6.7 How are eligible, non-eligible and capital dividends taxed in the hands of an individual? Are there any other tax implications? Why do they have different tax treatments?
Wahaj Awan
Eligible dividends are typically paid out by public corporations, from income that has been taxed at a higher corporate tax rate.
Non-eligible dividends are generally paid out by private corporations from income that has been taxed at a lower corporate tax rate. Note public corporations may sometimes declare a portion of their dividends as non-eligible (if some of their income has been taxed at lower corporate rates).
Once eligible or non-eligible dividends have been received by an individual, they are subject to gross-up rates. The grossed-up/taxable dividend is intended to reflect the corporate pre-tax income which is then taxed at the individual’s marginal tax rate. The individual is also given a dividend tax credit which is equivalent to the tax paid by the corporation on the dividends. (Refer to the “Integration” topic for an example).
|
Rates as of 2021 |
Gross-up rate (See ITA 82(1)(b)) |
Federal dividend tax credit (See ITA 121) |
|
Eligible dividends |
38% |
6/11 |
|
Non-eligible dividends |
15% |
9/13 |
(These rates can be found in the FITAC>Tax Rates and Tools under the heading “Eligible dividends reference tool”)
ITA 83(2) describes capital dividends as dividends paid by a corporation on the shares of the corporation’s capital stock.
ITA 83(2)(b) states “no part of the dividend shall be included in calculating the income of any shareholder of the corporation”. In other words, there is no tax on capital dividends.
Capital dividends are essentially the non-taxable 50% portion of a capital gain, which ‘flow-through’ tax free to the shareholder.
Suppose a private corporation has a capital gain of $2,000 and is paying out dividends on that amount. The tax treatment for the corporation and in the hands of the individual for this gain is as follows:
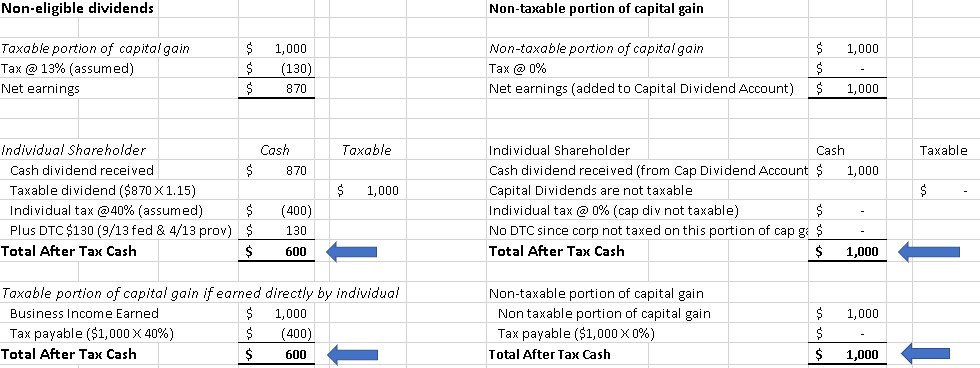
In the above example you should note that the after tax cash is the same ($1,000 from the capital dividend and $600 from the non-eligible dividend) regardless of whether the capital gain was earned by the corporation (with dividends paid out to the shareholder) or earned directly by the individual.
Interactive Content
Author: Danica McCormack, January 2020
Interactive Content
Author: Dilpreet Grewal, January 2020
Interactive Content
Author: Rini Vincent, January 2020
Interactive Content
Author: Harkamwar Toor, February 2020
References and Resources
- Income Tax Act, RSC 1985, c1, (5th Supp.) ss 82(1), 83(2), 89(1), 89(14)
- Video – “Integration” (Authors: Abjeet Khatra and Gursimran Kohli) – uses 2017 rates
- Article – “Eligible dividends” (Author: Government of Canada)
Image Description
Example comparing non-eligible dividends and the non-taxable portion of capital gain: A spreadsheet comparing the tax implications of non-eligible dividends and non-taxable portions of capital gains.
Non-Eligible Dividends:
- Corporate:
- Taxable portion of capital gain: $1,000
- Tax @ 13% (assumed): ($130)
- Net earnings: $870
- Individual Shareholder:
- Cash:
- Cash dividend received: $870
- Taxable:
- Taxable dividend ($870 x 1.15): $1,000
- Individual tax @ 40% (assumed): ($400)
- Plus Dividend Tax Credit (DTC) $130 (9/13 federal & 4/13 provincial)
- Total After Tax Cash: $600
- Cash:
- If Earned Directly by Individual:
- Taxable portion of capital gain: $1,000
- Tax payable ($1,000 x 40%): ($400)
- Total After Tax Cash: $600
Non-Taxable Portion of Capital Gain:
- Corporate:
- Non-taxable portion of capital gain: $1,000
- Tax @ 0%: $0
- Net earnings (added to Capital Dividend Account): $1,000
- Individual Shareholder:
- Cash:
- Cash dividend received (from Capital Dividend Account): $1,000
- Taxable:
- Capital Dividends are not taxable
- Individual tax @ 0% (capital dividends not taxable): $0
- No DTC since corporation is not taxed on this portion of capital gain: $0
- Total After Tax Cash: $1,000
- Cash:
- If Earned Directly by Individual:
- Non-taxable portion of capital gain: $1,000
- Tax payable ($1,000 x 0%): $0
- Total After Tax Cash: $1,000
Both scenarios show a comparison of after-tax cash amounts in different situations, indicating that non-taxable portions of capital gains result in higher after-tax cash.
[Return to Example comparing non-eligible dividends and the non taxable portion of capital gain]
“How are eligible, non-eligible and capital dividends taxed in the hands of an individual? Are there any other tax implications? Why do they have different tax treatments? ” from Introductory Canadian Tax Copyright © 2021 by Wahaj Awan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

