Chapter 5: Identify and explain Canada’s current strengths and weaknesses in natural resources, transportation, and communications, energy, and agriculture, among others.
5.1. Natural Resources Canada
Before you begin
Before you begin reading, check your understanding of some of the key terms you will read in this chapter:

Committed to improving the quality of life of Canadians by ensuring the country’s abundant natural resources are developed sustainably, competitively, and inclusively.
- Energy efficiency: Homes, buildings, industry, transportation, products, EnerGuide, ENERGY STAR.
- Minerals and mining: Exploration, resources, production, innovation, explosives, regulations.
- Forests and forestry: Sustainability, research, industry, and trade, boreal, wildfires, insects, transformation.
- Energy sources and distribution: Oil, gas, renewables, fossil and alternative fuels, electricity, nuclear, uranium, co-ops.
- Climate change: Green future, infrastructure programs, impacts and adaptations.
- Public consultations: Insight and information for the development of policies and programs.
- Maps, tools, and publications: Atlas of Canada, land surveys, air photos, satellite images, positioning, software.
- Science and data: Research programs, centers and labs, intellectual property, partnerships, analysis.
- Domestic and international markets: Transportation fuel prices, lumber, pulp and panel prices, minerals, and metals markets.
- Natural Resources and Indigenous Peoples: Land claims in the North, participation in mining activities, partnerships.
- Funding and partnerships: Opportunities, grants and contributions, incentive, and partnership programs.
- Simply Science stories: Explore Natural Resources Canada’s science through articles, podcasts, and videos.
Source
Government of Canada. (2023). Natural Resources Canada.
5.2. Major Macro Economic Indicators
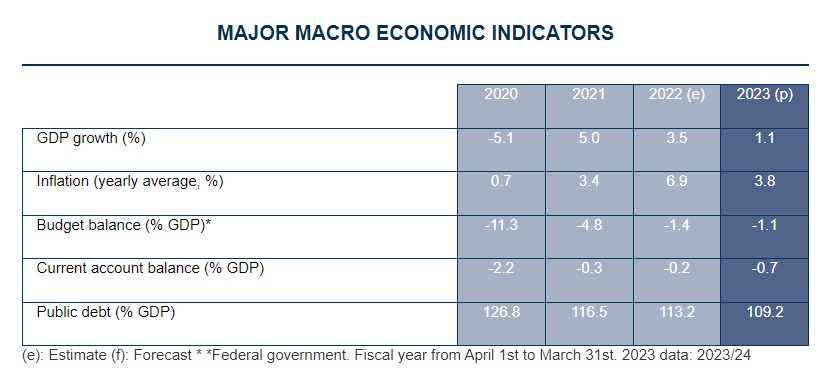
Source
COFACE for trade (2023, April). Canada – Major Macro Economic Indicators.
5.3. Canada: Strengths and weaknesses

Source
COFACE for trade (2023, April). Canada: Strengths and weaknesses.
Video: Strengths & Weaknesses of Canada’s Entrepreneurship Ecosystem | Sushee Perumal, MaxSold. TheFutureEconomy.ca.

