5.2 Animation & Transitions in Presentations
Introduction to Transitions
Slides don’t have to be static. On this page we’ll look at how to apply transition effects between slides; we’ll explore animations, from making bullet points appear to making objects move and dance in the most elaborate ways. We’ll also discuss the use of specialty apps such as Prezi.
Transitions are used to make the change between slides less abrupt. They can also serve to give you a bit of breathing space to help punctuate the points you’re making.
Some of PowerPoint’s transitions can look particularly whizzy, and it’s very easy to make your presentation to look like a 1980s pop video. Other transitions may make your audience a bit seasick, You may want to stick to one or two subtle choices!
If you’re presenting online, bear in mind that your frame-rate may be quite low, so what looks like a smooth transition on your computer might seem quite jerky and confusing through something like Zoom. You may be better off not using transitions and just having a simple ‘cut’ between each slide.
When applying a transition to a slide, that transition is applied to the appearance of that slide: its the effect that happens when you go into the slide, not the effect that happens when you leave it.
Watch How to Add Slide Transitions in Powerpoint (5 mins) on YouTube
Video source: Intellezy Learning. (2022, November 29). How to add slide transitions in PowerPoint [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OaJFUJf0iyk
Slide animation allows you to introduce, emphasize, and remove items from a slide. This can help focus attention on specific content.
Animation has long been a part of presentation, be it writing on a blackboard, using a piece of paper on an overhead projector to reveal more of a transparency, or using pop-up cards.
Watch Adding animations to Google Slides (4 mins) on YouTube
Video source: LAT EdTech. (2020, September 29). Adding animations to Google Slides [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AdsbPvOpGOo
In slide software, an animation effect can be achieved simply by duplicating an existing slide and then adding or removing content. But there are also built-in animation tools that allow animation of elements to take place within a single slide.
An example: Animation created in PowerPoint
The animation below was constructed in PowerPoint. It uses 14 separate animation effects over two slides, with a “Morph” transition between (see below) to get the hedgehog across the road without too much messing about.

Here’s a look at the first of the two slides:
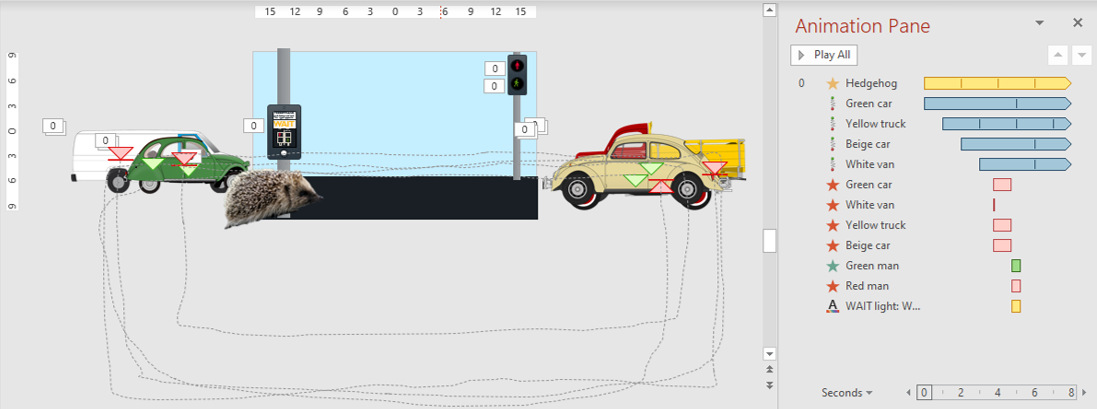
- The effects begin with the start of the slide (denoted by the “0” in the Animation Pane);
- First to happen is a “Teeter” effect on the hedgehog, which is set to repeat until the slide ends;
- Starting at the same time is the Custom Motion Path of the green car: it starts off the left edge of the slide, wobbles quickly across and off the other end, then moves in a square, far below the bottom of the slide, back to somewhere near where it started; This movement is set to take five seconds, repeating continuously;
- One second later, the yellow truck comes in from the opposite direction; its laps take only two seconds (making it a faster vehicle);
- In the next two seconds, the beige car and the white van also enter, each travelling at different speeds; again, the animation repeats continuously;
- Next up we have a series of “Fly Out” animations which cause any vehicles still on the screen to exit the slide (in the direction they’re travelling); originally these were intended to be triggered by a mouse click, allowing the traffic to pass for as long as the speaker needed; in this example they’re instead happening automatically, at 3.75 seconds into the slide (the white van’s exit animation is shorter than the rest just because it was near the edge of shot at that time and so needed less time to get out of the slide);
- Another time point comes a second later, when the green man appears on the crossing signal, the red man disappears, and the WAIT light changes colour from amber to grey.
