Collisions I Exercise 2: Identical Cart Collision
Exercise 2: Identical Cart Collision
2.1 Using your setup system from Exercise 1, have the carts collide (magnet-to-magnet). Start with one cart stationary and push the other cart to collide. You will want to expand the relevant region of the graph so that your measurement looks as close to the graph below as possible.
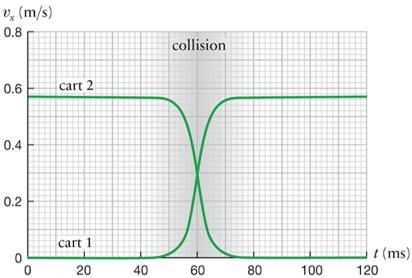
From your measurements, does it appear that the changes in velocity of the two carts are equal and opposite as Mazur asserts?
2.2 Mazur claims that identical carts will exhibit this velocity-exchange behaviour no matter what the starting conditions. Can you confirm this experimentally in the following variations of the magnet-to-magnet collision? (In each case, try to collect a set of data in which you can cleanly measure the velocities before and after the collision.) Note: You do not need to “Delete Last Run” every time, in fact you will want to be able to display previous runs. Instead, just press record again, and the previous run will be saved.
a) Have both carts in motion in the same (positive) direction before the collision.
b) Have the carts collide head-on (GENTLY) with different velocities. (The analysis is a little more complicated here. You’ll see….)
