Concepts Related to Metabolic Regulation
For the purposes of this concept discussion, the Concept of Metabolic Regulation is defined as the regulation of hormonal and enzymatic processes required to maintain homeostasis[1]. This resource provides a basic introduction to the concept of metabolic regulation, focusing primarily on the endocrine system and glucose regulation. The example concept map below provides a summary of the key information necessary to understand glucose regulation. You can revisit this map after you have completed the chapter. The information for the map was informed by several resources.[2]
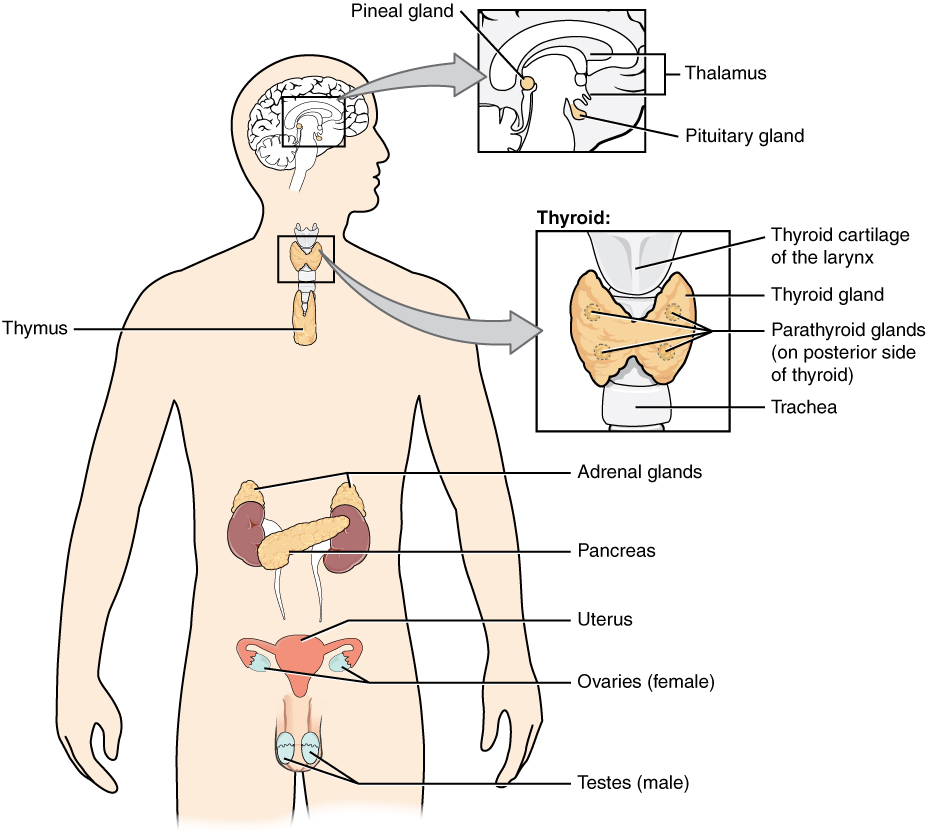
You may never have thought of it this way, but when you send a text message to two friends to meet you at a restaurant at six, you’re sending digital signals that you hope will affect their behavior—even though they are some distance away. Similarly, certain cells send chemical signals to other cells in the body that influence their behavior. This long-distance intercellular communication, coordination, and control are critical for homeostasis, and it is the fundamental function of the endocrine system.Whereas the nervous system uses neurotransmitters to communicate, the endocrine system uses hormones for chemical signaling. These hormone signals are sent by the endocrine organs. Hormones are transported primarily via the bloodstream throughout the body, where they bind to receptors on target cells, inducing a characteristic response. Some of the glands in the endocrine system include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands. See Figure 9.2b for an illustration of the endocrine system.[1] Some of these glands have both endocrine and nonendocrine functions. For example, the pancreas contains cells that function in digestion, as well as cells that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood glucose levels.[2]
This module will focus on medications that affect three major endocrine glands and their hormones: the adrenal glands, the pancreas, and the thyroid. See Table 9.1 for a list of hormones associated with each of these glands and their effects.[3]
| Endocrine gland | Hormone | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Adrenal (cortex) | Aldosterone | Increases blood Na+ levels |
| Adrenal (cortex) | Cortisol | Increases blood sugar levels |
| Adrenal (medulla) | Epinephrine and Norepinephrine | Stimulates fight-or-flight response |
| Pancreas | Insulin | Reduces blood glucose levels |
| Pancreas | Glucagon | Increases blood glucose levels |
| Thyroid | Thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3) | Stimulates basal metabolic rate |
| Thyroid | Calcitonin | Reduces blood Ca+ levels |
Regulation of Hormone Secretion
To prevent abnormal hormone levels and a potential disease state, hormone levels must be tightly controlled. Feedback loops govern the initiation and maintenance of hormone secretion in response to various stimuli.