The hedgehog crossing the road happens via a “Morph” transition, and its waddle out of shot happens in the next slide, using a repeated “Teeter” effect at the same time as a “Fly Out” to give the illusion of walking.
Easy animations with the “Morph” transition
PowerPoint has a special transition called Morph which creates an animation based on shared content between two slides. It allows you to generate really quite elaborate animations without the messing about normally required in the Animation Pane.

The above example is a three-slide animation created using the following method:
- A slide is created (slide 1) and a red triangle shape is drawn onto it;
- The slide is duplicated (copy/paste, or right-click and Duplicate Slide);
- On the duplicate slide (slide 2), the shape is modified: it is repositioned, rotated, resized, and given a new fill colour;
- The “Morph” transition is applied to slide 2 from the Transitions tab;
- The “Morph” transition identifies the triangle in the two slides as being the same object (albeit having undergone some modification) and generates an appropriate animation to bridge the two states;
- In the case of this example, slide 1 has then been duplicated again (as slide 3), again with a “Morph” transition, thereby returning the triangle to its original position (the same effect would happen simply by transitioning backwards and forwards between slides 1 and 2, but we needed to save this animation as a GIF).
Morph is only available in PowerPoint 2019 or later. But many of the Morph effects are backwardly compatible, so they will work to some degree or other on earlier versions of PowerPoint.
Tip: Morph
The more elaborate your Morph, the more strain it will put on your computer. If you’re going to be presenting on a lectern PC, bear in mind that it may not have as much processing power as the computer you used to make the slides in the first place.
Prezi Presentation Tips: Dos and Don’ts
Prezi is a visually based presentation software that supports a non-linear storytelling approach to presentations. With many affordances, including the ability for the audience or presenter to zoom in and zoom out of the screen, Prezis can be powerful but they can also be problematic.
You may have used or seen a Prezi presentation. In case you’re not sure, Prezi is a presentation tool, that instead of following a linear format (slide after slide), it uses zoom and pan to connect the frames, changing not only the dynamics of a presentation, but also changing the way the audience makes connections between the ideas presented. Or at least, that’s what’s supposed to be the main advantage of using Prezi over other tools. However, as you may have seen, the zooms and pans are used by presenters only as fancy transitions between frames, with a lot of us in the audience left wondering, “What’s the point in all of this? All of this coming in and out of the screen, it’s so confusing. Should’ve just stuck to the good old slides.”
Below are some tips to support creating effective Prezi Presentation.
Choosing Presentation Software
What many presenters don’t realize is that, when choosing one presentation tool over another one, you have to make the most of what it has to offer. Prezi’s strength is in its non-linearity, but that doesn’t mean that the frames should be displayed randomly on the screen. The non-linear flow allows for seemingly unrelated concepts to come together by making new meaningful connections between them. Meaning through visual metaphors can be created by significant (hierarchical for example) spatial positioning on the screen and differentiation or similarity of concepts can be achieved by exploring design elements (colors and shapes). The biggest lesson is to use less text and bullet points, and let the visuals and transitions tie in the concepts of your presentation.
Before starting work on your presentation, consider the following questions and concepts.
Consider
- What are the main goals of the presentation and what’s a good visual metaphor to represent it. This will be your main layout, which can be a path, map, tree, etc.
- What kinds of connections are there between your ideas and design the frames in relation to the layout.
- Where on the layout does it make the most sense to place each frame?
- How does it connect with the frame immediately before and after it?
- How does it connect in general with the other frames?
- Think about your presentation with a view of the whole in your mind, because at many times the audience will be able to see all the frames, and you want to draw the eye towards focus points.
- Think about what visual/temporal patterns you’re creating with your presentation and how that’s going to influence the pattern of thoughts and learning process in the audience.
For a visual summary of these ideas and more tips for Prezi (made with Prezi!), please refer to this Prezi and video below it that walks through it.
Watch Prezi Presentation Design Tips – by Ethos3 and Prezi (15 mins) on YouTube
Video source: Ethos3. (2015, August 26). Prezi presentation design tips – by Ethos3 and Prezi [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xYFws1GvP3k

