Chapter 1: Teamwork in the Golf and Club Business
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Define different types of teams within the golf/club business and define key characteristics.
- Explain the importance of teams within the golf and club business.
- Identify factors that contribute to team cohesion or division.
- Describe the importance of learning to participate in team-based activities.
- Identify the skills needed by team members and the roles that members of a team might play.
- Explain the skills and behaviours that foster effective team leadership.
What Is a Team?
A team (or a work team) is a group of people with complementary skills who work together to achieve a specific goal. [1] Every team is organized around a shared objective-there is something to accomplish.
“Teamwork is the ability to work together toward a common vision. The ability to direct individual accomplishments toward organizational objectives. It is the fuel that allows common people to attain uncommon results.” – Andrew Carnegie
A group is different. A group of golf club managers (ie, Golf Professional, Superintendent, Food and Beverage Manager), for example, might meet with the general manager of the course owner monthly to discuss their progress in maintaining their operational budget. However, each manager is focused on the goals of his or her department because each is held accountable for meeting those goals.
To put teams in perspective, let’s identify five key characteristics.
- Share accountability for achieving specific common goals
- Function interdependently
- Require stability
- Hold authority and decision-making power
- Operate in a social context [2]
The Team and the Organization

Why do golf courses or clubs rely so much on teams to improve operations? GM Geoff Curphey CCM of the London Club (a popular private social club) relies on teams to create an exceptional experience for their members and their invited guests [3] A great team made up of a diverse background of individuals can bring new ideas and initiatives to the Club environment to move the Club forward in a positive direction
Today, it seems obvious that teams can address a variety of challenges in club activities. Before we go any further, however, we should remind ourselves that the data we’ve just cited aren’t necessarily definitive. For one thing, they may not be objective—companies are more likely to report successes than failures. As a matter of fact, teams don’t always work. According to one study, team-based projects fail 50 to 70 percent of the time. [4]
The Effect of Teams on Performance
Research shows that companies build and support teams because of their effect on overall workplace performance, both organizational and individual. If we examine the impact of team-based operations according to a wide range of relevant criteria, we find that overall organizational performance generally improves. The following figure lists several areas in which we can analyze workplace performance and indicates the percentage of companies that have reported improvements in each area. [5]
| Area of Performance | Firms Reporting Improvement |
|---|---|
| Product and service quality | 70% |
| Customer service | 67% |
| Worker satisfaction | 66% |
| Quality of work-life | 63% |
| Productivity | 61% |
| Competitiveness | 50% |
| Profitability | 45% |
| Absenteeism | turnover | 23% |
Types of Teams
Teams, then, can improve the company and individual performance in a number of areas. Not all teams, however, are formed to achieve the same goals or are charged with the same responsibilities. Nor are they organized in the same way. Some, for instance, are more autonomous than others—less accountable to those higher up in the organization. Some depend on a team leader who’s responsible for defining the team’s goals and making sure that its activities are performed effectively. Others are more or less self-governing: though a leader lays out overall goals and strategies, the team itself chooses and manages the methods by which it pursues its goals and implements its strategies. [6] Teams also vary according to their membership. Let’s look at several categories of teams.
Manager-Led Teams

As its name implies, in the manager-led team, the manager is the team leader and is in charge of setting team goals, assigning tasks, and monitoring the team’s performance. The individual team members have relatively little autonomy. For example, the key employees of a professional hockey team (a manager-led team) are highly trained (and highly paid) athletes, but their activities on the ice are tightly controlled by a head coach. As team manager, the coach is responsible for both developing the strategies by which the team pursues its goal of winning games and for the outcome of each game and season. He’s also solely responsible for interacting with managers above him in the organization. The players are responsible mainly for executing plays. [7]
Self-Managing Teams
Self-managing teams (also known as self-directed teams) have considerable autonomy. They are usually small and often absorb activities that were once performed by traditional supervisors. A manager or team leader may determine overall goals, but the members of the self-managing team control the activities needed to achieve those goals.
