Nearpod: A Digital Tool
Nearpod: A Digital Tool that supports Formative Assessment
Universal Design for Learning leverages the neuroscience of learning to enhance and personalize education for everyone (CAST, 2018). Nearpod has several features that allows the instructor to perform formative assessments at the same time they are teaching new concepts.
Engagement
As UDL emphasizes internal motivation to learn, Nearpod offers several ways of engaging students’ prior knowledge and progress throughout a lesson.
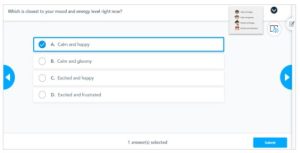
Polls
Teachers can ask students to answer quick “polls” at the beginning and throughout lessons to better understand what they already know, checking their prior knowledge. In addition, they can ask their students to share opinions about various subjects along the way, as well as check for understanding, thereby validating their individuality in the learning process.
Collaborate Board
Teachers can ask for students’ contribution to the lesson at the beginning , middle or end of a lesson through interactive collaborative boards in which they can choose their modality of sharing – typing, audio recording, image sharing or even GIFs or emoji reactions to other collaborators. Collaborations are shared on a common bulletin board where student names can be visible or anonymous to allow the real-time sharing of ideas.
Representation
Employing multiple means of representation supports student learning by accommodating diverse comprehension styles and providing adaptable options for both learning and responding. (Almeqdad et al., 2023).
Embedded Videos
In addition to still photographs and diagrams, teachers can embed videos directly into their lessons from you tube or upload personal videos or even excerpts from longer productions. These videos can turn into active learning through questions, collaborative boards, open-ended questions or polls placed directly into the video so that students are actively engaged in responding to the video.
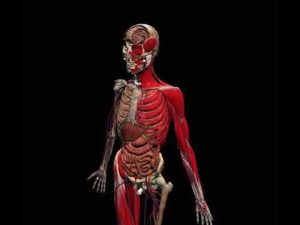
3D Elements
Nearpod has a library of over 100 3D objects such as animals, the human body, places, microscopic organisms and more. These elements can be used as a hook for a lesson or the main focus of a science or social studies lesson. Many full-lessons for all subject areas between K-12 exist in the library and can be embedded directly from the application into the teacher’s lesson. Features include rotating 360 degrees in a 3D space, zooming in and out.
Virtual Reality Field Trips
Students can go on a virtual field trip to different places around the world to actually explore the historic sites that they are studying in class. This meaningful “representation” of the history or culture being studied comes to life and students can further participate in the field trips by answering questions or participating in collaborative discussions throughout the” trip.”
Action and Expression
The UDL principle of action and expression recognizes that students have different communication strengths; some excel in writing, while others are more effective verbally. It supports this diversity by offering various ways for students to express their learning. (Almeqdad et al., 2023 & La et al., 2018).
Different Modalities of Response
Nearpod allows different modalities of contributing to collaborative boards. Students can share their thoughts using text, an image, an audio response, a video responding to a discussion or even a GIF or emoji to support a peer’s comment or contribution.
Accommodations in Lesson Delivery
The immersive reader function may be mobilized for students who benefit from an audio read-aloud function for asking questions on quizzes, open-ended questions or collaborative boards. If a video is embedded in the lesson, the teacher can also enable closed captioning.
Student-paced Option:
In certain key parts of a lesson, such as an interactive video with embedded activities such as quizzes or open-ended questions, teachers may enable a “Student-paced” option in which the individual can complete these slides at their own pace rather than feeling rushed and overwhelmed by the teacher-controlled slide deck. The feeling of being left-behind, which happens frequently in a class with multiple levels, is no longer an issue for the student who needs more time to process and complete the given lesson.
References
Almeqdad, Q.I., Alodat, A.M. Alquaraan, M.F., Mohaidat, M.A., & Al-Makhzoomh, A.k. (2023). The effectiveness of universal design for learning: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. Cogent Edcuation, 10(1), 2218191. https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2023.2218191
CAST (2018). Universal design for learning version 2.2. Retrieved from http://udlguidlelines.cast.org
Maxwell, L. (2019). Nearpod. School Librarian, 67(1), 20–20.