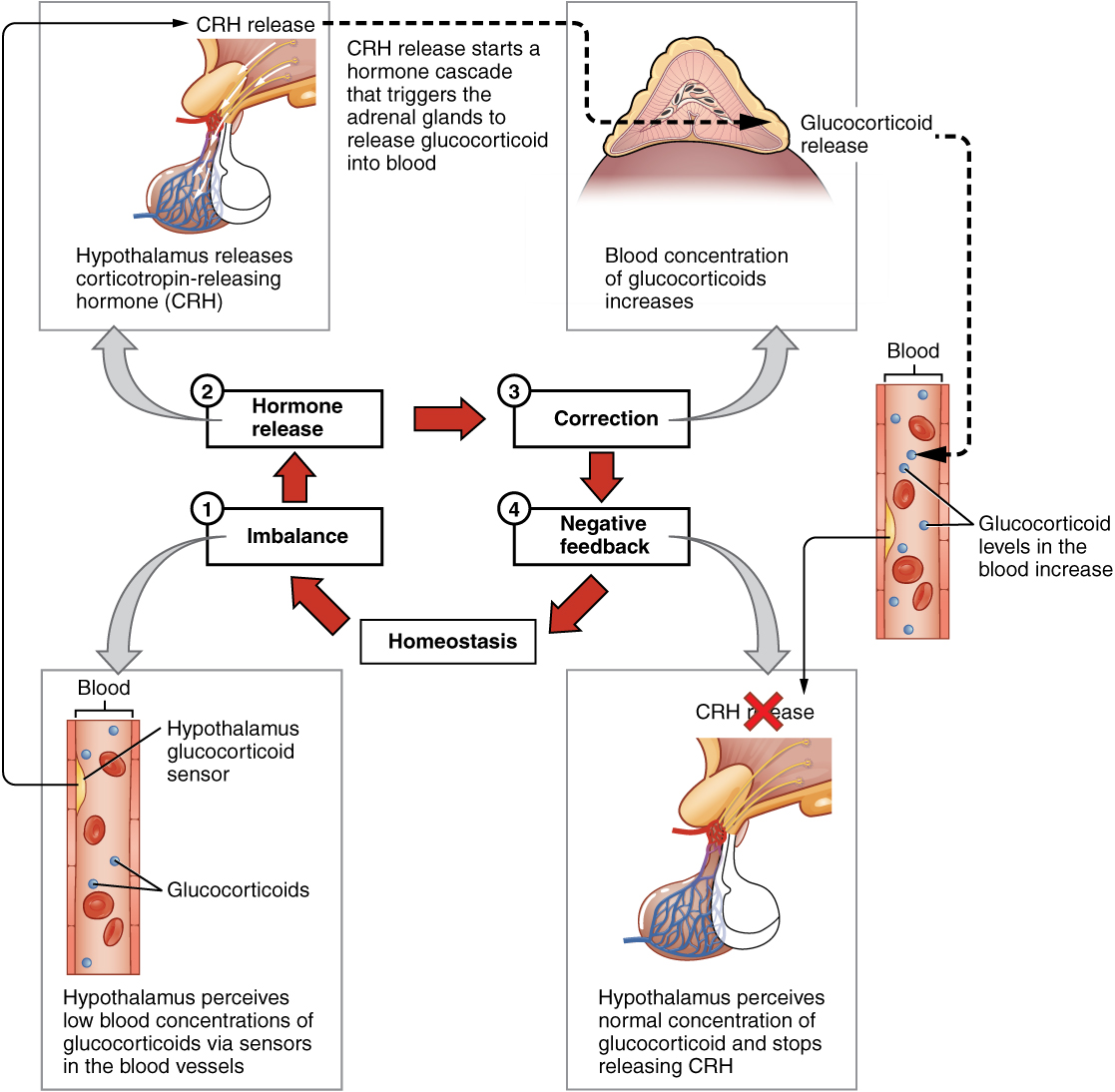
The most common method of hormone regulation is the negative feedback loop. Negative feedback is characterized by the inhibition of further secretion of a hormone in response to adequate levels of that hormone. This allows blood levels of the hormone to be regulated within a narrow range. An example of a negative feedback loop is the release of glucocorticoid hormones from the adrenal glands, as directed by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. As glucocorticoid concentrations in the blood rise, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland reduce their signaling to the adrenal glands to prevent additional glucocorticoid secretion.[4] See Figure 9.2c for an illustration of a negative feedback loop.[5]
Endocrine Gland Stimuli
Endocrine glands can be stimulated by humoral stimuli, by stimulation of another hormone, or by neural stimuli. Humoral stimuli are changes in blood levels of non-hormone chemicals that cause the release or inhibition of a hormone to maintain homeostasis. For example, osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect changes in blood osmolarity (the concentration of solutes in the blood plasma). If blood osmolarity is too high, meaning that the blood is not dilute enough, osmoreceptors signal the hypothalamus to release ADH (antidiuretic hormone). ADH causes the kidneys to reabsorb more water and reduce the volume of urine produced. This reabsorption causes a reduction of the osmolarity of the blood by diluting the blood to the appropriate level. Another example of humoral stimuli is the regulation of blood glucose. High blood glucose levels cause the release of insulin from the pancreas, which increases glucose uptake by cells and liver storage of glucose as glycogen.