![]() Self-managing teams are the organizational hallmark of The London Club and are an important aspect of the success of the Club. It is important to come to agreed/shared goals and then have your teams execute on their own. A self-directed team, when provided the appropriate guidance, will thrive on its own. Team members will have a feeling of fulfillment when completing projects on their own and not being managed at every point of the process. [8]
Self-managing teams are the organizational hallmark of The London Club and are an important aspect of the success of the Club. It is important to come to agreed/shared goals and then have your teams execute on their own. A self-directed team, when provided the appropriate guidance, will thrive on its own. Team members will have a feeling of fulfillment when completing projects on their own and not being managed at every point of the process. [8]
Not every self-managed team enjoys the same degree of autonomy. Clubs vary widely in choosing which tasks teams are allowed to manage and which ones are best left to upper-level management only. As you can see, self-managing teams are often allowed to schedule assignments, but they are rarely allowed to fire coworkers.
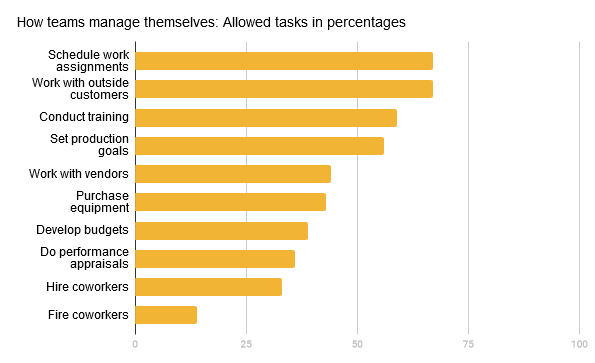
Image Description
The chart shows the percentage of self-managed teams that are permitted to carry out different activities. The longest bars, around 70%, are for scheduling work assignments and working with outside customers. Conducting training and setting production goals are next, just above half of the teams. Mid-range tasks—working with vendors, purchasing equipment, developing budgets, doing performance appraisals, and hiring coworkers—are allowed for roughly one-third to just under half of teams. The shortest bar, around 15%, is firing coworkers, indicating this responsibility is rarely given to teams.
Cross-Functional Teams
Many golf clubs use cross-functional teams—teams that, as the name suggests, cut across an organization’s functional areas (operations, marketing, finance, and so on). A cross-functional team is designed to take advantage of the special expertise of members drawn from different functional areas of the club. When a club is exploring the feasibility of a major capital project, the GM might enlist specific employees, such as the Golf Professional, Food and Beverage Manager, Superintendent, etc., to provide input on the project and operational considerations. Stakeholders, such as club members, can form ad hoc committees or a task force to provide a perspective as well.
Virtual Teams
The speed of transformation from traditional teams to virtual teams reached its peak and became a trend in the workplace due to the COVID-19 global pandemic. This crisis forced some clubs to create virtual teams for the first time in their history. Technology now makes it possible for teams to function not only across organizational boundaries like functional areas but also across time and space. Technologies such as videoconferencing allow people to interact simultaneously and in real-time, offering a number of advantages in conducting the business of a virtual team. [9] Members can participate from any location or at any time of day, and teams can “meet” for as long as it takes to achieve a goal or solve a problem—a few days, weeks, or months.
Read: Forever Changed by Rob Foster, MBA for the Club Manager Quarterly (Club Managers Association of Canada). The article discusses how the pandemic has had a considerable impact on how we communicate and, in some cases, has made it more efficient than ever before!
Why Teamwork Works
Now that we know a little bit about how teams work, we need to ask ourselves why they work. Not surprisingly, this is a fairly complex issue. In this section, we’ll explore why teams are often effective and when they are ineffective.
First, let’s begin by identifying several factors that contribute to effective teamwork. Teams are most effective when the following factors are met:
- Members communicate effectively.
