2.2. Solved Examples: Vectors and Scalars; Vector Components
Example 1
A car moves at [latex]45 \text{ m/s}[/latex], [latex]40\text{°}[/latex] north of east. Find the x and y components of the velocity vector.
Diagram:
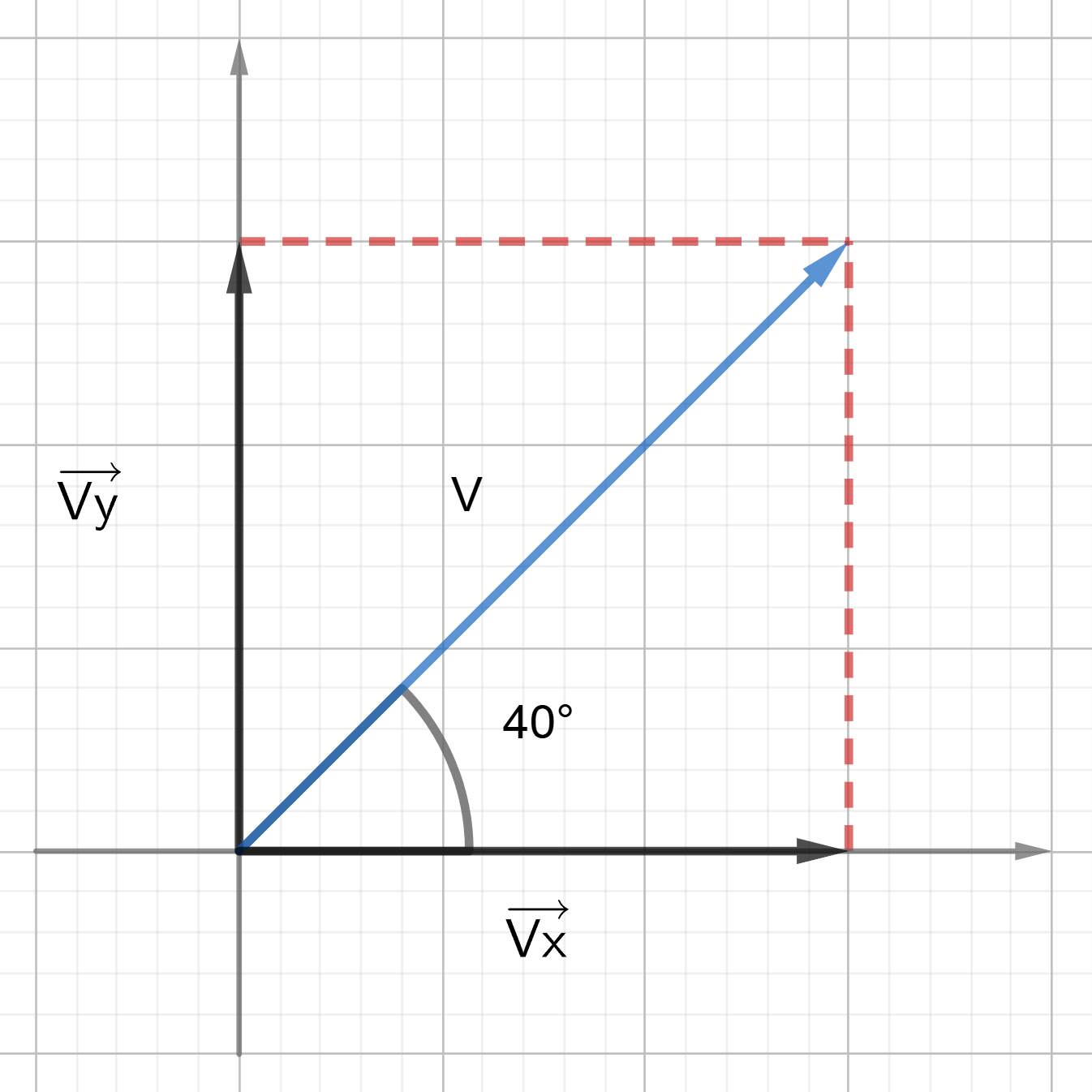
Solution:
[latex]v_{x} = v \times \cos \theta = 45 \times \cos 40^\circ = 34.47 \text{ } \frac{m}{s} \simeq 34 \text{ } \frac{m}{s}[/latex]
[latex]v_{y} = v \times \sin \theta = 45 \times \sin 40^\circ = 28.93 \text{ } \frac{m}{s} \simeq 29 \text{ } \frac{m}{s}[/latex]
Example 2
A crate is subjected to a [latex]125 \text{ N}[/latex] force directed [latex]30 \text{°}[/latex] west of south. Find the components of the force.