An endocrine gland may also secrete a hormone in response to the presence of another hormone produced by a different endocrine gland. For example, the thyroid gland secretes T4 into the bloodstream when triggered by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) that is released from the anterior pituitary gland.
In addition to these chemical signals, hormones can also be released in response to neural stimuli. An example of neural stimuli is the activation of the fight-or-flight response by the sympathetic nervous system. When an individual perceives danger, sympathetic neurons signal the adrenal glands to secrete norepinephrine and epinephrine. The two hormones dilate blood vessels, increase the heart and respiratory rate, and suppress the digestive and immune systems. These responses boost the body’s transport of oxygen to the brain and muscles, thereby improving the body’s ability to fight or flee.[6]
The Hypothalamus–Pituitary Complex
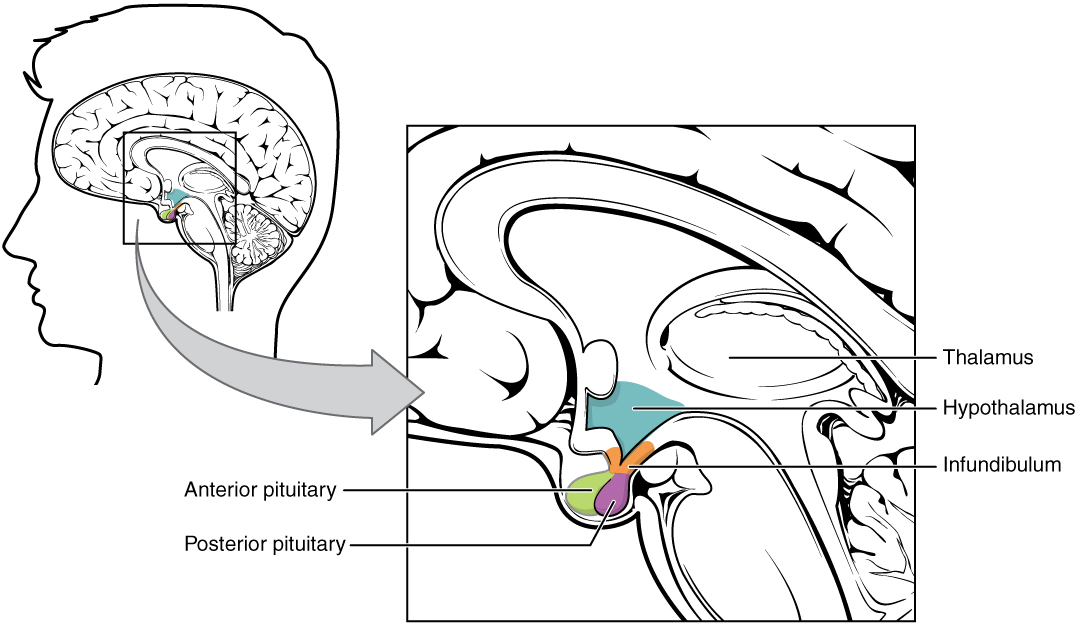
The hypothalamus–pituitary complex can be thought of as the “command center” of the endocrine system. This complex secretes several hormones that directly produce responses in target tissues, as well as hormones that regulate the synthesis and secretion of hormones of other glands. In addition, the hypothalamus–pituitary complex coordinates the messages of the endocrine and nervous systems. In many cases, a stimulus received by the nervous system must pass through the hypothalamus–pituitary complex to be translated into hormones that can initiate a response. See Figure 9.2d for an illustration of the hypothalamus–pituitary complex.[7] The hypothalamus connects to the pituitary gland by the stalk-like infundibulum. The pituitary gland consists of an anterior and posterior lobe, with each lobe secreting different hormones in response to signals from the hypothalamus.