- Members depend on each other. When team members rely on each other to get the job done, team productivity and efficiency tend to be high.
- Members trust one another.
- Members work better together than individually. When team members perform better as a group than alone, collective performance exceeds individual performance.
- Members become boosters. When each member is encouraged by other team members to do his or her best, collective results improve.
- Team members enjoy being on the team.
- Leadership rotates.
Some of these factors may seem intuitive. Because such issues are rarely clear-cut, we need to examine the issue of group effectiveness from another perspective—one that considers the effects of factors that aren’t quite so straightforward.
Group Cohesiveness
The idea of group cohesiveness refers to the attractiveness of a team to its members. If a group is high in cohesiveness, membership is quite satisfying to its members. If it’s low in cohesiveness, members are unhappy with it and may try to leave it. [10]
Numerous factors may contribute to team cohesiveness, but in this section, we’ll focus on five of the most important:
- Size – The bigger the team, the less satisfied members tend to be. When teams get too large, members find it harder to interact closely with other members; a few members tend to dominate team activities, and conflict becomes more likely.
- Similarity – People usually get along better with people like themselves, and teams are generally more cohesive when members perceive fellow members as people who share their own attitudes and experience.
- Success – When teams are successful, members are satisfied, and other people are more likely to be attracted to their teams.
- Exclusiveness – The harder it is to get into a group, the happier the people who are already in it. Team status also increases members’ satisfaction.
- Competition – Membership is valued more highly when there is motivation to achieve common goals and outperform other teams.
Maintaining team focus on broad organizational or club goals is crucial. If members get too wrapped up in immediate team goals, the whole team may lose sight of the larger organizational goals toward which it’s supposed to be working. Let’s look at some factors that can erode team performance.
Groupthink
It’s easy for leaders to direct members toward team goals when members are all on the same page—when there’s a basic willingness to conform to the team’s rules. When there’s too much conformity, however, the group can become ineffective: it may resist fresh ideas and, what’s worse, may end up adopting its own dysfunctional tendencies as its way of doing things. Such tendencies may also encourage a phenomenon known as groupthink —the tendency to conform to group pressure in making decisions while failing to think critically or to consider outside influences.
Motivation and Frustration
Remember that teams are composed of people, and whatever the roles they happen to be playing at a given time, people are subject to psychological ups and downs. As members of workplace teams, they need motivation, and when motivation is low, so are effectiveness and productivity. The difficulty of maintaining a high level of motivation is the chief cause of frustration among members of teams. As such, it’s also a chief cause of ineffective teamwork, and that’s one reason why more employers now look for the ability to develop and sustain motivation when they’re hiring new managers. [12]
Other Factors that Erode Performance
Let’s take a quick look at three other obstacles to success in introducing teams into an organization: [13]
- Unwillingness to cooperate – Failure to cooperate can occur when members don’t or won’t commit to a common goal or set of activities. What if, for example, half the members of a turf crew team want to cut greens with a walker mower and the other half want to use a tri-plex ride mower? The entire team may get stuck on this point of contention for weeks or even months. Lack of cooperation between teams can also be problematic for an organization. Luckily, the Superintendent makes these decisions for the team by weighing the pros and cons of each method.
- Lack of managerial support – Every team requires organizational resources to achieve its goals, and if management isn’t willing to commit the needed resources— say, provide the necessary equipment to properly manicure the course— the turf team will probably fall short of those goals.
- Failure of managers to delegate authority – Team leaders are often chosen from the ranks of successful supervisors—first-line managers give instructions on a day-to-day basis and expect to have them carried out. This approach to workplace activities may not work very well in leading a team—a position in which success depends on building a consensus and letting people make their own decisions.
The Team and Its Members
Life is all about group work. “I’ll work extra hard and do it myself, but please don’t make me have to work in a group.”
