Mary’s Health Part D: Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer
Mary’s depressive behavior persists. She lies in bed and has not attempted to participate in any indoor or outdoor activities.
One day, as Mary’s daughter Nancy is changing her brief, she notices that extreme redness on Mary’s skin. After seeing the doctor, it was determined Mary was developing a Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer on her coccyx area.
The nurse informs Nancy that if Mary continues in this cycle, her ulcer can significantly deteriorate in a short period of time.
Pressure Ulcer Etiology
Symptoms
- Discolored, reddened skin
- Warm and skin hardness
- Pain
Risks
- Impaired sensory input
- Impaired motor function
- Alteration in level of consciousness
- Orthopedic devices
Factors influencing ulcer formation
- Shearing force
- Friction
- Moisture
- Nutrition
- Age
Nurses need to assess skin frequently for signs of breakdown
A wound can occur if the tissue compression from the medical device remains unrelieved on the area of the body where the device is in contact with skin or mucosal membranes
Integumentary Changes
Mary’s Immobility increased the risk for pressure ulcer formation (Bony prominences) from prolonged ischemia to tissue.
Recommended intervention to prevent alterations include movement.
Because of her ulcer, Mary must be repositioned every 2 hours to minimize pressure, reduce friction, and prevent sheer.
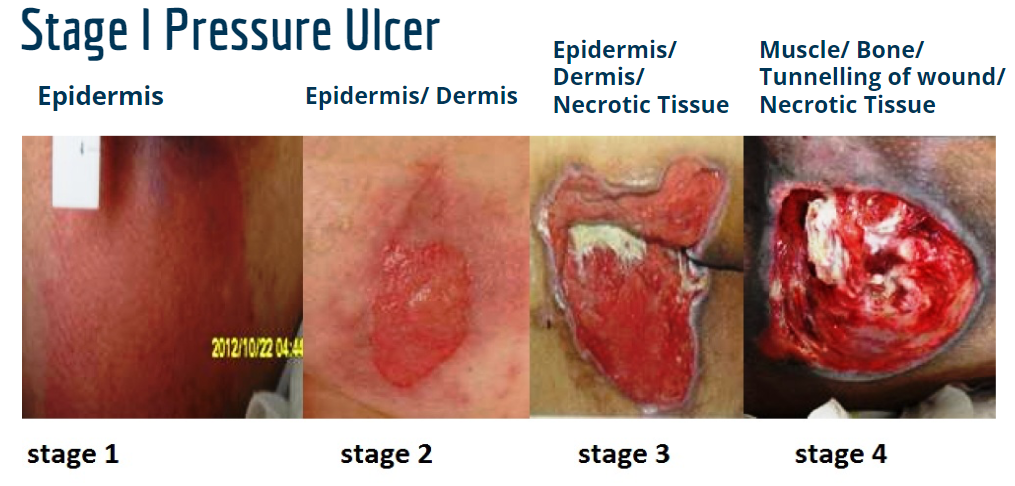
Stage I Pressure Ulcer
Critical Thinking & Application
Using your knowledge and skills, how could you identify Mary’s stage 1 pressure ulcer. List the characteristics that would match the stage of the ulcer that is in.
Intact skin, non-blanchable redness, localized area usually over a bony prominence and darkly pigmented skin may not have visible blanching-its color may differ from the surrounding area
How do you prevent hazards of immobility?
Proper positioning and repositioning , Range of Motion (ROM) exercises, Fluid intake
Risk Assessment
- Braden Scale
- Six factors – sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, friction & sheer
Pillow support and off loading the injured bony prominences
The nurse sends Mary and Nancy home with further instructions for Mary’s Ulcer care.
These are the recommended positions to relieve Mary of her ulcer.