Posterior Pituitary
The posterior pituitary gland does not produce hormones, but stores and secretes two hormones produced by the hypothalamus: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Blood osmolarity, the concentration of sodium ions and other solutes, is constantly monitored by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus. Blood osmolarity may change in response to the consumption of certain foods and fluids, as well as in response to disease, injury, medications, or other factors. In response to high blood osmolarity, which can occur during dehydration or following a very salty meal, the osmoreceptors signal the posterior pituitary to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Its effect is to cause increased water reabsorption by the kidneys. As more water is reabsorbed by the kidneys, a greater amount of water is returned to the blood, thus causing a decrease in blood osmolarity. The release of ADH is controlled by a negative feedback loop. As blood osmolarity decreases, the hypothalamic osmoreceptors sense the change and prompt a corresponding decrease in the secretion of ADH. As a result, less water is reabsorbed by the kidneys.
Drugs can also affect the secretion of ADH or imitate its effects. For example, alcohol consumption inhibits the release of ADH, resulting in increased urine production that can eventually lead to dehydration and a hangover. Vasopressin is a synthetic ADH medication used to treat very low blood pressure. It is called vasopressin because in very high concentrations it also causes constriction of blood vessels in addition to the retention of water. Vasopressin is also used to treat a disease called diabetes insipidus (DI) that causes dehydration due to an underproduction of ADH. [8]
Anterior Pituitary