Like it or not, you’ve probably already noticed that you’ll have team-based assignments in college. More than two-thirds of all students report having participated in the work of an organized team, and as a student in a Professional Golf Management program, you will certainly find yourself engaged in team-based activities. [14]
Why do we put so much emphasis on something that, reportedly, makes many students feel anxious and academically drained? Here’s one college student’s practical-minded answer to this question:
“In the real world, you have to work with people. You don’t always know the people you work with, and you don’t always get along with them. Your boss won’t particularly care, and if you can’t get the job done, your job may end up on the line. Life is all about group work, whether we like it or not. And school, in many ways, prepares us for life, including working with others.” [15]
In placing so much emphasis on teamwork skills and experience, business colleges are doing the responsible thing—preparing students for the business world. A survey of Fortune 1000 companies reveals that 79 percent use self-managing teams and 91 percent use other forms of employee workgroups. Another survey found that the skill that most employers value in new employees is the ability to work in teams. [16]
Consider the advice of former Chrysler Chairman Lee Iacocca: “A major reason that capable people fail to advance is that they don’t work well with their colleagues”. [17] The importance of the ability to work in teams was confirmed in a survey of leadership practices of more than sixty of the world’s top organizations. [18]
When top executives in these organizations were asked what causes the careers of high-potential leadership candidates to derail, 60 percent of the organizations cited “inability to work in teams.” Interestingly, only 9 percent attributed the failure of these executives to advance to a “lack of technical ability.”
To put it in plain terms, the question is not whether you’ll find yourself working as part of a team. You will. The question is whether you’ll know how to participate successfully in team-based activities.
What Skills Does the Team Need?
Sometimes we hear about a sports team made up of mostly average players who win a championship because of coaching genius, flawless teamwork, and superhuman determination. [19] But not terribly often. In fact, we usually hear about such teams simply because they’re newsworthy—exceptions to the rule. Typically a team performs well because its members possess some level of talent. Members’ talents must also be managed in a collective effort to achieve a common goal.
In the final analysis, a team can succeed only if its members provide the skills that need managing. In particular, every team requires some mixture of four sets of skills:
- Communication Skills – Because how you communicate can positively and negatively affect relationships within the team and outside the team with managers, customers, stakeholders, etc.
- Technical skills – Because teams must perform certain tasks, they need people with the skills to perform them. For example, if your project calls for a lot of math work, it’s good to have someone with the necessary quantitative skills. Such as scoring a golf tournament!
- Decision-making and problem-solving skills – Because every task is subject to problems, and because handling every problem means deciding on the best solution, it’s good to have members who are skilled in identifying problems, evaluating alternative solutions, and deciding on the best options.
- Interpersonal skills – Because teams need direction and motivation and depend on communication, every group benefits from members who know how to listen, provide feedback, and resolve conflict. This comes in handy as a pro shop attendant or a server in the restaurant Some members must also be good at communicating the team’s goals and needs to outsiders.
The key is ultimately to have the right mix of these skills. Remember, too, that no team needs to possess all these skills—never mind the right balance of them—from day one. In many cases, a team gains certain skills only when members volunteer for certain tasks and perfect their skills in the process of performing them. For the same reason, effective teamwork develops over time as team members learn how to handle various team-based tasks. In a sense, teamwork is always a work in progress.
What Roles Do Team Members Play?
