Transmission Model of Communication
The Transmission Model of communication (see Figure below) describes communication as a linear, one-way process in which a sender intentionally transmits a message to a receiver (Ellis & McClintock, 1990). This model focuses on the sender and the message within a communication encounter. Although the receiver is included in the model, this role is viewed as more of a target or end point rather than part of an ongoing process. In this case, one presumes that the receiver either successfully receives and understands the message or does not. As such, this model is not representative of effective communication for how messages are received.
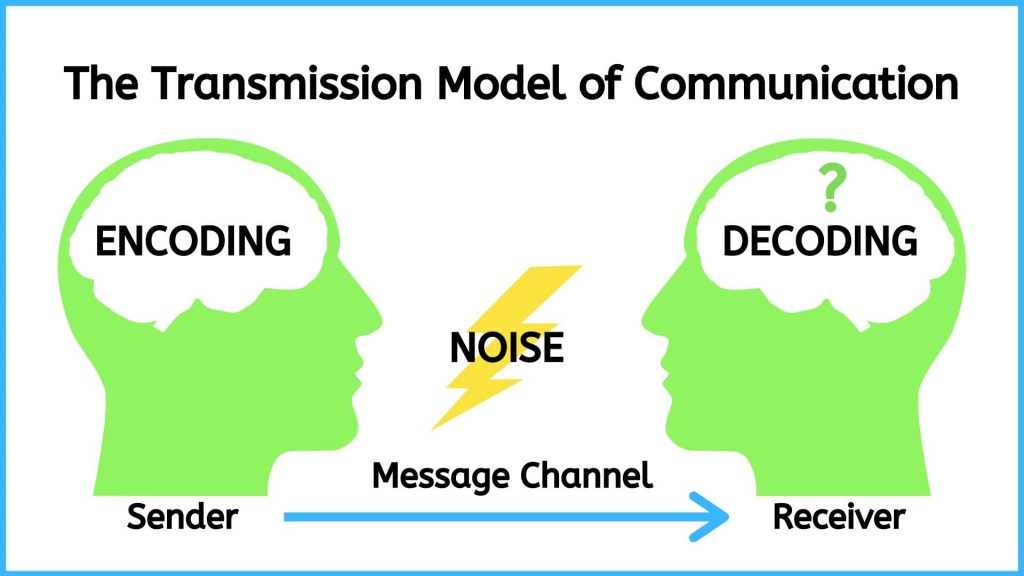
Figure: The Transmission Model of Communication
Because this model is sender- and message-focused, responsibility is put on the sender to help ensure the message is successfully conveyed. This model emphasizes clarity and effectiveness, but it also acknowledges that there are barriers to effectively sending communication. Noise is anything that interferes with a message being sent between participants in a communication encounter. Even if a speaker sends a clear message, noise may interfere with a message being accurately received and decoded. The Transmission Model of communication accounts for environmental and semantic noise.
- Environmental noise is any physical noise present in a communication encounter. Other people talking in a crowded hallway could interfere with your ability to transmit a message and have it successfully decoded.
- Semantic noise refers to an interference that occurs in the encoding and decoding process resulting in different interpretations of what is being communicated (e.g., lack of understanding, clarity, and confusion of words and meanings).
Attribution Statement
Content was adapted from (with editorial changes):
Communication in the Real World: An Introduction to Communication Studies by University of Minnesota. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

