17 Linear Equations
![]() A linear equation is a statement in the form
A linear equation is a statement in the form ![]() , where
, where ![]() is a variable.
is a variable.
The variable that makes the statement true is called a solution of the equation.
![]() How to solve
How to solve ![]() ?
?
– combine all variable terms in one side
– combine all constants terms on the other
– divide both sides by the coefficient of the variable.
![]()
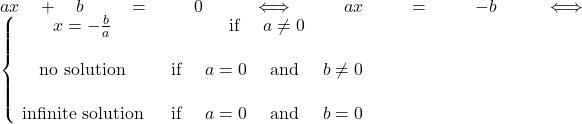
Exercise 1
Show/Hide Solution.
We have
![]()
![]()
![]()
Exercise 2
Show/Hide Solution.
For ![]() , we have
, we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Exercise 3
Show/Hide Solution.
For ![]() , we have
, we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

