Exercise 3: Ball Thrown Up
Exercise 3.1 (1 mark)
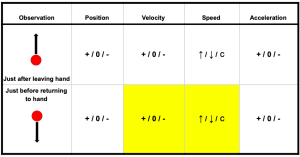
Fill in chart by circling one of each:
+ (positive) / 0 (zero) / – (negative)
and
↑ (increasing with time) / ↓ (decreasing with time) / c (constant with time)
Remember: Velocity and acceleration have a magnitude and direction.
On Crowdmark choose the correct version(s) of the table.
Exercise 3.2 (1 mark)
a. The velocity is zero and the speed is decreasing since the object is experiencing a constant negative acceleration.
b. The velocity is negative and the speed is decreasing since the object is experiencing a constant positive acceleration.
c. The velocity is positive and the speed is constant.
d. The velocity is zero and the speed is increasing since the object is experiencing a constant negative acceleration.
e. The velocity is negative and the speed is increasing since the object is experiencing a constant negative acceleration.
Before you continue!
Before continuing, be sure you have completed Exercises 3.1 and 3.2 on Crowdmark for grading.

