36 Main Ideas
Concept Map
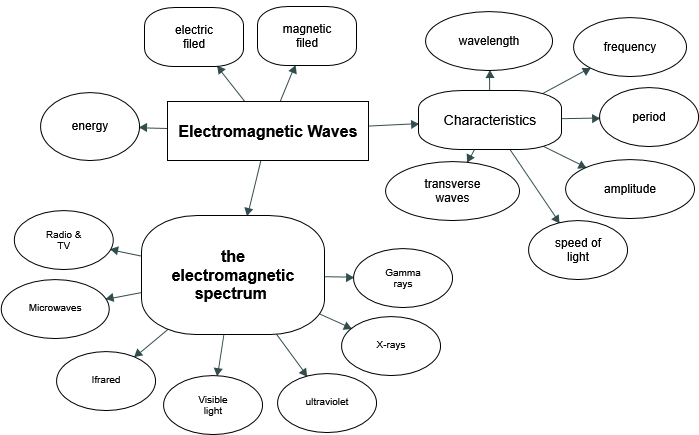
Key Terms
amplitude
the height, or magnitude, of an electromagnetic wave
- electromagnetic spectrum
- the full range of wavelengths or frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
- electromagnetic waves
- radiation in the form of waves of electric and magnetic energy
frequency
the number of complete wave cycles (up-down-up) passing a given point within one second (cycles/second)
- gamma ray
- extremely high frequency electromagnetic radiation emitted by the nucleus of an atom, either from natural nuclear decay or induced nuclear processes in nuclear reactors and weapons.
- hertz
- an SI unit denoting the frequency of an electromagnetic wave, in cycles per second
- microwaves
- electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the range from 1 mm to 1 m; they can be produced by currents in macroscopic circuits and devices
- oscillate
- to fluctuate back and forth in a steady beat
- radar
- a common application of microwaves. Radar can determine the distance to objects as diverse as clouds and aircraft, as well as determine the speed of a car or the intensity of a rainstorm
- radio waves
- electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the range from 1 mm to 100 km; they are produced by currents in wires and circuits and by astronomical phenomena
speed of light
in a vacuum, such as space, the speed of light is a constant 3 x 108 m/s
transverse wave
a wave, such as an electromagnetic wave, which oscillates perpendicular to the axis along the line of travel
- visible light
- the narrow segment of the electromagnetic spectrum to which the normal human eye responds
- wavelength
- the distance from one peak to the next in a wave
- X-ray
- invisible, penetrating form of very high frequency electromagnetic radiation, overlapping both the ultraviolet range and the gamma-ray range
More terms can be found in the textbook, chapter 24

