7.2. Solved Examples: Force of Friction and Normal Force; Free Body Diagrams
Example 1
A [latex]17 \, \text{kg}[/latex] toolbox sits on a level floor. A worker uses a rope and pulls the toolbox with a force F (see diagram below). The coefficients of static friction and kinetic friction between the toolbox and the floor are [latex]0.65[/latex], respectively [latex]0.40[/latex].
- Find the pulling force needed to just set the toolbox in motion.
- If then, the toolbox continues to move with an acceleration of [latex]0.20 \,\text{m/s}^2[/latex], find the new force needed to maintain this acceleration.
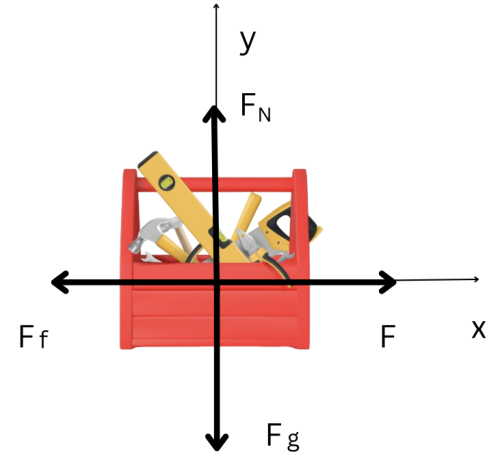
[latex]m = 17 \text{ kg}[/latex]
[latex]\mu_s = 0.65[/latex]
[latex]\mu_k = 0.40[/latex]
[latex]a = 0.20 \text{ m/s}^2[/latex]
[latex]\text{(a)} \quad F = ?[/latex]
[latex]\text{(b)} \quad F_1 = ?[/latex]
Solution:
- The pulling force must overcome the friction for the toolbox to start moving.
[latex]F > F_f[/latex], but [latex]F_f = \mu_s F_N[/latex]
Analyze the motion on the axis (axes). Ask the question: Is this a situation of equilibrium?
Since [latex]F_N[/latex] is positioned on the y axis, we need to ask the equilibrium question about the [latex]y[/latex] axis.
On the y axis we have a situation of equilibrium because the toolbox is not moving on the [latex]y[/latex] axis. This means that:
[latex]F_{\text{net}, y} = 0[/latex]
[latex]F_{\text{net}, y} = F_N - F_g = 0, \quad \text{or} \quad F_N = F_g[/latex]
On the other hand,
[latex]F_g = m \times g[/latex]
Substitute the expressions into [latex]F_f[/latex] :
[latex]F_f = \mu_s \times m \times g = 0.65 \times 17 \times 9.8 = 108.29 \text{ N}[/latex]
Answer:
[latex]F > 108.29 \text{ N}[/latex]
- Analyze the motion on the axis (axes).
Ask the question: Is this a situation of equilibrium? Since F is positioned on the x axis, we need to ask the equilibrium question about the [latex]x[/latex] axis.On the [latex]x[/latex] axis we do not have a situation of equilibrium because the toolbox is moving with an acceleration. In this case we use Newton’s second law and the net force on the x axis to solve the question:[latex]\text{(a)} \quad F_{\text{net}} = m \times a[/latex]
[latex]\text{(b)} \quad F_{\text{net}} = F - F_f[/latex]
Since expressions (a) and (b) represent the same net force, we can equal them:
[latex]F - F_f = m \times a[/latex]
Solving for [latex]F[/latex]:
[latex]F = F_f + m \times a = \mu_k \times m \times g + m \times a = 0.40 \times 17 \times 9.8 + 17 \times 0.20 = 70.04 \text{ N}[/latex]
Answer:
[latex]F = 70.04 \text{ N}[/latex]
Notes
- Recall: Equilibrium occurs when either the object is at rest, or it moves at a constant speed.
Equations to use:[latex]F_{\text{net}, x} = 0[/latex]
[latex]F_{\text{net}, y} = 0[/latex]
- Recall: An object moving with an acceleration is not in a situation of equilibrium.
Equations to use:[latex]F_{\text{net}} = m \times a[/latex]
[latex]F_{\text{net}} = \sum \vec{F}[/latex]
Try it!
- A sled is being pulled by a child with a rope that makes a [latex]30°[/latex] angle with the vertical. The sled is moving horizontally at a constant speed. Which one of the following statements are true?
- Equilibrium situation on both [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] axes
- Equilibrium situation only on [latex]y[/latex]
- Equilibrium situation only on [latex]x[/latex]
- The normal force is always directed:
- Parallel to the contact surface
- Opposing the motion of the object
- Perpendicular on the contact surface
- If an object moves horizontally at a constant speed due of a horizontal pulling force of [latex]50 \text{ N}[/latex], what is the force of friction?
- Not enough information to calculate it
- [latex]50 \text{ N}[/latex]
- [latex]490 \text{ N}[/latex]
Image Attributions
- Figure 7.5 adapted from:
- Tool Box by pikisuperstar courtesy of Freepik

