Supporting Dual Coding

Supporting Dual Coding
Below are various means of supporting dual coding. You can incorporate some of these assets and interactive opportunities into your courses and you can share these ideas with your students to that they have a means of building dual coding into their own study sessions.
Customizable Tools to Support Dual Coding
This tool has been designed to be customizable by faculty, and can be embedded directly into your LMS content. For further information on how to utilize this tool in your LMS see the Interactive-Components page.
Flip Cards
Flip cards can be used to promote dual coding by including both an image and text to describe the same topic.
Flip Cards Exemplar
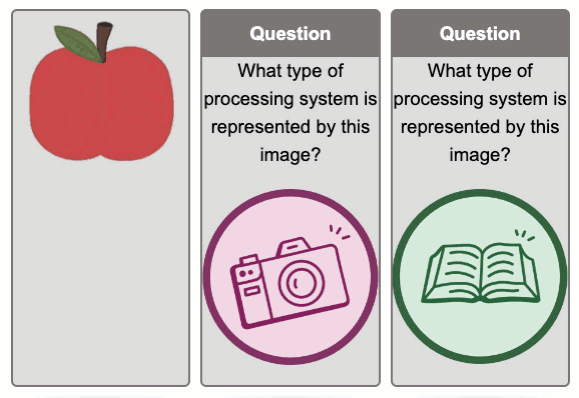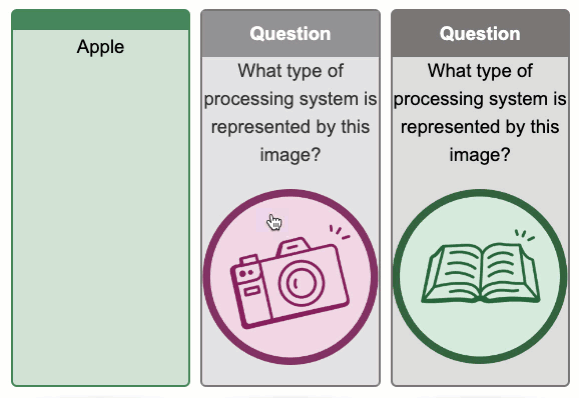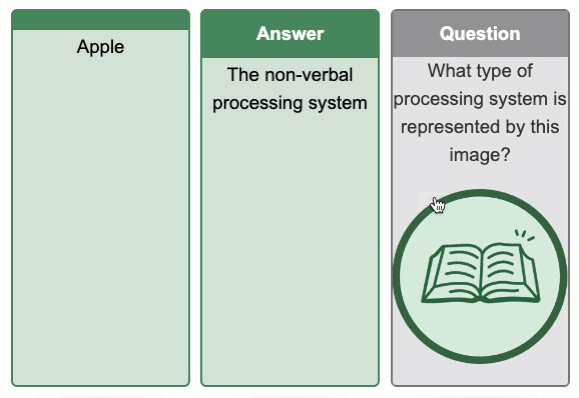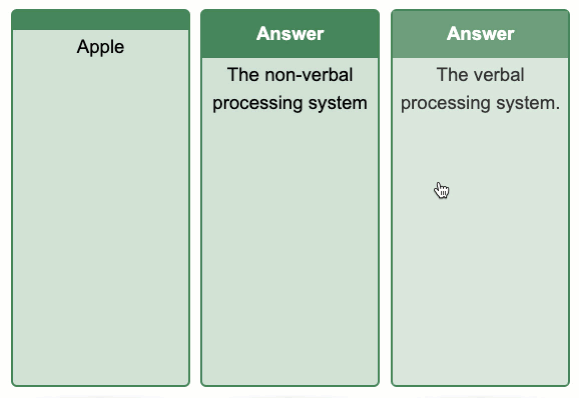
Tips for Using Flip Cards
- Design flip cards to help students identify what information they need to know. Students often struggle with identifying what information is key and what is supplementary.
- Use a digital flip card deck to encourage students to stick with information until it is transferred to long-term memory. When students have the option to remove cards, they will often do so before they have retained the information (Karpicke, https://learninglab.psych.purdue.edu/downloads/2009/2009_Karpicke_JEPGeneral.pdf)
- Ensure that images include appropriate alt text that describes the intent of the image and not the appearance of the image. If using the image to quiz students, ensure that the alt text does not include the answer.
EdTech Tools to Support Dual Coding
There are many EdTech tools that can support you in incorporating dual coding into the learning experiences you create. In addition, making students aware of some of the simpler tools below can support them in building strategies for more effective independent learning.
Using Dual Coding Outside the Digital Space
To support students in building their own tool box of study strategies, encourage students to engage in some of the following activities as they are preparing for your assessments.
Important Consideration
All images used in digital tools must have alternative (alt) text that describes their meaning. When including images in a dual coding activity, ensure that the alt text does not include the answer to the corresponding question (e.g. if asking students to name planets based on their images, include descriptor words in the alt text instead of the planet names).
Tips to Support Dual Coding
Below are some quick tips that you can use when you are building your learning experiences to embed retrieval practice directly into the learning.
- Use visuals that directly relate to the text or verbal material or to your own prior knowledge or understanding.
- Present text content next to the visual tool to help students make connections.
- Use visuals with minimal or no background detail, to ensure focus is on the main subject. Avoid photos and live videos when possible, because they increase cognitive load.
Checking Your Knowledge
References
Photography on this page used with permission from the Durham College Online Photo Database.
Boser, U. (n.d.). Science of learning: Research meets practice – dual coding. The Learning Agency Lab. https://www.the-learning-agency-lab.com/learning-strategies/dual-coding/
Clark, J.M., & Paivio, A. (1991). Dual coding theory and education. Educational Psychology Review, 3(3), 149-210. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320076
The Learning Scientists. (n.d.). Dual coding. The Learning Scientists. https://www.learningscientists.org/dual-coding
Weinstein, Y., Madan, C.R. & Sumeracki, M.A. (2018). Teaching the science of learning. Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41235-017-0087-y
Weinstein Y., & Smith, M. (2016, September 1). Learn how to study using… dual coding. The Learning Scientists. https://www.learningscientists.org/blog/2016/9/1-1
© Durham College. All rights reserved.