As a student and later in the workplace, you’ll be a member of a team more often than a leader. Team members can have as much impact on a team’s success as its leaders. A key is the quality of the contributions they make in performing non-leadership roles. [20]
What, exactly, are those roles? At this point, you’ve probably concluded that every team faces two basic challenges:
- Accomplishing its assigned task
- Maintaining or improving group cohesiveness
Whether you affect the team’s work positively or negatively depends on the extent to which you help it or hinder it in meeting these two challenges. [21] We can thus divide teamwork roles into two categories, depending on which of these two challenges each role addresses. These two categories (task-facilitating roles and relationship-building roles) are summarized here:
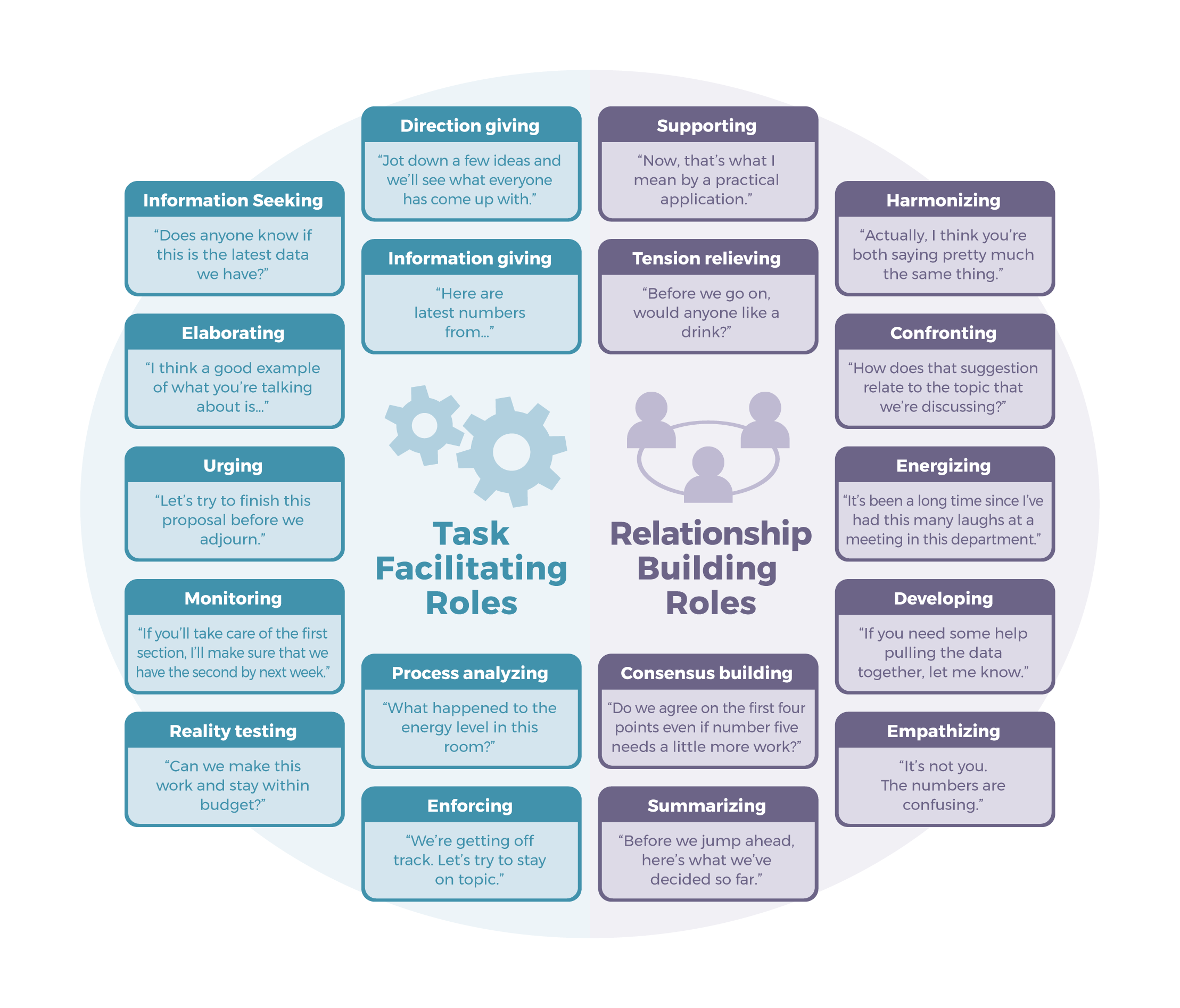
Image Description
Infographic showing two categories of team roles arranged in a circular layout.
