19 Pancreas
Endocrine Pancreas:
Let’s dive back into the pancreas, the multitasking organ that plays a critical role in digestion and blood glucose regulation. We previously explored the exocrine functions of the pancreas in chapter 1, but it also has tremendous endocrine function through its pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans which comprise <1% of the cells in the pancreas.
Each pancreatic islet is composed of 4 hormone secreting cells:
Table 21 Hormone secreting cells of the pancreas
| Pancreatic cells | Description |
| Alpha or A cells | About 17% of pancreatic islets cells which produce glucagon |
| Beta or B cells | About 70% of pancreatic islet cells that produce insulin |
| Delta or D cells | Constitute ~7% of the cells and secrete somatostatin (identical to growth-hormone-inhibiting hormone in the hypothalamus) |
| F cells | Secrete pancreatic polypeptide which signals satiety |
Figure 36 Pancreatic cells
Insulin and Glucagon Regulation:
Insulin and glucagon – both peptide hormones – play an integral role in maintaining blood glucose levels, and both operate within 2 negative-feedback loops.
- Low blood sugar (a condition known as hypoglycemia) stimulates secretion of glucagon from pancreatic alpha cells.
- Glucagon acts on hepatocytes to accelerate conversion of glycogen to glucose and promotes gluconeogenesis (conversion of glucose from lipids or amino acids)
- As a result blood glucose levels rise, restoring homeostasis.
- If blood glucose rises (a condition called hyperglycemia) (as seen just after eating) this may signal release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells.
- Insulin has multiple functions. It signals hepatocytes to reduce gluconeogenesis (the production of glucose) and instead promotes glycogenesis, converting free glucose into glycogen for storage. Additionally, insulin stimulates the synthesis of fatty acids (lipogenesis) and facilitates the uptake of glucose form the bloodstream into cells.
- As a result blood glucose falls to normal levels restoring homeostasis.
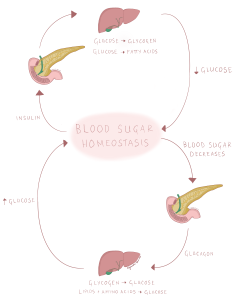
Figure 37 Blood sugar homeostasis reacting to stimuli
As you can see the effects of hypoglycaemia or hyperglycaemia promote the expression of either glucagon or insulin. When one hormone is active, the other is inhibited via negative feedback, keeping your blood sugar within a healthy range.
Do you remember the functions of the pancreas?

Hint: The pancreas is a versatile organ that is critical for our survival. This meme describes the importance of the pancreas and all of its major functions! Click here to re-visit the pancreas’s digestive functions.

