4.2 Process of New Product Development
The New Product Development (NPD) process is a systematic sequence of activities undertaken by organizations to conceive, design, test, and evaluate the market viability of new products or services. The overarching objective of a robust NPD process is to drive organizational growth and ensure long-term sustainability by introducing offerings that meet evolving customer needs and provide a competitive advantage. This process typically involves a series of well-defined stages, as outlined below:
Step 1: Idea Generation
The first step in the new product development process is idea generation. This phase involves a systematic and continuous search for new product development opportunities. Organizations explore various sources and methods to support their ideas, aiming to identify innovative concepts that can lead to successful products. This step includes several types of analyses, each contributing uniquely to the idea generation process:
Dimensional Analysis:
Dimensional analysis examines all physical characteristics of a product, providing a comprehensive list of these attributes. This analysis helps organizations understand the fundamental aspects of their product’s design and functionality. By asking questions such as “Why is the product designed this way?”, “How could the product be improved?” and “What would happen if one or more characteristics were altered?” Organizations can identify potential areas for enhancement or innovation. This method encourages a deep dive into the product’s physical properties, fostering creative thinking about possible modifications and improvements.
Problem Analysis:
Problem analysis focuses on identifying issues consumers face with existing products or services. Organizations conduct thorough investigations to uncover the challenges and frustrations experienced by users. By understanding these problems, organizations can develop new products that better meet consumer needs. This analysis often involves collecting feedback from customers, analyzing complaints, and studying usage patterns to pinpoint specific areas where current products fall short. The insights gained from problem analysis are crucial for designing solutions that address real-world issues, and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Benefit Structure Analysis:
Benefit structure analysis identifies the benefits consumers seek in a product. Organizations use questionnaires and surveys to gather this information directly from customers, ensuring the new product aligns with consumer desires. This analysis involves compiling a list of desired features and benefits, which serves as a blueprint for product development. By understanding what consumers value most, organizations can prioritize these elements in their design process, creating products that resonate with their target audience. This method helps bridge the gap between consumer expectations and product offerings, leading to more successful and well-received products.
Scenario Analysis:
Scenario analysis involves assessing market opportunities for new products or services. Companies analyze current market trends, competitive landscapes, and potential future developments to understand the opportunities and challenges they may face. This analysis helps organizations anticipate changes in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and economic conditions that could impact their product’s success. By exploring various scenarios, companies can develop strategic plans to navigate the complexities of the market, positioning their new products for optimal performance. Scenario analysis is a forward-looking approach that equips organizations with the insights needed to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Step 2: Idea Screening
Idea screening is the second step in the new product development process. After identifying potential ideas, it is essential for the firm to screen them to ensure only the most promising concepts move forward. During idea screening, the firm eliminates poor, unsound, unsuitable, and unattractive ideas, focusing only on feasible ideas with potential for sustainability and growth. This step is crucial for refining the pool of ideas and ensuring that resources are invested in the most viable options.
Idea Screening Questions

In the idea screening phase, companies seek answers to the following questions:
- Will the product be beneficial for the customer in the target market?
- This question assesses whether the proposed product will meet the needs and preferences of the target market. Companies evaluate the potential benefits the product offers to customers, ensuring it addresses their pain points and provides value.
- What is the current and expected future competition for the product idea?
- Understanding the competitive landscape is vital. Companies analyze existing competitors and anticipate future competition to determine if the product can stand out in the market. This involves studying competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning.
- What are the industry sales and market trends on which the product idea is based?
- Companies examine industry sales data and market trends to gauge the potential demand for the product. This analysis helps in understanding the market dynamics and identifying growth opportunities. It includes evaluating historical sales figures, current market conditions, and future projections.
- Is it technically feasible for the firm to manufacture such a product?
- Technical feasibility is a critical consideration. Companies assess whether they have the necessary technology, expertise, and resources to produce the product. This involves evaluating manufacturing capabilities, supply chain logistics, and potential technical challenges.
- Will the product be profitable for the firm when it is manufactured and delivered to the customer at the target price?
- Profitability is a key factor in idea screening. Companies analyze the cost of production, pricing strategies, and potential profit margins to ensure the product will be financially viable. This includes calculating the cost of materials, labour, distribution, and marketing, as well as estimating the expected revenue.