Left side – Task Facilitating Roles (blue/teal):
- Information Seeking: “Does anyone know if this is the latest data we have?”Elaborating: “I think a good example of what you’re talking about is…”
- Elaborating: “I think a good example of what you’re talking about is…”
- Urging: “Let’s try to finish this proposal before we adjourn.”
- Monitoring: “If you’ll take care of the first section, I’ll make sure that we have the second by next week.”
- Reality Testing: “Can we make this work and stay within budget?”
- Direction Giving: “Jot down a few ideas and we’ll see what everyone has come up with.”Information Giving: “Here are latest numbers from…”
- Information Giving: “Here are latest numbers from…”
- Process Analyzing: “What happened to the energy level in this room?”
- Enforcing: “We’re getting off track. Let’s try to stay on topic.”Center label: “Task Facilitating Roles” with gear icons.
Right side – Relationship Building Roles (purple):
- Supporting: “Now, that’s what I mean by a practical application.”
- Tension Relieving: “Before we go on, would anyone like a drink?”
- Harmonizing: “Actually, I think you’re both saying pretty much the same thing.”
- Confronting: “How does that suggestion relate to the topic that we’re discussing?”
- Energizing: “It’s been a long time since I’ve had this many laughs at a meeting in this department.”
- Developing: “If you need some help pulling the data together, let me know.”
- Empathizing: “It’s not you. The numbers are confusing.”
- Consensus Building: “Do we agree on the first four points even if number five needs a little more work?”
- Summarizing: “Before we jump ahead, here’s what we’ve decided so far.”
Task-Facilitating Roles
Task-facilitating roles address challenge number one—accomplishing the team goals. As you can see from Table P.6, such roles include not only providing information when someone else needs it but also asking for it when you need it. In addition, it includes monitoring (checking on progress) and enforcing (making sure that team decisions are carried out). Task facilitators are especially valuable when assignments aren’t clear or when progress is too slow.
Relationship-Building Roles
When you challenge unmotivated behavior or help other team members understand their roles, you’re performing a relationship-building role and addressing challenge number two—maintaining or improving group cohesiveness. This type of role includes activities that improve team “chemistry,” from empathizing to confronting.
Bear in mind three points about this model:
- Teams are most effective when there’s a good balance between task facilitation and relationship-building.
- It’s hard for any given member to perform both types of roles, as some people are better at focusing on tasks and others on relationships.
- Overplaying any facet of any role can easily become counterproductive. For example, elaborating on something may not be the best strategy when the team needs to make a quick decision; and consensus building may cause the team to overlook an important difference of opinion.
Blocking Roles
Finally, show what you know in terms of blocking behaviours and the tactics used when someone is using the behaviour. So-called blocking roles consist of behavior that inhibits either team performance or that of individual members. Every member of the team should know how to recognize blocking behavior. If teams don’t confront dysfunctional members, they can destroy morale, hamper consensus building, create conflict, and hinder progress.
Class Team Projects
In your academic career, you’ll participate in a number of team projects. To get insider advice on how to succeed on team projects in college, let’s look at some suggestions offered by students who have gone through this experience. [22]
- Draw up a team charter – At the beginning of the project, draw up a team charter that includes: the goals of the group; ways to ensure that each team member’s ideas are considered; timing and frequency of meetings. A more informal way to arrive at a team charter is to simply set some ground rules to which everyone agrees. Your instructor may also require you to sign an existing team contract or charter similar to the one below.
- Contribute your ideas. Share your ideas with your group – The worst that could happen is that they won’t be used (which is what would happen if you kept quiet).
- Never miss a meeting or deadline – Pick a weekly meeting time and write it into your schedule as if it were a class. Never skip it.
- Be considerate of each other – Be patient, listen to everyone, involve everyone in decision making, avoid infighting, and build trust.
- Create a process for resolving conflict – Do so before conflict arises. Set up rules to help the group decide how the conflict will be handled.
