Growth in the Hemispheres and Corpus Callosum: Between ages 3 and 6, the left hemisphere of the brain grows dramatically. This side of the brain or hemisphere is typically involved in language skills. The right hemisphere continues to grow throughout early childhood and is involved in tasks that require spatial skills, such as recognizing shapes and patterns.
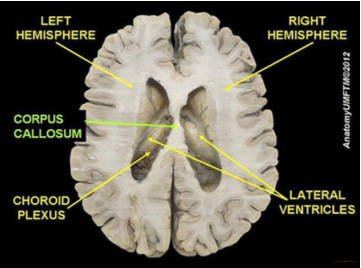
The corpus callosum is located a couple of inches below the longitudinal fissure, which runs the length of the brain and separates the two cerebral hemispheres (Garrett, 2015). Because the two hemispheres carry out different functions, they communicate with each other and integrate their activities through the corpus callosum. Additionally, because incoming information is directed toward one hemisphere, such as visual information from the left eye being directed to the right hemisphere, the corpus callosum shares this information with the other hemisphere.
The corpus callosum undergoes a growth spurt between ages 3 and 6, and this results in improved coordination between right and left hemisphere tasks. For example, in comparison to other individuals, children younger than 6 demonstrate difficulty coordinating an Etch A Sketch toy because their corpus callosum is not developed enough to integrate the movements of both hands (Kalat, 2016).
Neuroplasticity: The control of some specific bodily functions, such as movement, vision, and hearing, is performed in specified areas of the cortex, and if these areas are damaged, the individual will likely lose the ability to perform the corresponding function. For instance, if an infant suffers damage to facial recognition areas in the temporal lobe, it is likely that he or she will never be able to recognize faces (Farah, Rabinowitz, Quinn, & Liu, 2000). On the other hand, the brain is not divided up in an entirely rigid way. The brain’s neurons have a remarkable capacity to reorganize and extend themselves to carry out particular functions in response to the needs of the organism, and to repair damage. As a result, the brain constantly creates new neural communication routes and rewires existing ones. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to change its structure and function in response to experience or damage. Neuroplasticity enables us to learn and remember new things and adjust to new experiences. Our brains are the most “plastic” when we are young children, as it is during this time that we learn the most about our environment. On the other hand, neuroplasticity continues to be observed even in adults (Kolb & Fantie, 1989).

