Classes of medication, categorized according to neuroreceptor, are further discussed in more detail below. Figure 4.5a summarizes how ANS drugs are classified.
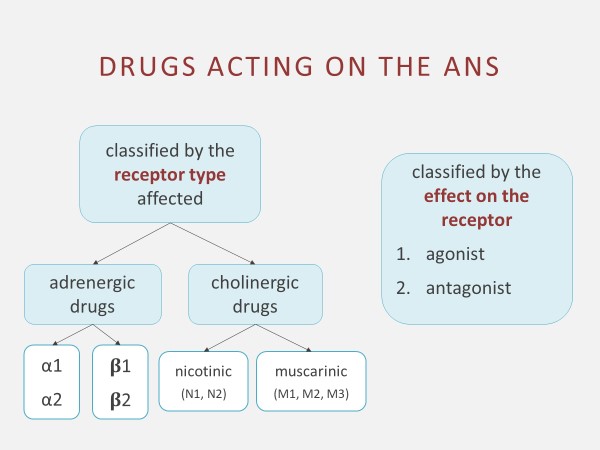
Table 4.5[1] further contrasts agonist and antagonist medications for each ANS neuroreceptor.
| Receptor | Stimulation (Agonist) | Inhibition (Antagonist) |
|---|---|---|
| Nicotinic |
|
|
| Muscarinic |
|
|
| Alpha-1 (found in smooth muscles) |
|
|
| Alpha-2 (found in brain and periphery) |
|
|
| Beta-1 (found on heart and kidneys) |
|
|
| Beta-2 (found on the lungs) |
|
|
| Catecholamines stimulate multiple adrenergic receptors |
|
|
Supplementary Videos: See the supplementary videos below related to sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system medications.
Parasympathetic Nervous System Drugs
Image Descriptions
Figure 4.5a Classification of drugs acting on the ANS Image Description
Drugs acting on the ANS are classified by the receptor type affected:
- Adrenergic drugs
- α1, α2
- β1, β2
- Cholinergic drugs
- nicotinic (N1, N2)
- muscarinic (M1, M2, M3)
Drugs acting on the ANS are classified by the effect on the receptor:
- agonist
- antagonist
- This work is a derivative of Daily Med by U.S. National Library of Medicine in the public domain ↵
- Forciea, B. (2018, January 12). Sympathetic nervous system drugs. [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. Video used with permission. https://youtu.be/-e_s-jTPtm4 ↵
- Forciea, B. (2018, February 2). Parasympathetic nervous system drugs. [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. Video used with permission. https://youtu.be/ZSRk_NkbBPg ↵