- Use the strengths of each team member – All students bring different strengths. Utilize the unique value of each person.
- Don’t do all the work yourself – Work with your team to get the work done. The project output is often less important than the experience.
What Does It Take to Lead a Team?
To borrow from Shakespeare, “Some people are born leaders, some achieve leadership, and some have leadership thrust upon them.” At some point in a successful career, you will likely be asked to lead a team. What will you have to do to succeed as a leader?
Like so many of the questions that we ask in this book, this question doesn’t have any simple answers. We can provide one broad answer: a leader must help members develop the attitudes and behavior that contribute to team success: interdependence, collective responsibility, shared commitment, and so forth.
Team leaders must be able to influence their team members. Notice that we say influence: except in unusual circumstances, giving commands and controlling everything directly doesn’t work very well. [23] As one team of researchers puts it, team leaders are more effective when they work with members rather than on them. [24] Hand-in-hand with the ability to influence is the ability to gain and keep the trust of team members. People aren’t likely to be influenced by a leader whom they perceive as dishonest or selfishly motivated.
Assuming you were asked to lead a team, there are certain leadership skills and behaviours that would help you influence your team members and build trust. Let’s look briefly at some of them:
- Demonstrate integrity – Do what you say you’ll do and act in accordance with your stated values. Be honest in communicating and follow through on promises.
- Be clear and consistent – Let members know that you’re certain about what you want and remember that being clear and consistent reinforces your credibility.
- Generate positive energy – Be optimistic and compliment team members. Recognize their progress and success.
- Acknowledge common points of view – Even if you’re about to propose some kind of change, recognize the value of the views that members already hold in common.
- Manage agreement and disagreement – When members agree with you, confirm your shared point of view. When they disagree, acknowledge both sides of the issue and support your own with strong, clearly-presented evidence.
- Encourage and coach – Buoy up members when they run into new and uncertain situations and when success depends on their performing at a high level.
- Share information. –Give members the information they need and let them know that you’re knowledgeable about team tasks and individual talents. Check with team members regularly to find out what they’re doing and how the job is progressing.
For this course, we will be using teams to learn in and outside of our formal class time. A team contract is important to ensure all members have input on how the team will work together. This contract can also be referenced if a team member is not working to the expectations.
Key Terms
Team (or a work team) is a group of people with complementary skills who work together to achieve a specific goal.
Group is a collection of individuals who coordinate their individual efforts.
A manager-led team includes a manager is the team leader and is in charge of setting team goals, assigning tasks, and monitoring the team’s performance.
A self-managed team is a small group of employees who take full responsibility for delivering a service or product through peer collaboration without a manager’s guidance. This team often works together long-term to make decisions about a particular process.
Cross-functional teams are teams where team members come from different organizational functional areas.
Virtual team usually refers to a group of individuals who work together from different geographic locations and rely on communication technology such as email, instant messaging, and video or voice conferencing services in order to collaborate to achieve a common goal.
Group cohesiveness is the tendency for a group to be in unity while working towards a goal.
Groupthink is the tendency to conform to group pressure in making decisions while failing to think critically or to consider outside influences.
A team contract is an agreement between you and your teammates about how your team will operate. The team focuses on issues that the team considers most important. All team members must sign the contract indicating their agreement.
Key Takeaways
- A team (or a work team) is a group of people with complementary skills and diverse areas of expertise who work together to achieve a specific goal.
- Work teams have five key characteristics:
- They are accountable for achieving specific common goals.
- They function interdependently.
- They are stable.
- They have authority.
- They operate in a social context.
- Work teams may be of several types:
- In the traditional manager-led team, the leader defines the team’s goals and activities and is responsible for its achieving its assigned goals.
- The leader of a self-managing team may determine overall goals, but employees control the activities needed to meet them.
- A cross-functional team is designed to take advantage of the special expertise of members drawn from different functional areas of the company.
