8.3 – Ventilator
Medical Ventilators

Terminology:
- Ventilation is movement of air in and out of lungs and is pulmonary specific
- Respiration is wider context of breathing, or combination of respiratory and cardiovascular system for gas exchange.
Types of Ventilators:
- Positive pressure ventilator: create pressure gradient by adding positive pressure to airway.
- Negative pressure ventilator: expose the surface of the chest wall to sub-atmospheric pressure during inspiration; The expiration occurs when the pressure around the chest wall becomes atmospheric
- Fluidic ventilators
- Pediatric ventilators
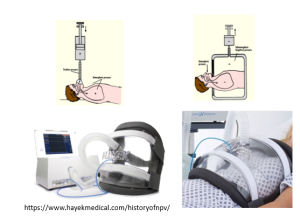
Closed Positive ventilator (CC0 1.0 DEED)
https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?search=ventilator&title=Special:MediaSearch&type=image

Modes of Ventilators:
- Negative end-expiratory pressure (NEEP): it is a sub-atmospheric pressure that develops at the airway at the end of expiration.
- Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP): it is a pressure applied at the end of expiration to maintain alveolar recruitment. The airway pressure is kept positive and is not allowed to return to the atmospheric pressure.
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP): it is a positive pressure applied to the airway in inspiration and expiration.
- Continuous-flow ventilation (CFV): it is a constant flow ventilation and maintains normal gas exchange.
Attributes
- Figure 8.3.1: An image of a Nellcor Puritan Bennett 760. Credit to S. Ghoreyshi, licensed under CC BY 4.0
- Figure 8.3.2:
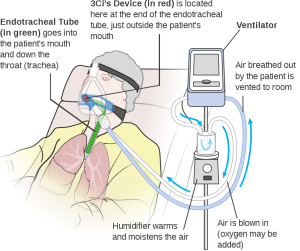
- Figure 8.3.3: Placement of 3Ci’s Device with an Intubated Patient by Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
- Figure 8.3.4: Closed circuit ventilators by Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CCO 1.0

