7.7 Risk Reporting
Risk reporting is a critical process in organizational risk management, serving as the primary means of communicating vital risk-related information to key stakeholders, particularly senior management and the board of directors. This process involves systematically collecting, analyzing, and presenting data about an organization’s risk landscape, enabling informed decision-making and effective risk oversight.
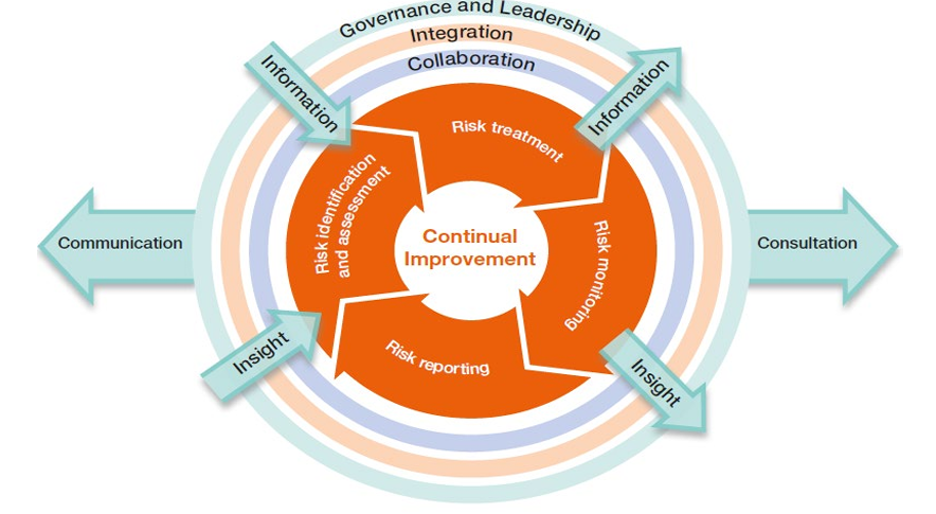
Image Description
A series of circles and arrows with Continual Improvement in the centre. In the first circle, Risk treatment, Risk monitoring, Risk reporting, and Risk identification and assessment. There are two arrows pointing in called lnsight and Information, and two pointing out labelled Insight and Information. The next three circles (inside to outside) are Collaboration, Integration, Governance and Leadership. An arrow from the outside circle pointing left is Communication and an arrow pointing right is labelled Consultation.
- Contents: Risk reporting aims to provide a clear, comprehensive picture of the organization’s significant risks. This includes identifying key risks, assessing their potential impact and likelihood, and detailing the status of risk mitigation efforts. Effective risk reports highlight emerging risks and trends, ensuring that leadership remains aware of evolving threats and opportunities.
- Format: Risk reporting may combine visual elements like risk dashboards or heat maps with more detailed narrative reports. This approach allows for quick comprehension of the overall risk profile while providing depth where needed. The reporting frequency typically follows a regular schedule, often quarterly, supplemented by ad-hoc reports for significant risk events or changes in the risk landscape.
- Internal Audit Role: It plays a crucial role in this process, offering independent assurance on the effectiveness of risk management processes and providing valuable insights on risk trends. Their involvement enhances the credibility and objectivity of risk reporting, supporting the board and senior management in their oversight responsibilities.
- Best Practices: Best practices in risk reporting emphasize clarity, conciseness, and relevance. Reports should focus on the most significant risks, provide context and analysis beyond raw data, and include recommendations for risk mitigation where appropriate. This approach ensures that risk information is not only comprehensive but also actionable.
Effective risk reporting is fundamental to fostering a risk-aware culture throughout the organization. Providing a clear view of the risk landscape enables leadership to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and navigate the complex, ever-changing business environment with greater confidence and resilience (Financial Reporting Council, 2014; PWC, 2011; UK Government, 2023).