- On virtual teams, geographically dispersed members interact electronically in the process of pursuing a common goal.
- Group cohesiveness refers to the attractiveness of a team to its members. If a group is high in cohesiveness, membership is quite satisfying to its members; if it’s low in cohesiveness, members are unhappy with it and may even try to leave it.
- As the business world depends more and more on teamwork, it’s increasingly important for incoming members of the workforce to develop skills and experience in team-based activities.
- Every team requires some mixture of three skill sets:
-
- Technical skills: skills needed to perform specific tasks.
- Decision-making and problem-solving skills: skills needed to identify problems, evaluate alternative solutions, and decide on the best options.
- Interpersonal skills: skills in listening, providing feedback, and resolving conflict.
- Thompson, L. L. (2008). Making the Team: A Guide for Managers. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Thompson, L. L. (2008). Making the Team: A Guide for Managers. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, pp. 4-5. See also Alderfer, C.P. (1977). Group and Intergroup Relations. In J. R. Hackman & J. L. Suttle (Eds.), Improving Life at Work (pp. 277–96). Palisades, CA: Goodyear. ↵
- . Geoff Curphey (General Manager) in discussion with the author, June 2022. ↵
- Fisher, K. (1999). Leading Self-Directed Work Teams: A Guide to Developing New Team Leadership Skills (rev. ed). New York: McGraw-Hill Professional. See also Greenberg, J., & Baron, R. A. (2008). Behaviour in Organizations (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Adapted from Lawler, E. E., Mohaman, S. A., & Ledford, G. E. (1992). Creating high-performance organizations: Practices and results of employee involvement and total quality in Fortune 1000 Companies. San Francisco: Wiley. ↵
- Greenberg, J., & Baron, R. A. (2008). Behaviour in Organizations (9th ed). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. See also Thompson, L. L. (2008). Making the Team: A Guide for Managers. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Thompson, L. L. (2008). Making the Team: A Guide for Managers. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Geoff Curphey (General Manager) in discussion with the author, June 2022 ↵
- Robbins, S. P., & Timothy A. J. (2009). Organizational Behaviour (13th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Adept Scientific. (2009). Lockheed Martin Chooses Mathcad as a Standard Design Package for F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Project. Retrieved from: http://www.adeptscience.co.uk/media-room/press_room/lockheed-martin-chooses-mathcad-as-a-standard-design-package-for-f-35-joint-strike-fighter-project.html ↵
- Geoff Curphey (General Manager) in discussion with the author, June 2022 ↵
- Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. (2009). Organizational Behaviour (13th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Greenberg, J., & Baron, R. A. (2008). Behaviour in Organizations (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Thompson, L. L. (2008). Making the Team: A Guide for Managers. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Whetten, D. A., & Cameron K. S. (1991). Developing Management Skills (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Flavin, B. (2018, March 7). The Importance of Teamwork Skills in Work and School. Rasmussen College, College Life Blog. Retrieved from: http://www.rasmussen.edu/student-life/blogs/college-life/importance-of-teamwork-skills-in-work-and-school/ ↵
- Whetten, D. A., & Cameron K. S. (1991). Developing Management Skills (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Iacocca, L., & Novak. W. (2007). Iacocca. New York: Bantam. ↵
- Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. (2009). Organizational Behavior (13th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Whetten, D. A., & Cameron K. S. (1991). Developing Management Skills (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Whetten, D. A., & Cameron K. S. (1991). Developing Management Skills (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Feenstra, K. (n.d.). Study Skills: Teamwork Skills for Group Projects. Retrieved from: http://powertochange.com/students/academics/groupproject/ ↵
- Whetten, D. A., & Cameron, K. S. (1991). Developing Management Skills (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. ↵
- Feenstra, K. (n.d.). Study Skills: Teamwork Skills for Group Projects. Retrieved from: http://powertochange.com/students/academics/groupproject/ ↵