In contrast to the posterior pituitary, the anterior pituitary does manufacture hormones. However, the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary is regulated by two classes of hormones secreted by the hypothalamus called releasing hormones. Releasing hormones then stimulate the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary (see Figure 9.2e[9]). The anterior pituitary produces seven hormones. These are the growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), beta endorphin, and prolactin. Of the hormones of the anterior pituitary, TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are collectively referred to as tropic hormones (trope- = “turning”) because they turn on or off the function of other endocrine glands. This module will focus on the effects of TSH and ACTH.
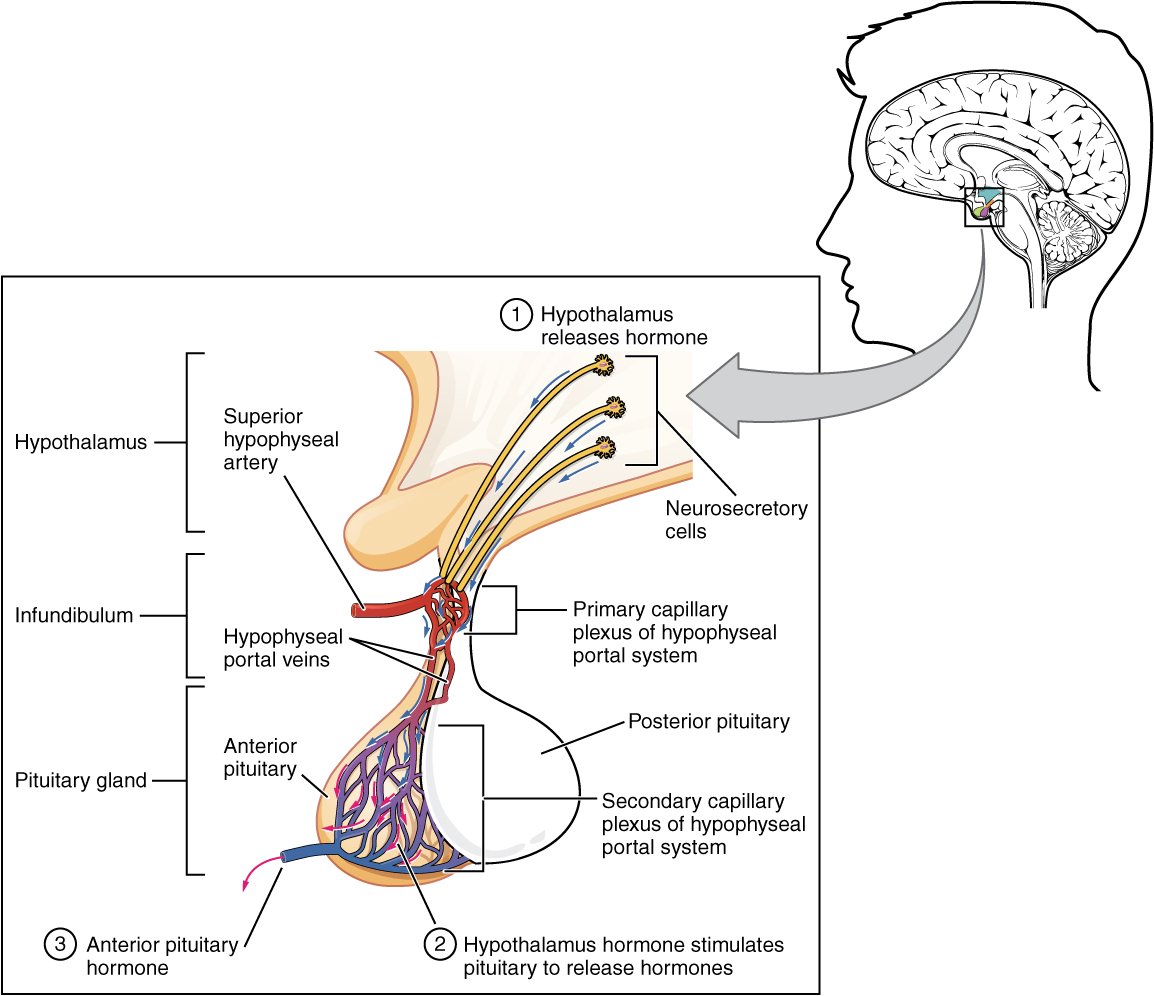
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
The activity of the thyroid gland is regulated by the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH is released from the anterior pituitary in response to the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus and triggers the secretion of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. In a classic negative feedback loop, elevated levels of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream then trigger a drop in production of TRH and subsequently, the production of TSH. TSH is further discussed in the “Thyroid” submodule.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
The adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is released from the anterior pituitary in response to the corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus. ACTH then stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete corticosteroid hormones such as cortisol. A variety of stressors can also influence the release of ACTH, and the role of ACTH in the stress response is discussed under the “Adrenal” submodule.[10]
Interactive Activity
Image Description
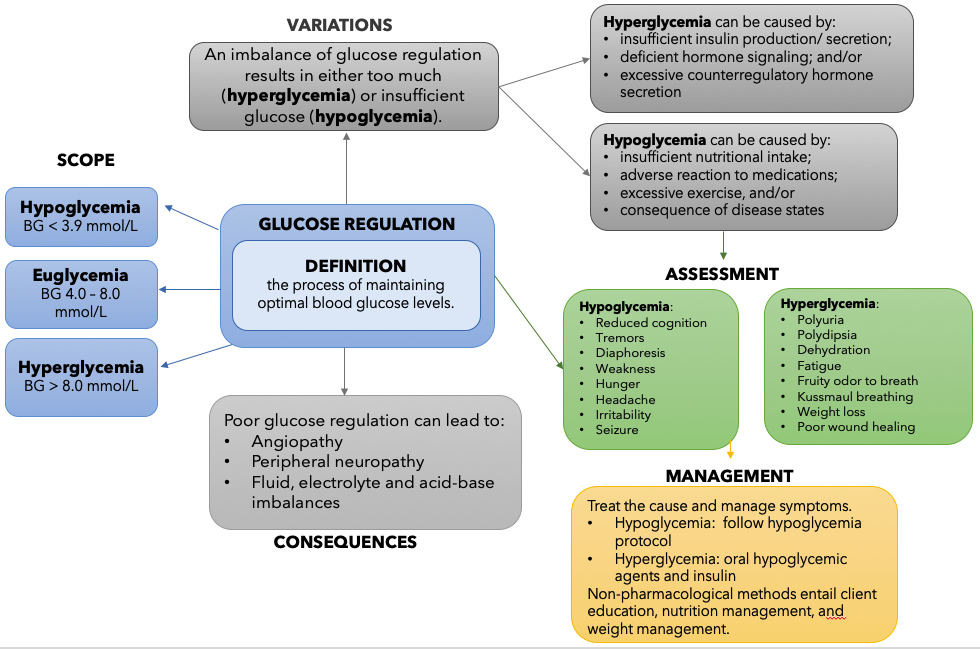
Figure 9.2a Glucose Regulation Concept Map description: This flowchart describes the Concept of Glucose Regulation. In the centre of the chart, Glucose Regulation is defined.
