6 Mouth, Tongue, Oral Cavity
The Mouth and Oral Cavity:
Digestion begins in the mouth via two processes: mechanical digestion involving chewing (mastication) with the teeth to tear and crush food, and chemical digestion involving saliva. The mouth is also the site of chemical digestion as saliva helps break down food using enzymes. The mouth houses 3 major pairs of salivary glands as depicted in the figure below:
Table 7 Types of salivary glands
| Gland name | Location: |
| Parotid glands | located inferior and anterior to the ears |
| Submandibular glands | located within the floor of the mouth. |
| Sublingual glands | located beneath the tongue. |
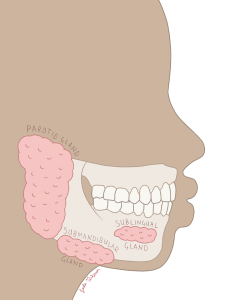
Figure 6 Sagittal view of salivary glands
Salivary Gland Contents:
Each gland produces saliva which is 99.5% water and 0.5% solutes, including ions, dissolved gasses, and various inorganic substances. Additionally, there are a number of enzymes including salivary amylase (which breaks down polysaccharides), lingual lipase (which becomes active in the stomach to process dietary triglycerides), and bacteriolytic lysozymes (destroys bacteria).