Step 3: Concept Testing
Concept testing involves presenting the product concept to consumers to gauge their reactions and intentions at this early stage of development. This process helps companies determine whether any changes are needed before proceeding further. Concept testing is crucial for avoiding costly mistakes by identifying potential issues and areas for improvement early on. It is a quick and inexpensive method for measuring consumer enthusiasm and gathering valuable feedback.
During concept testing, companies typically seek to understand the following:
- Consumer Reactions
- Intentions to Purchase
- Suggestions for Improvement
- Perceived Value
- Market Fit
Overall, concept testing is an essential step in the new product development process, providing valuable insights that help companies refine their product concepts and increase the likelihood of market success.
Step 4: Market Strategy Development
The next step in the new product development process is market strategy development. At this stage, firms carefully define key aspects that will guide the product’s entry and growth in the market. This includes determining the target market size and structure, establishing how the product will be positioned against competitors, and setting specific goals for sales, market share, and profitability for the initial years after launch.
Additionally, companies decide on the planned pricing strategy, distribution channels, and allocate a marketing budget to support the product during its introduction and early growth phases. Effective market strategy development is essential for maximizing the product’s chances of success in a competitive marketplace.
Overall, market strategy development is a comprehensive process that lays the foundation for the product’s successful launch and growth in the market.
Step 5: Business and Financial Analysis

Business and financial analysis is an important step in the new product development process. It involves estimating the total costs involved in developing and marketing the product, including research, production, and distribution expenses. Firms also assess how much investment they can allocate based on their financial capacity.
To evaluate profitability, companies perform cost-benefit analyses, comparing expected revenues with costs. Key financial measures such as break-even point and return on investment (ROI) help determine whether the product is financially viable.
Additionally, firms decide how to finance the project. They may use equity funds (owners’ capital) or debt funds (loans from banks or other lenders), or a combination of both. The choice depends on the firm’s financial strategy and resources.
In summary, business and financial analysis helps firms understand the costs, investment needs, profitability, and funding options to support successful product development.
Step 6: Test Marketing
Test marketing is a crucial step in the new product development process. In this stage, the new product is launched on a limited scale, typically in one or more carefully selected geographic areas or market segments. The primary goal is to evaluate the product’s real-world performance before committing to a full-scale launch.
Through test marketing, firms can observe how actual consumers respond to the product under normal market conditions. This process provides valuable insights into consumer behaviour, including purchase patterns, usage, and overall satisfaction. Companies can also assess the effectiveness of their marketing strategies, such as pricing, promotion, and distribution methods.
The feedback and data collected during test marketing help firms identify potential improvements or modifications needed for the product or its marketing approach. Ultimately, test marketing reduces the risks associated with a nationwide or global product launch by allowing companies to make informed decisions based on actual market reactions.
Step 7: Commercialization
Commercialization is the final and most significant step in the new product development process. Once the product has successfully passed the test marketing phase, the firm is ready to launch the product to its entire target market. This stage marks the beginning of the product’s entry into the introductory phase of the product life cycle.
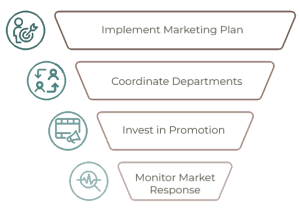
During commercialization, the company implements its complete marketing plan, which includes large-scale production, widespread distribution, and full-scale promotional activities. This involves coordinating efforts across various departments, such as manufacturing, sales, logistics, and customer service, to ensure a smooth and successful market introduction.
Commercialization also requires significant investment in advertising, sales promotions, and distribution channels to build product awareness and encourage consumer adoption. The company closely monitors the market response, sales performance, and customer feedback to make any necessary adjustments in strategy.
Overall, commercialization is a critical phase that determines the long-term success of the new product in the marketplace. It transforms the product from a concept into a commercially available offering, aiming to achieve strong market presence and profitability.
“8. New Product Development” from Operations Management by Sudhanshu Joshi is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.—Modifications: Used sections 5.1-5.7; reworded; added further content.

