63 Renal Architecture
What are the kidneys?
While the kidneys may appear to be quite plain from the outside, a cross-section reveals a highly intricate internal structure. The kidney can be divided into two anatomical sections: the superficial, outermost layer, known as the renal cortex, and the interior portion, known as the renal medulla. This organization allows different functions to be localized, with the cortex being primarily involved in filtering blood into urine while the medulla handles urine concentration and water conservation.
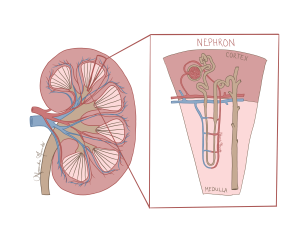
Figure 121 Coronal cross section of the left kidney (left) and a zoomed image of the nephron (right)
Spanning both the cortex and the medulla is the fundamental structure that filters the blood: the nephron. The nephron is responsible for producing urine. Each kidney contains around one million nephrons that carry out the key processes of filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.