The definition of the Concept of Glucose Regulation is: the process of maintaining optimal blood glucose levels.
Next, there are 3 arrows pointing from the definition to the Scope of Glucose Regulation. The scope is divided into 3 categories: Hypoglycemia (BG < 3.9 mmol/L), Euglycemia (BG 4.0 – 8.0 mmol/L), and Hyperglycemia (BG > 8.0 mmol/L).
Next, one arrow points from the definition to the Variation of Glucose Regulation. An imbalance of glucose regulation results in either too much (hyperglycemia) or insufficient glucose (hypoglycemia). Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are further described.
- Hyperglycemia can be caused by: insufficient insulin production/ secretion; deficient hormone signaling; and/or excessive counterregulatory hormone secretion.
- Hypoglycemia can be caused by: insufficient nutritional intake; adverse reaction to medications; excessive exercise, and/or consequence of disease states.
Next, an arrow points down towards Assessment for Glucose Regulation. Here, a summary of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia symptoms are listed.
- Hypoglycemia: Reduced cognition, Tremors, Diaphoresis, Weakness, Hunger, Headache, Irritability, Seizure.
- Hyperglycemia: Polyuria, Polydipsia, Dehydration, Fatigue, Fruity odor to breath, Kussmaul breathing, Weight loss, Poor wound healing.
Figure 9.2b Overview of the Endocrine System
From top to bottom, the endocrine system consists of:
- the pineal gland that includes thalamus and pituitary gland
- thyroid that includes thyroid cartilage of the larynx, thyroid glad, parathyroid glands (on posterior side of thyroid), and trachea
- thymus
- adrenal glands
- pancreas
- uterus and ovaries of females
- testes of males
Figure 9.2c Negative Feedback Loop
The negative feedback loop of homeostasis has 4 component:
- Imbalance – hypothalamus perceives low blood concentrations of glucocorticoids via sensors in the blood vessels.
- Hormone release – hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). CRH release starts a hormone cascade that triggers the adrenal glands to release glucocorticoid into blood
- Correction – blood concentration of glucocorticoids increases
- Negative feedback – hypothalamus perceives normal concentration of glucocorticoid and stops releasing CRH
- "1801 The Endocrine System.jpg" by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0 Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-1-an-overview-of-the-endocrine-system ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- "1805 Negative Feedback Loop.jpg" by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0 Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-2-hormones ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- "1806 The Hypothalamus-Pituitary Complex.jpg" by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0 Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-3-the-pituitary-gland-and-hypothalamus ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- "1808 The Anterior Pituitary Complex.jpg" by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0 Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-3-the-pituitary-gland-and-hypothalamus ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
Chemical signals sent by the endocrine organs and transported via the bloodstream throughout the body where they bind to receptors on target cells and induce a characteristic response.
Characterized by the inhibition of further secretion of a hormone in response to adequate levels of that hormone.
Changes in blood levels of non-hormone chemicals that cause an endocrine gland to release or inhibit a hormone to maintain homeostasis. For example, high blood sugar causes the pancreas to release insulin.
The concentration of solutes (such as sodium and glucose) in the blood.
Released in response to stimuli from the nervous system. For example, the activation of the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine in the fight-or-flight response is stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system.
The “command center” of the endocrine system that secretes several hormones that directly produce responses in target tissues, as well as hormones that regulate the synthesis and secretion of hormones of other glands. In addition, the hypothalamus–pituitary complex coordinates the messages of the endocrine and nervous systems.
Specialized cells within the hypothalamus that are sensitive to the concentration of sodium ions and other solutes in the bloodstream.
A disease characterized by underproduction of ADH that causes chronic dehydration.
Hormones that turn on or off the function of other endocrine glands, including ACTH, FSH, LH, and TSH.

