Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the means of mechanoreception for hearing.
The Vestibular System (Equilibrium)
Along with hearing, the inner ear is responsible for encoding information about equilibrium, the sense of balance. A similar mechanoreceptor—a hair cell with stereocilia—senses head position, head movement, and whether our bodies are in motion. These cells are located within the vestibule of the inner ear. Head position is sensed by the utricle and saccule, whereas head movement is sensed by the semicircular canals. The neural signals generated in the vestibular ganglion are transmitted through the vestibulocochlear nerve to the brain stem and cerebellum.
The semicircular canals are three ring-like extensions of the vestibule. One is oriented in the horizontal plane, whereas the other two are oriented in the vertical plane. The base of each semicircular canal, where it meets with the vestibule, connects to an enlarged region known as the ampulla. The ampulla contains the hair cells that respond to rotational movement, such as turning the head while saying “no.” The stereocilia of these hair cells extend into the cupula, a membrane that attaches to the top of the ampulla.
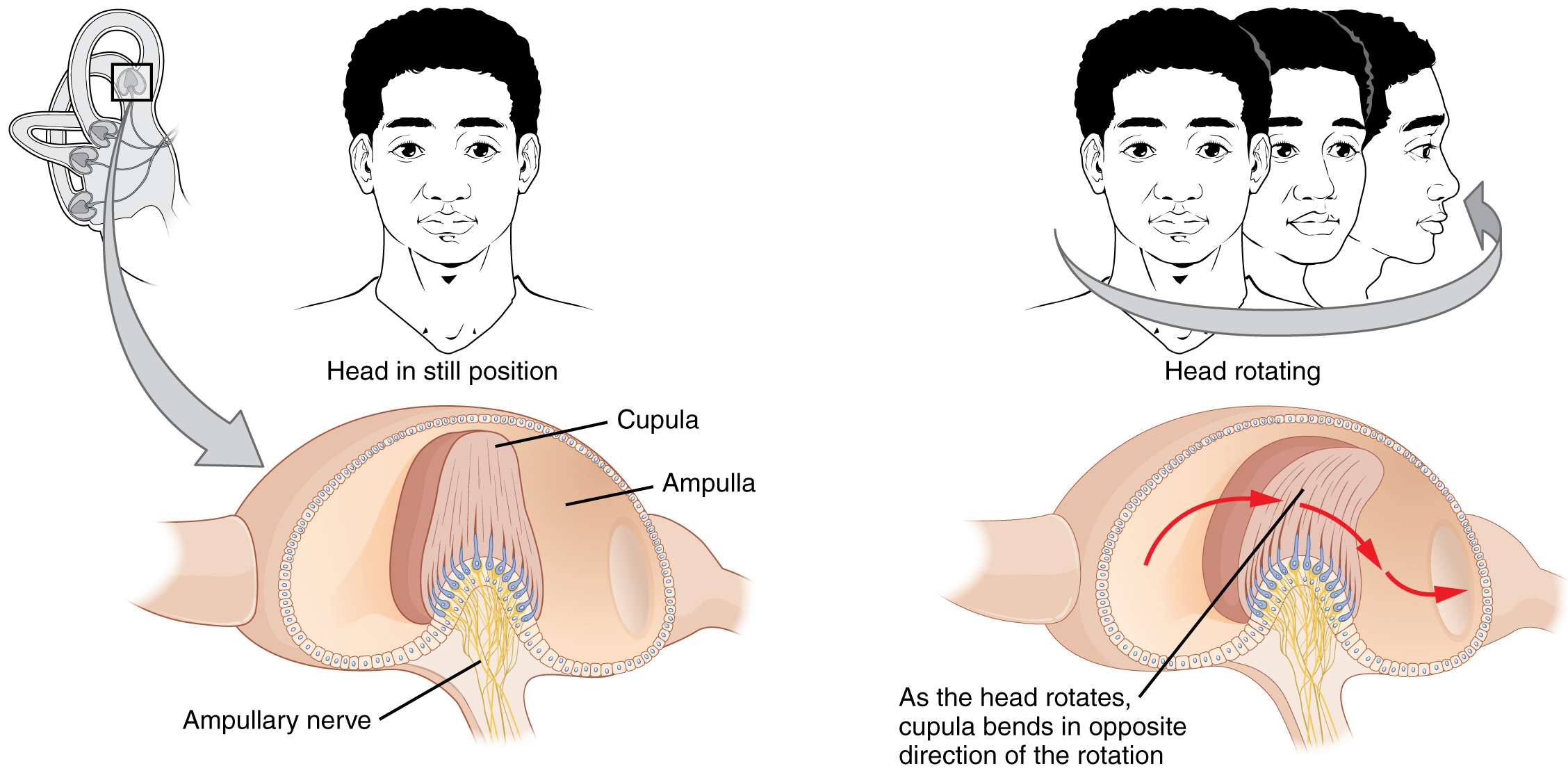
Rotational movement of the head is encoded by the hair cells in the base of the semicircular canals. As one of the canals moves in an arc with the head, the internal fluid moves in the opposite direction, causing the cupula and stereocilia to bend. The movement of two canals within a plane results in information about the direction in which the head is moving, and activation of all six canals can give a very precise indication of head movement in three dimensions.
