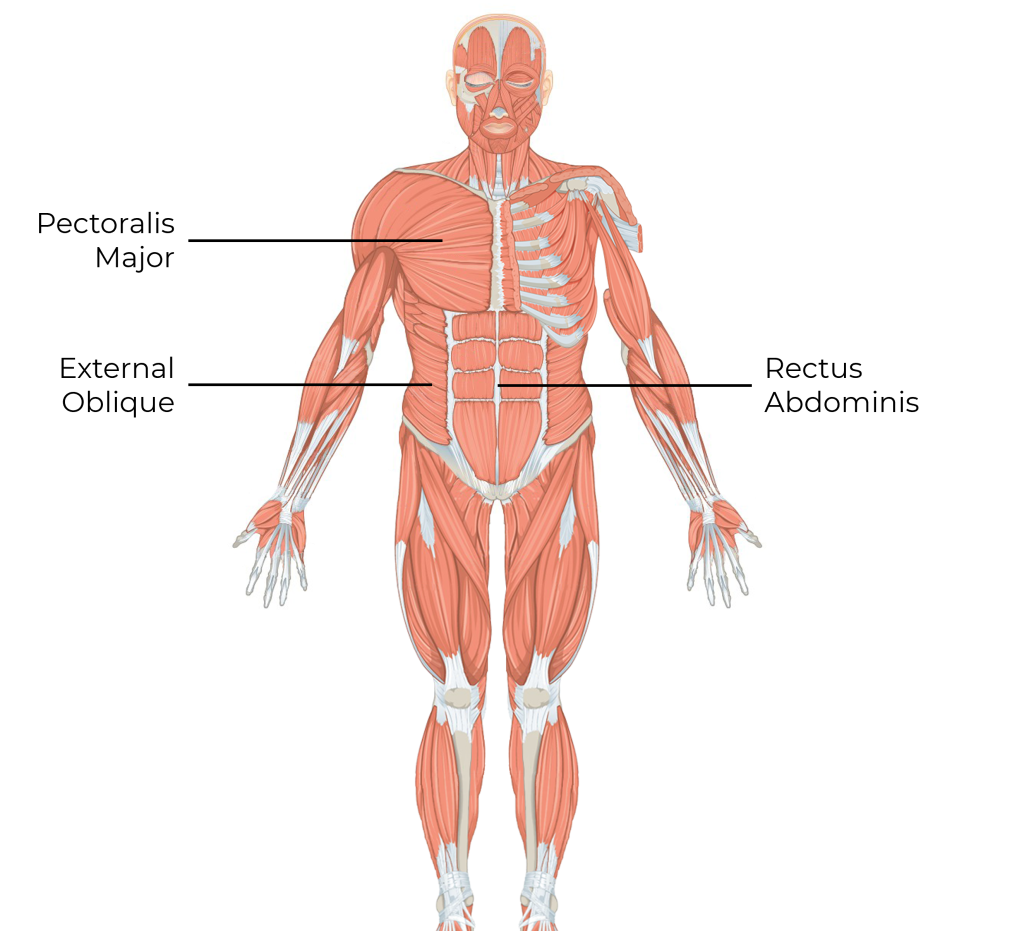
5.7 Muscles of the Thorax and Abdomen
Pectoralis Major, External Obliques and Rectus Abdominus
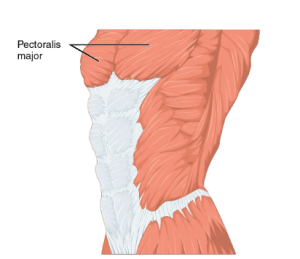
Pectoralis Major
Action: Internally rotates, adducts, and flexes the arm.
This is the large chest muscle that is commonly referred to as the “pecs” short for pectoralis major.
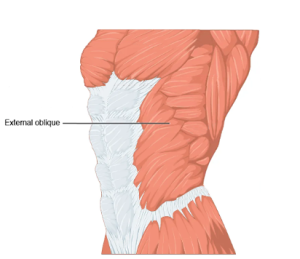
External Oblique
Action: Flexes and rotates the vertebral column.
The external oblique is named for the direction of its muscle fibres as well as its anatomical position. The term ‘oblique’ is Latin for ‘slanting’ or ‘sideways’ and refers to muscle fibres that run diagonally. External refers to the fact that the muscle is superficial, external, or on the outside of the body.
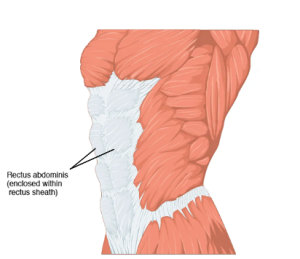
Rectus Abdominus
Action: Flexes trunk
The rectus abdominus (6-pack muscle) is named for the direction of its muscle fibres as well as its anatomical location. The term ‘rectus’ is Latin for ‘straight’ and refers to muscle fibres that run vertically (straight up and down). Abdominus refers to the muscle’s location within the abdominal region.
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
Action: Aids in respiration (breathing) by decreasing or increasing pressure in the chest cavity to draw air into or force air out of the lungs, respectively.
The diaphragm is the umbrella shaped muscle located inferior to the lungs.
Video: “respiratory system-7 role of diaphragm in breathing” by Saurabh Jha [0:44] is licensed under the Standard YouTube License.Transcript and closed captions available on YouTube.