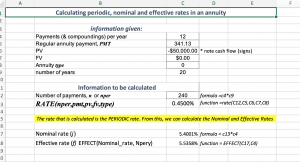
Try recreating the spreadsheet above on your own.
Click this link to see the completed spreadsheet: Calculating periodic, nominal and effective rates in an annuity – Template
For more information about using the RATE function, see Microsoft Support