Central Processing of Vestibular Information
Balance is coordinated through the vestibular system, the nerves of which are composed of fibers from the vestibular ganglion that carries information from the utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals. The system contributes to controlling head and neck movements in response to vestibular signals. An important function of the vestibular system is coordinating eye and head movements to maintain visual attention.
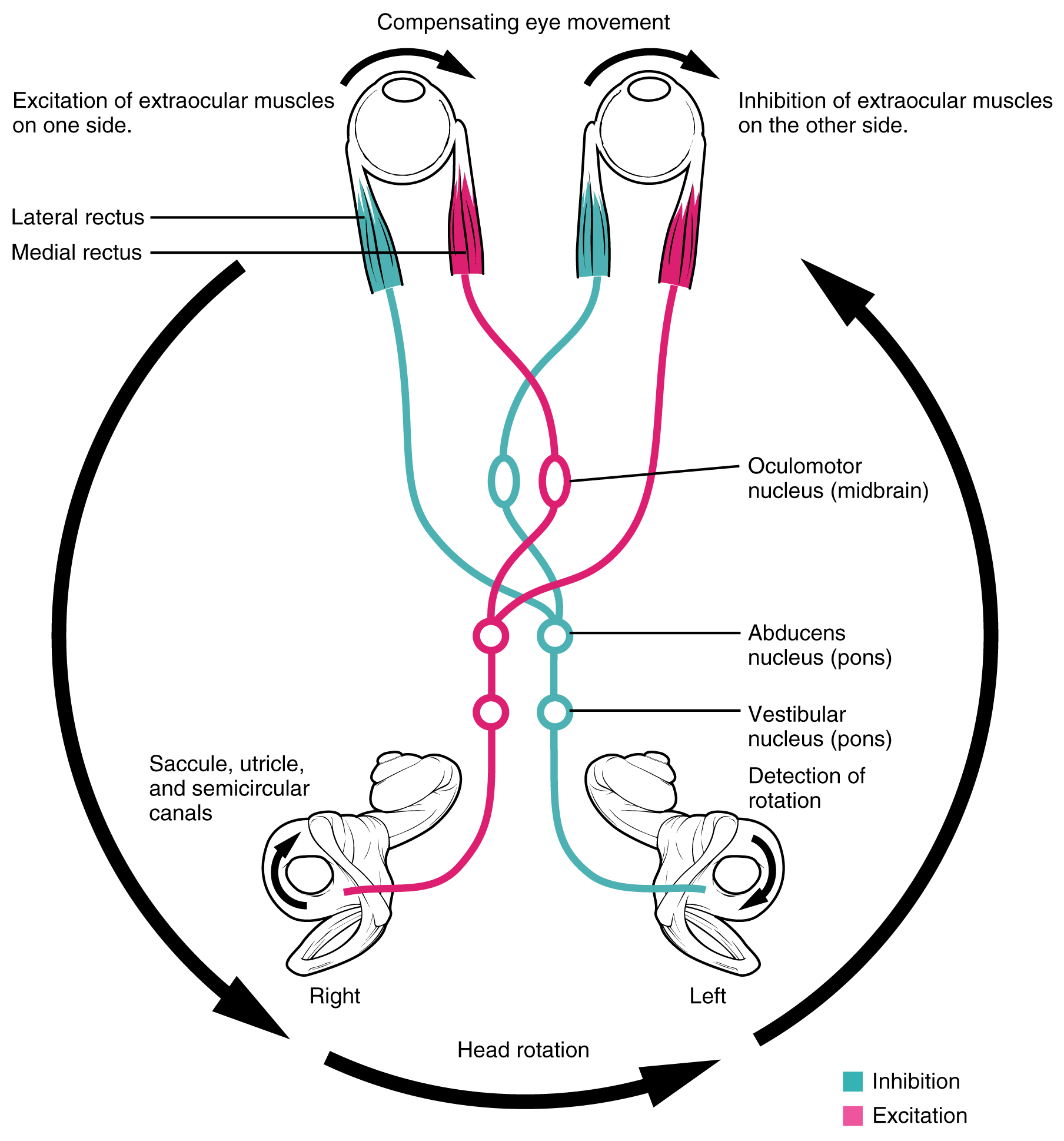
Neurons in the vestibular nuclei project their axons to targets in the brain stem. One target is the reticular formation, which influences respiratory and cardiovascular functions in relation to body movements. A second target of the axons of neurons in the vestibular nuclei is the spinal cord, which initiates the spinal reflexes involved with posture and balance. To assist the visual system, fibers of the vestibular nuclei project to the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nuclei to influence signals sent along the cranial nerves. These connections constitute the pathway of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR), which compensates for head and body movement by stabilizing images on the retina (Figure 15.4.3). Finally, the vestibular nuclei project to the thalamus to join the proprioceptive pathway of the dorsal column system, allowing conscious perception of equilibrium.
This work, Anatomy & Physiology, is adapted from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, licensed under CC BY. This edition, with revised content and artwork, is licensed under CC BY-SA except where otherwise noted.
Images, from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, are licensed under CC BY except where otherwise noted.
Access the original for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.