Diagram:
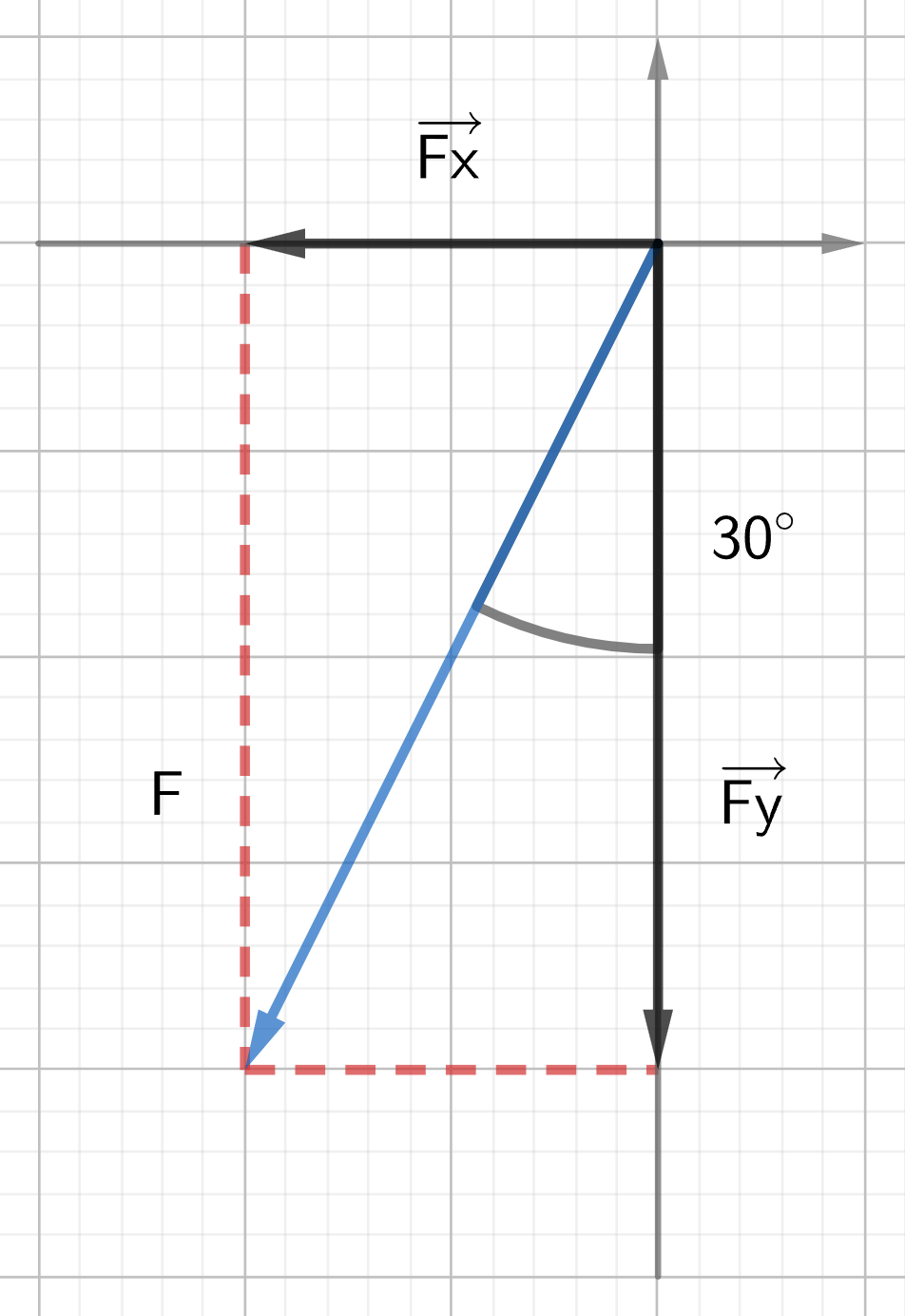
Solution:
Since the given angle is an angle with the y-axis, we first need to calculate the angle with the x-axis (the reference angle).
[latex]\alpha = 90^\circ - 30^\circ = 60^\circ[/latex]
The components are:
[latex]F_{ x} = -F \times \cos \alpha = -125 \times \cos 60^\circ = -62.5 \text{ } N[/latex][latex]F_{y} = -F \times \sin \alpha = 125 \times \sin 60^\circ = -108.25 \text{ } N \simeq -108 \text{ } N[/latex]
Note: When using the reference angle to calculate the components, the sign has to be adjusted depending on the quadrant in which the vector is positioned. In the example above, the vector is in the third quadrant, meaning both the x component and y component are negative.
Image Attributions
- Figure 2.2 - 2.3: Created with Geogebra and licensed under CC-BY-NC-SA 3.0.

