4.1 – Introduction
Kirchhoff’s circuit laws, first published by Gustav Kirchhoff in 1845, address the conservation of energy and charge in electrical circuits.
Although derived from James Clerk Maxwell’s equations, Kirchhoff’s Laws – Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) – were established using Georg Ohm’s work as a foundation.
These laws are fundamental for analyzing closed circuits, allowing us to determine circuit parameters even in complex configurations, as illustrated below.
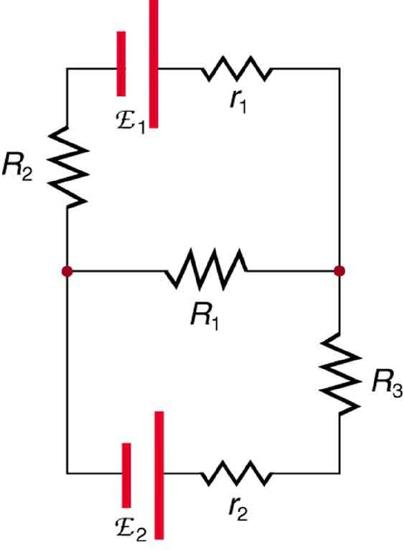
Kirchhoff’s laws are applicable under specific conditions, notably, the voltage law is a simplification of Faraday’s law of induction. While suitable for circuits with resistors and capacitors, it’s an approximation in circuits involving changing currents and magnetic fields.
Learning Outcomes
- Apply Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Law to electronic troubleshooting
- Describe the principles of a defibrillator
- Understand the principles of operation of common electromechanical devices – Relays
- Apply repair and troubleshooting processes to electromechanical devices – Relays
Attributions
This chapter is adapted from:
- College Physics 2e by Openstax, licensed under CC BY 4.0
- Modular Electronics Learning (ModEL) project (Opens a PDF) by Tony R. Kuphaldt, licensed under CC BY 4.0
- First Aid by English Wikibooks, licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5

