1.1 Introduction
In this textbook, you’ll learn how to recruit employees and choose well, from the attraction phase through the selection phase, and how to avoid related legal liabilities.
Importance of Recruitment and Selection
Recruiting and selecting new employees can make or break a company. An employee represents, in the financial sense, a very high-risk investment. A company’s personnel costs may be a business’ single largest expense. Choose well, and your employees can be a source of competitive advantage. On the other hand, a poor choice can represent a critical liability. Human Resources is a very broad field. Recruitment and selection are but one component of the HR system.
Figure 1.1.1 (below) shows recruitment and selection grouped around the broader function of talent management, which includes recruitment, selection, retention and development of superior employees.
What is Human Resources?
Human Resources (HR) includes a broad range of functions and responsibilities that focus on managing and supporting the employees in an organization. HR ensures that the organization operates smoothly by handling everything related to employee management, from hiring to retirement. Talent management is a core function of Human Resources. Talent management includes processes that help attract, develop, and retain high-performing employees, a key element of gaining a competitive advantage.
To this end, the HR talent management process contains the following sequenced activities:
- Job analysis and design
- Human resource planning and forecasting
- Employee recruitment
- Employee selection
- Training and development
- Performance planning and evaluation
- Compensation and benefits
In this textbook, we will examine only the recruitment and selection functions of talent management.
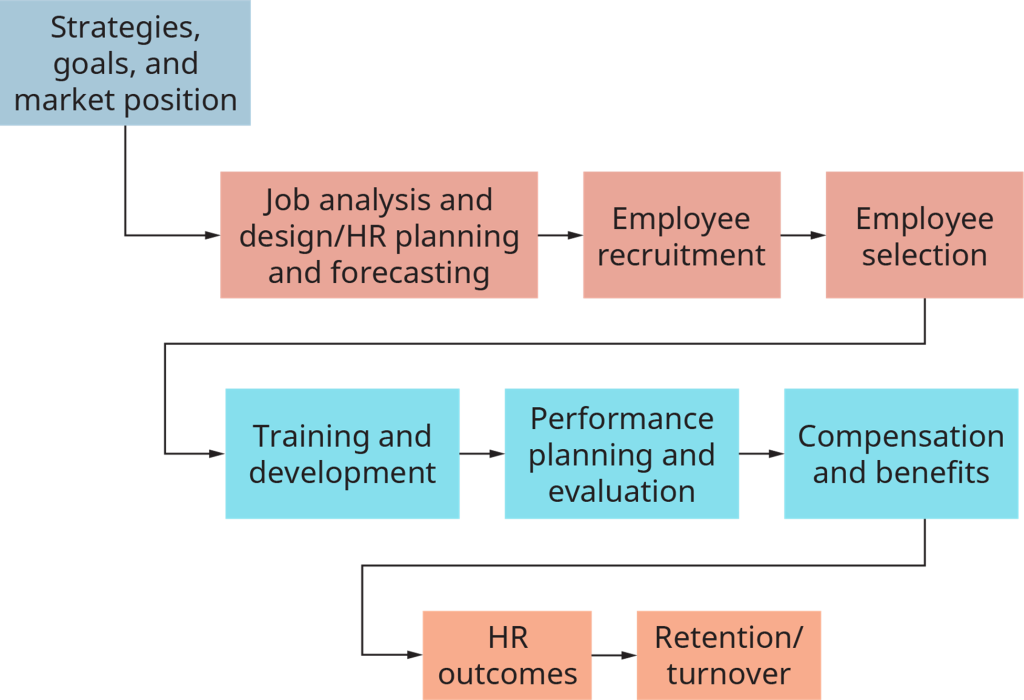
Image Description
The image contains a flowchart of the responsibilities of a Human Resources department. The points read:
- Strategies, goals, and market position
- Job analysis and design/HR planning and forecasting
- Employee recruitment
- Employee selection
- Training and development
- Performance planning and evaluation
- Compensation and benefits
- HR outcomes
- Retention/turnover
Recruitment is the process of attracting a pool of potential candidates for a job opening.
Selection involves assessing and choosing the best-fit candidate from that pool.
Recruitment
The goal of the recruitment process is to generate a pool of qualified candidates. It is the first step in the hiring process.
Recruiting is the art of attraction, a process that requires a clear understanding of what makes the company unique as well as what type of person a company wants to attract.
Recruitment of talented employees is an essential part of any company’s ability to maintain a successful organization. Recruiting employees consists of actively compiling a diverse pool of potential candidates who can be considered for employment. It is beneficial to attract not just a large quantity of applicants but a group of applicants with the necessary skills for the position. A good recruitment policy will do this in a timely, cost-efficient manner. The ultimate goal of any human resources recruitment policy is to develop relationships with potential employees before they may actually be needed. In different industries, the constant need for talent creates a highly competitive market for individuals, and it is important for any hiring manager to be aware of these factors as they develop recruitment programs and policies.
Selection
The next step in the hiring process is choosing job candidates from a previously generated applicant pool. After obtaining a large, qualified applicant base through recruitment, managers need to identify those applicants with the greatest potential for success in the organization. Selective hiring is critical because it reduces future staff turnovers, reduces costs, and increases morale and productivity. To find the best fit, managers create a list of relevant criteria composed of critical skills, behaviours, and attitudes for each position. HR managers should choose candidates based on how they think they will fit within the culture of the organization, in addition to their technical skills and competencies.
“Why it Matters: Recruiting and Selecting new Employees” from Business Communication Skills for Managers by Nina Burokas is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license, except where otherwise noted.—Modifications: Used first paragraph.
“7.1 What is Human Resources” from Introduction to Management by Kathleen Rodenburg, Michael Conway, and Karley Dajka is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license, except where otherwise noted.—Modifications: Used HR Management Process.
“Recruiting Workers” from Small Business Management from Saylor Academy is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license, except where otherwise noted.—Modifications: Used first paragraph.
“The Psychology of Recruiting and Selecting Employees” from Human Resource Management from Saylor Academy is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license, except where otherwise noted.—Modifications: Used Selection section.
OpenAI. (2024, August 20). ChatGPT. [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
Prompt: “Provide definitions for the terms Recruitment and Selection in the context of Human Resource Management.”

