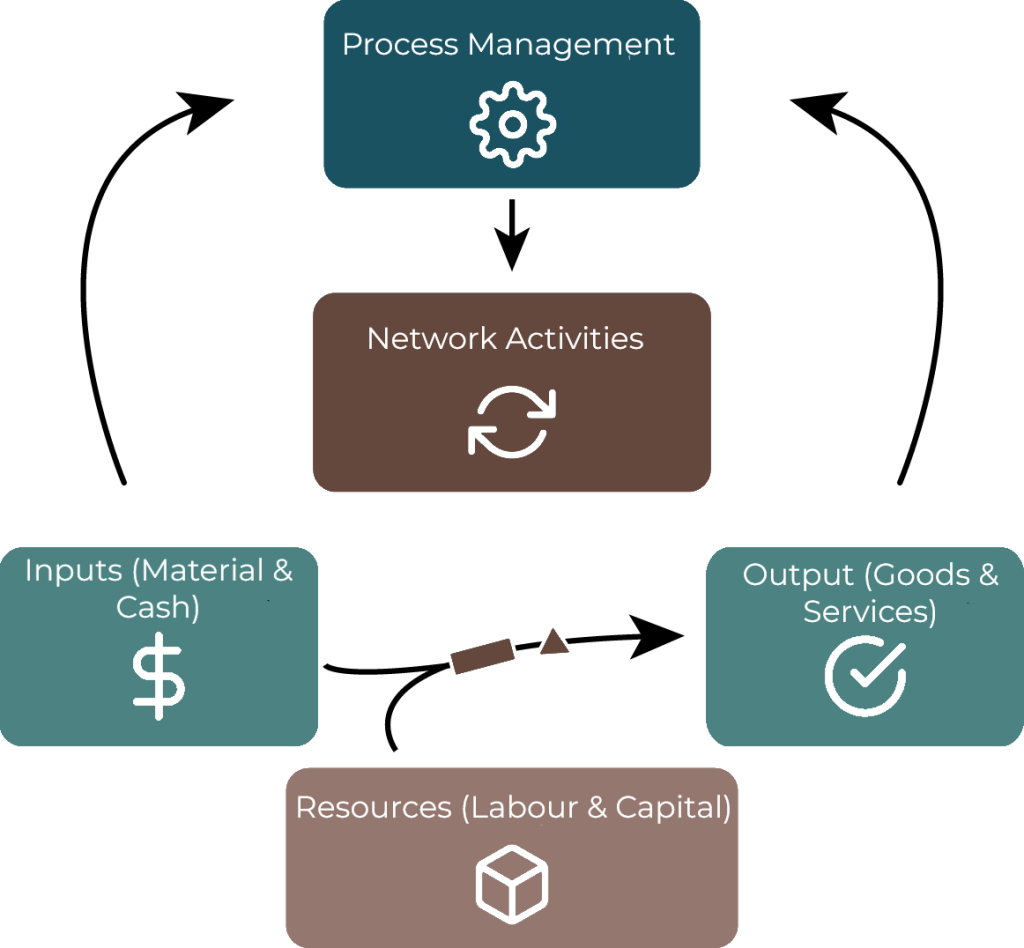
5.2 Process Management
Process management refers to the systematic planning, execution, and monitoring of business processes to ensure they operate efficiently and effectively. A business process is a structured network of interrelated activities that utilize available resources to transform inputs into valuable outputs.
At its core, process management involves the application of managerial principles and practices aimed at optimizing process performance over time. The ultimate goal is to align process outcomes with the strategic objectives of the organization, thereby enhancing overall effectiveness and profitability.
Process management typically encompasses both business processes (such as customer service, procurement, and logistics) and manufacturing processes (such as production and quality control).
It involves a comprehensive set of activities, including:
- Defining the process structure and objectives
- Visualizing workflows and interdependencies
- Measuring performance using relevant metrics
- Controlling process execution to ensure consistency
- Reporting outcomes for transparency and accountability
- Improving processes through continuous refinement and innovation
To meet evolving customer requirements and maintain a competitive advantage, organizations must leverage a combination of knowledge, skills, tools, techniques, and systems. These elements form the foundation of effective process management and enable organizations to deliver value in a sustainable and profitable manner.
“4. Process Management: Types of Process and its Implication in Operation Strategy” from Operations Management by Sudhanshu Joshi is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.—Modifications: Used sections 2-2.2; reworded; added further content.

